Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (NADP+)
Mammalian dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase catalyses the reduction of uracil or thymine to dihydrouracil or dihydrothymine respectively. This reaction represents an important step in the pathway of pyrimidine degradation in cells, but is particularly important to medicine because the anticancer drug 5-flourouracil, though shown to be effective, is also a substrate for this enzyme, thus its effectiveness is reduced. The development of specific inhibitors is therefore paramount in order to reduce the cost and side effects of treatment with this drug.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q28943
 (1.3.1.2)
(1.3.1.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Sus scrofa (pig)

- PDB
-
1h7x
- Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) from pig, ternary complex of a mutant enzyme (C671A), NADPH and 5-fluorouracil
(2.01 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.70
 (see all for 1h7x)
(see all for 1h7x)
- Cofactors
- Tetra-mu3-sulfido-tetrairon (4), Fadh2(2-) (1), Fmnh2(2-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.3.1.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
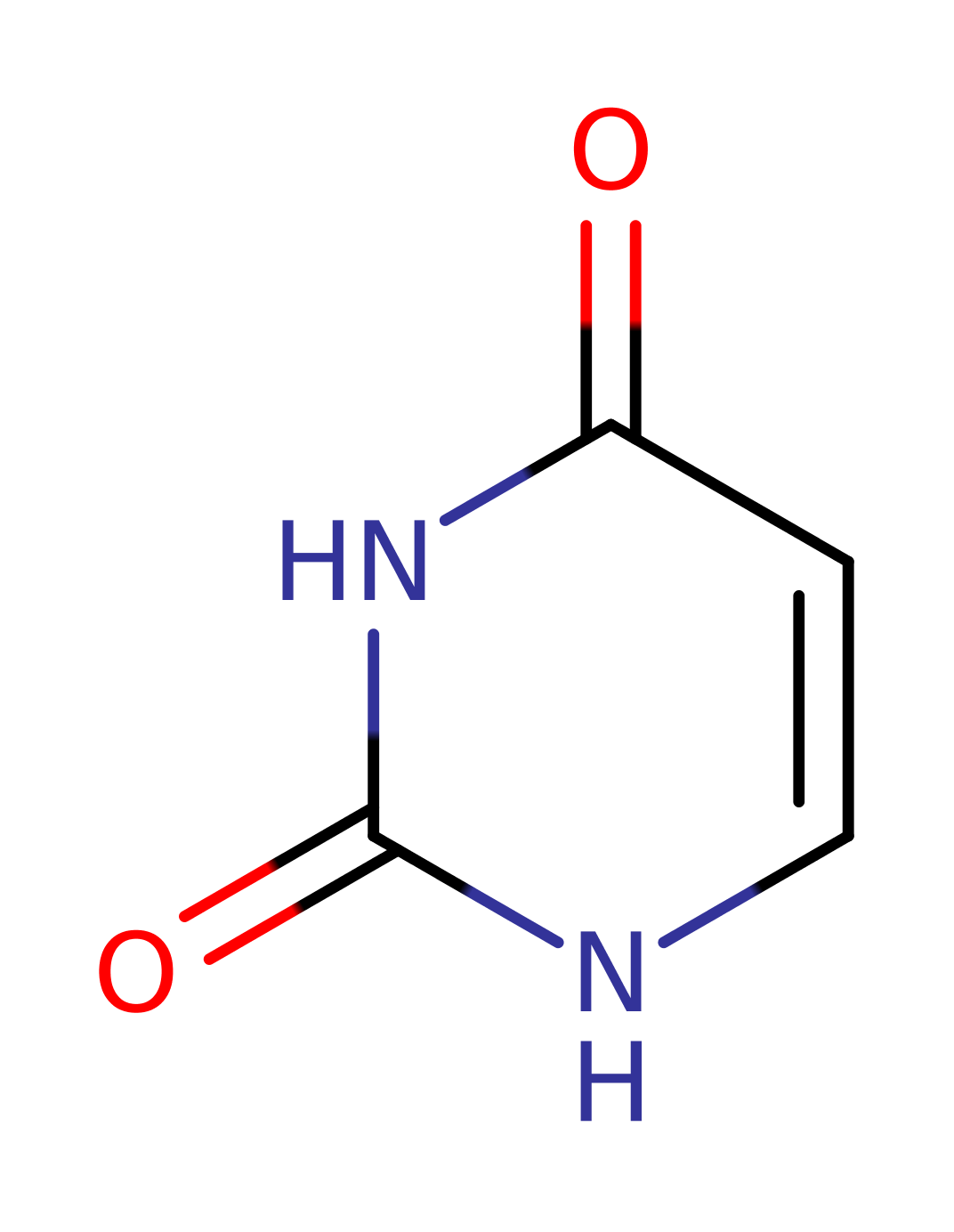
The enzyme uses electrons from NADPH to reduce the uracil substrate. However, the electrons are not passed directly to uracil but instead are transferred from NADPH to FAD and then from FAD to FMN. Finally the FMN acts as a nucleophile to transfer a hydride ion to the double bond of the uracil. This creates a transient carbanion at the second carbon of the double bond, allowing protonation by Cys 671 to occur, completing the reaction.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1h7x) | ||
| Lys709, Lys574 | Lys709C, Lys574C | Both residues stabilise the reduced FMN. It is not known whether there is formal proton transfer or just simple ionic interactions. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys671 | Ala671C | Ats as general acid base to protonate the transient carbanion formed after hydride transfer to the uracil. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, cofactor used, michael addition, overall reactant used, proton transfer, overall product formed, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Dobritzsch D et al. (2001), EMBO J, 20, 650-660. Crystal structure of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase, a major determinant of the pharmacokinetics of the anti-cancer drug 5-fluorouracil. DOI:10.1093/emboj/20.4.650. PMID:11179210.
- Schnackerz KD et al. (2004), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1701, 61-74. Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase: a flavoprotein with four iron-sulfur clusters. DOI:10.1016/j.bbapap.2004.06.009. PMID:15450176.
- Rosenbaum K et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 17598-17609. Porcine Recombinant Dihydropyrimidine Dehydrogenase: Comparison of the Spectroscopic and Catalytic Properties of the Wild-Type and C671A Mutant Enzymes†. DOI:10.1021/bi9815997. PMID:9860876.

Step 1. Binding of NADPH results in a conformational change which facilitates the transfer of a hydride from its pro-S position to the re-face of FAD at N5. Following this step two single electron transfers then occur via the FeS clusters to FMN.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, cofactor used
Step 2. The reduction of uracil occurs in two steps with hydride transfer from reduced FMN to C6 first. The reduced FMN is stabilised by Lys709 and Lys574 but it is not know whether a formal proton transfer occurs or just electrostatic interactions used. The intermediate enolate formed is stabilised by delocalisation of electrons.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys574C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys709C | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
michael addition, hydride transfer, overall reactant used
Step 3. Cys671 acts as a general acid to protonate C5, forming the product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys574C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys709C | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala671C | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed
Step 4. In an inferred reaction step Cys671 is reprotonated to regenerate the native state of the enzyme.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala671C | proton acceptor |




 Download:
Download: