2-dehydro-3-deoxy-phosphogluconate aldolase
2-ket-3-deoxy-phosphogluconate (KDPG) aldolase is a Class I aldolase of the glycolytic pathway. It catalyses the reversible cleavage of KDPG into the three carbon units pyruvate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. The enzymatic aldol reaction is highly efficient, regioselective and shows high facial stereoselectivity. The mechanism shown here is the formation KDGP from pyruvate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0A955
 (4.1.2.14, 4.1.3.16)
(4.1.2.14, 4.1.3.16)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1fq0
- KDPG ALDOLASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI
(2.1 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.70
 (see all for 1fq0)
(see all for 1fq0)
- Cofactors
- Fadh2(2-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.1.2.14)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
In the aldol condensation direction, Glu45 acts as a general base towards the protonated Lys133 through a structurally conserved water molecule. This activates the lysine residue towards nucleophilic attack the the pyruvate carbonyl, which with concomitant protonation of the hydroxyl group from Glu45 results in the elimination of water and formation of an imine intermediate. Glu45 initiates tautomerisation through proton transfer with the eliminated water, forming a carbinolamine. The glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is then attacked by this intermediate at its carbonyl functionality, with simultaneous protonation from Glu45. This residue then acts as a base towards a hydrolytic water which attacks the imine, and initiates the collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate, releasing the free Lys133, Glu45, KDPG and reforming the conserved water molecule.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1fq0) | ||
| Arg49 | Arg49A | The close proximity of the residue's positively charged side chain to the catalytic nucleophile Lys133 influences the residue's pKa, increasing its acidity and so the interaction enhances Lys133 nucleophilic character. | modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys133 | Lys133A | The residue acts as a nucleophile towards the substrate carbonyl, forming a Schiff imine with elimination of water. This water then remains in the active site to facilitate proton relay between the substrate and Glu45. Its pKa is modified through electrostatic interaction with Arg49 and the general base Glu45 via a water molecule. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
| Glu45 | Glu45A | The residue acts as a general base within a proton relay with a water molecule to deprotonate Lys133, and therefore activate the residue to act as a nucleophile towards the substrate carbonyl. It also acts as a general acid towards the eliminated water. Because of the distance between the most likely substrate binding position and the residue, it is thought that most of its acid/base interactions are mediated through a structurally conserved water molecule. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, schiff base formed, bimolecular elimination, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, aldol addition, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate terminated, intramolecular eliminationReferences
- Fullerton SW et al. (2006), Bioorg Med Chem, 14, 3002-3010. Mechanism of the Class I KDPG aldolase. DOI:10.1016/j.bmc.2005.12.022. PMID:16403639.
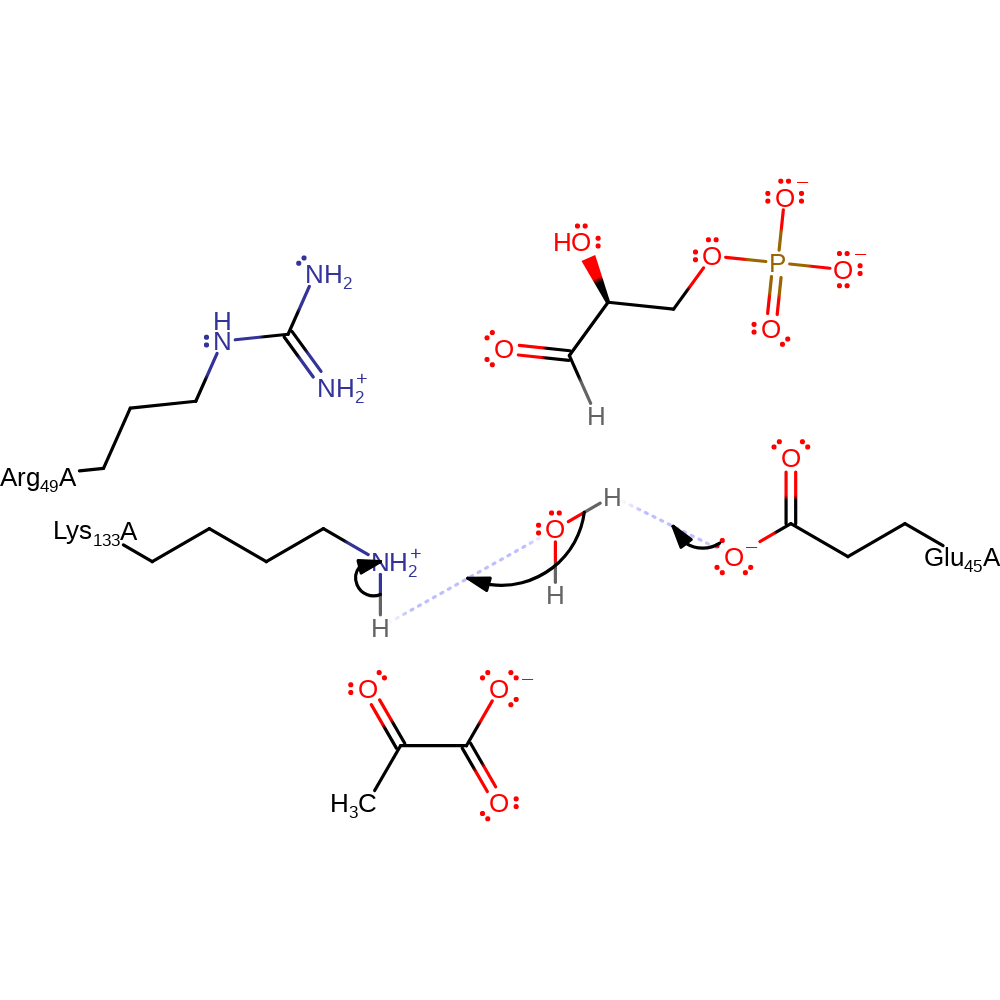
Step 1. Glu45 deprotonates Lys133 via a water molecule, activating the lysine. The positively charged Arg 49 acts to increase the acidity of the protonated lysine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg49A | electrostatic stabiliser, modifies pKa |
| Lys133A | proton donor |
| Glu45A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer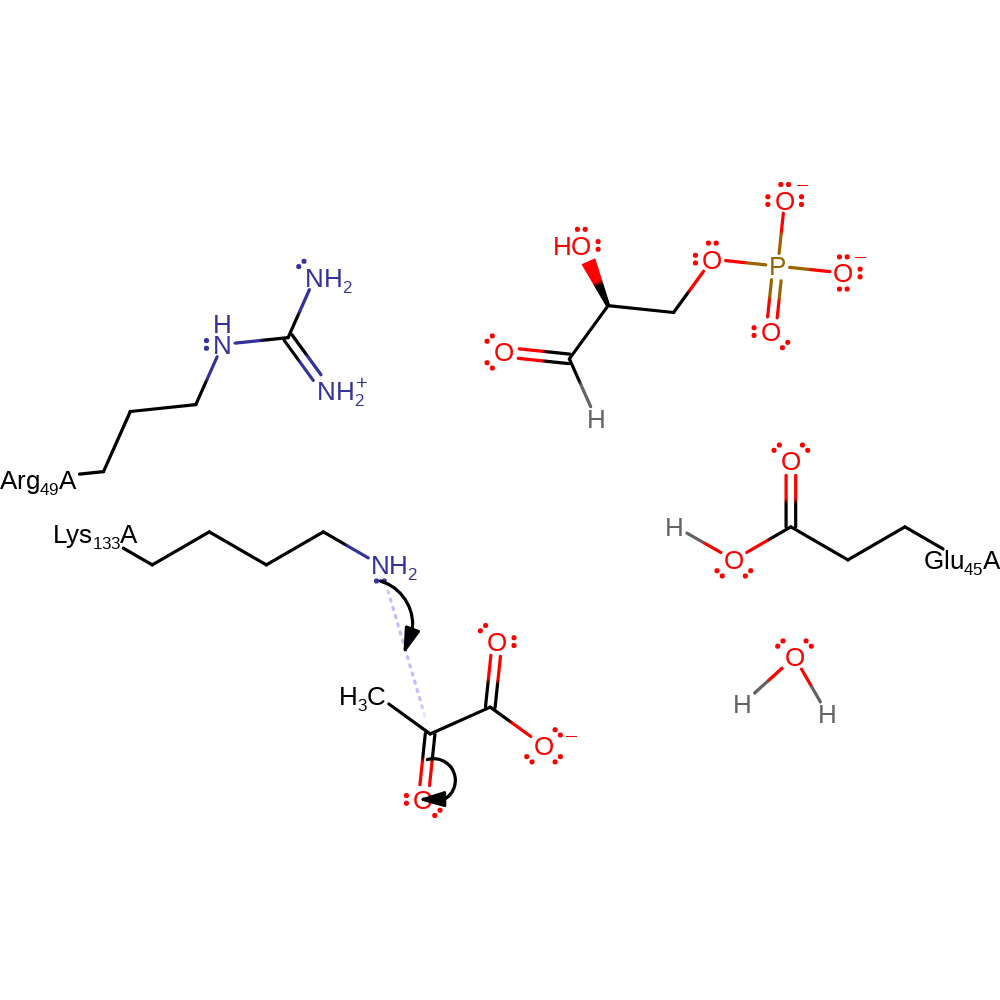
Step 2. The activated Lys133 performs a nucleophilic attack on the pyruvate carbonyl.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys133A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation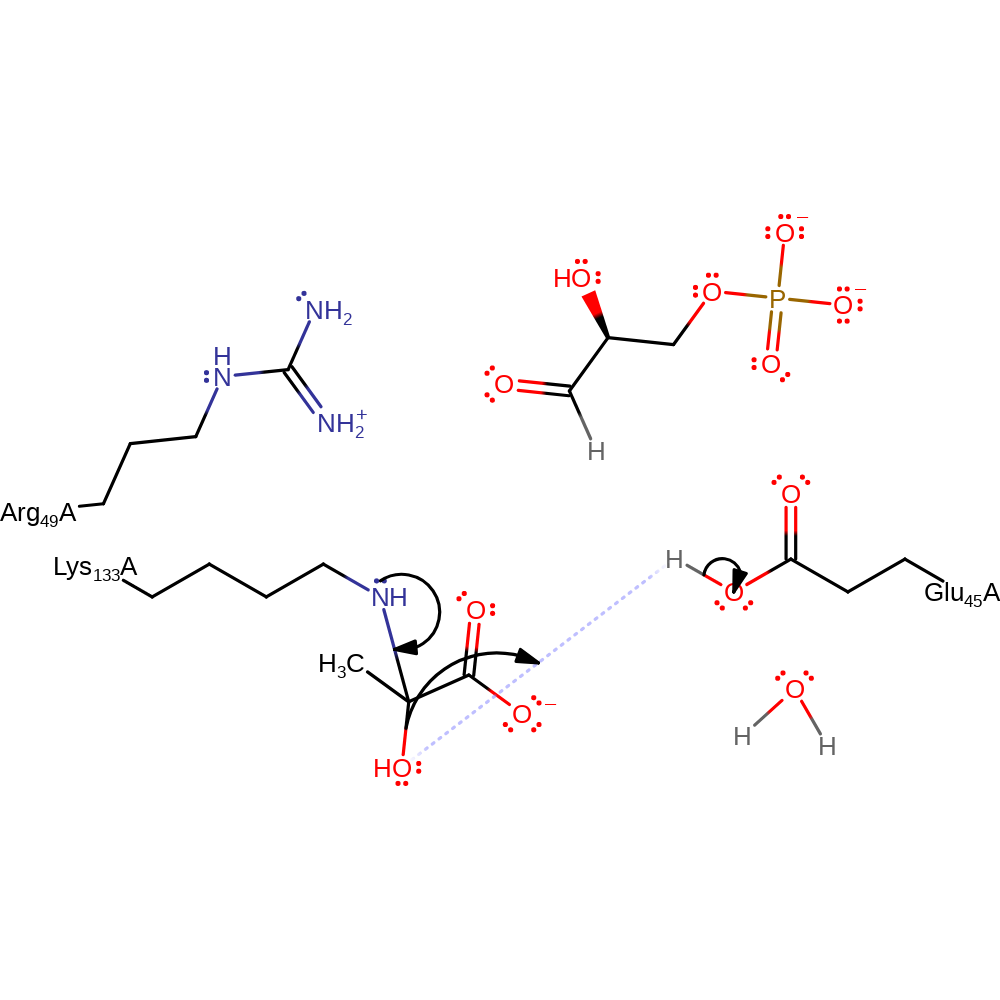
Step 3. The concomitant protonation of the hydroxyl by Glu45 leads to water being eliminated and an imine intermediate being formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu45A | proton donor |
| Lys133A | electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, schiff base formed, ingold: bimolecular elimination
Step 4. Glu45 initiates tautomerisation via proton transfer with the eliminated water, forming a carbinolamine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys133A | electron pair acceptor |
| Glu45A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation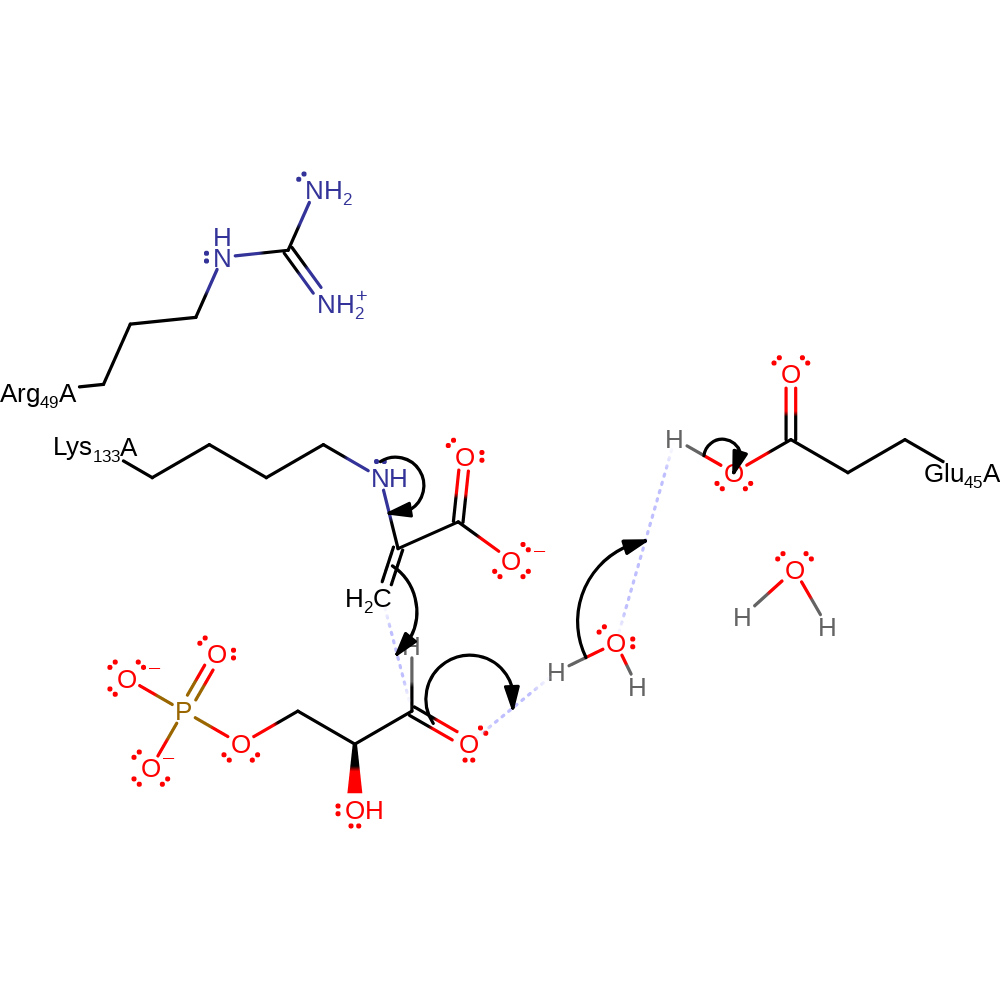
Step 5. The glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is then attacked by this intermediate at its carbonyl functionality in an aldol addition, with simultaneous protonation from Glu45 via the water molecule.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu45A | proton donor |
| Lys133A | electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
aldol addition, proton transfer, overall reactant used, schiff base formed
Step 6. A hydrolytic water then attacks the imine upon deprotonation by Glu45 forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu45A | proton acceptor |
| Lys133A | electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer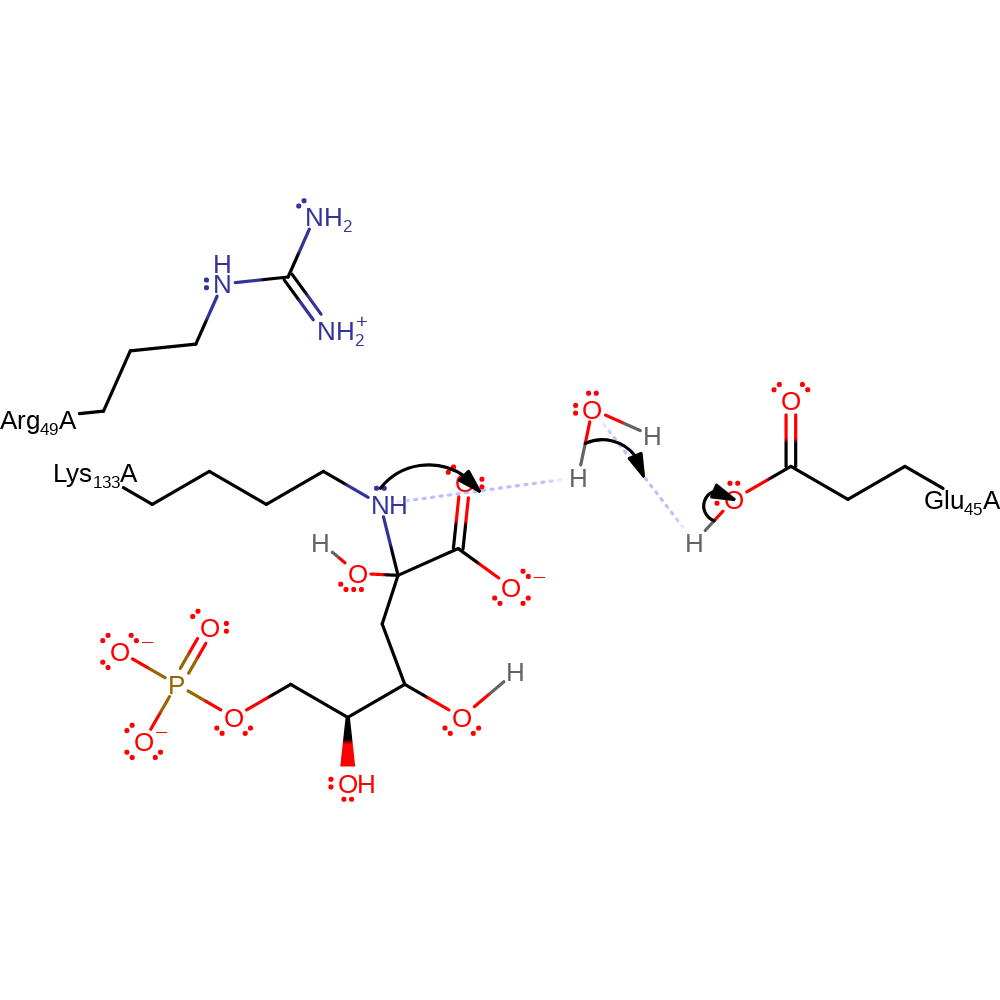
Step 7. The amine group of the intermediate accepts a proton from Glu45 via a water molecule, to create a better leaving group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu45A | proton donor |
| Lys133A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer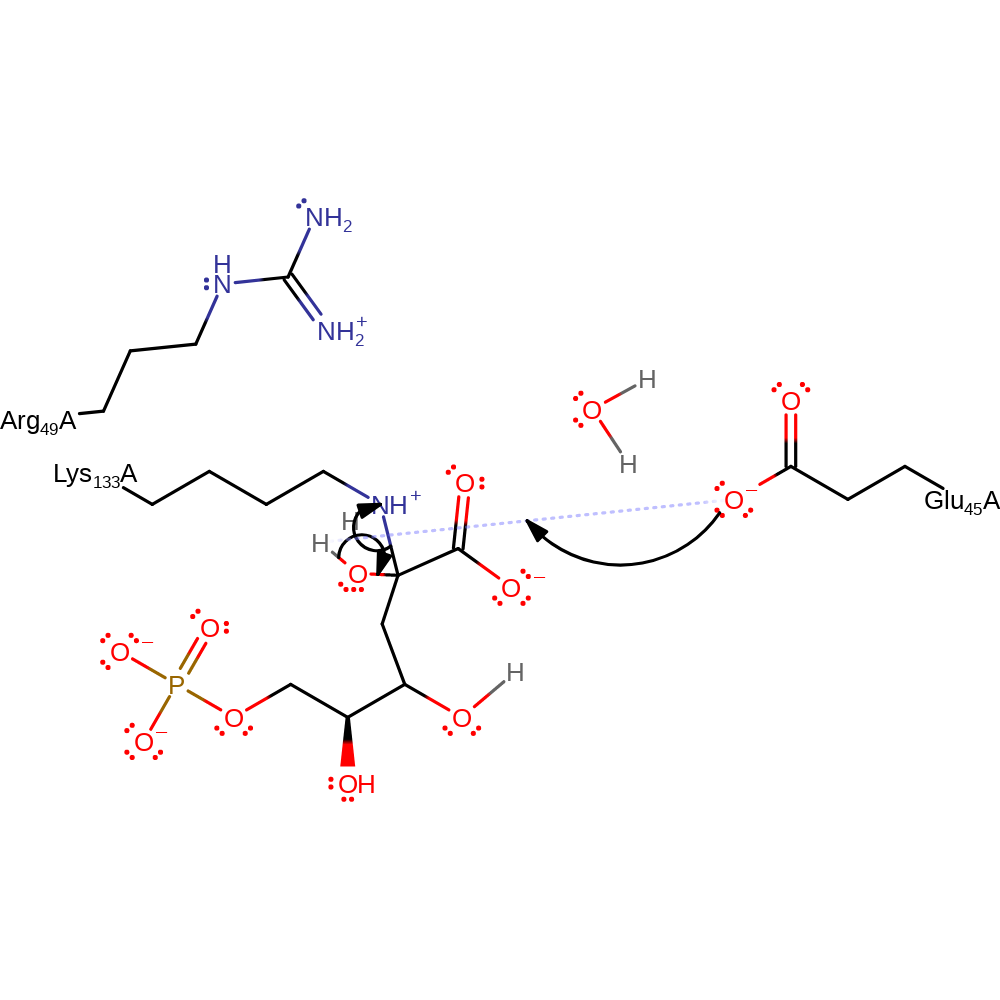
Step 8. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses releasing Lys133 and forming the product with concomitant deprotonation of the hydroxyl by Glu45.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu45A | proton acceptor |
| Lys133A | nucleofuge |




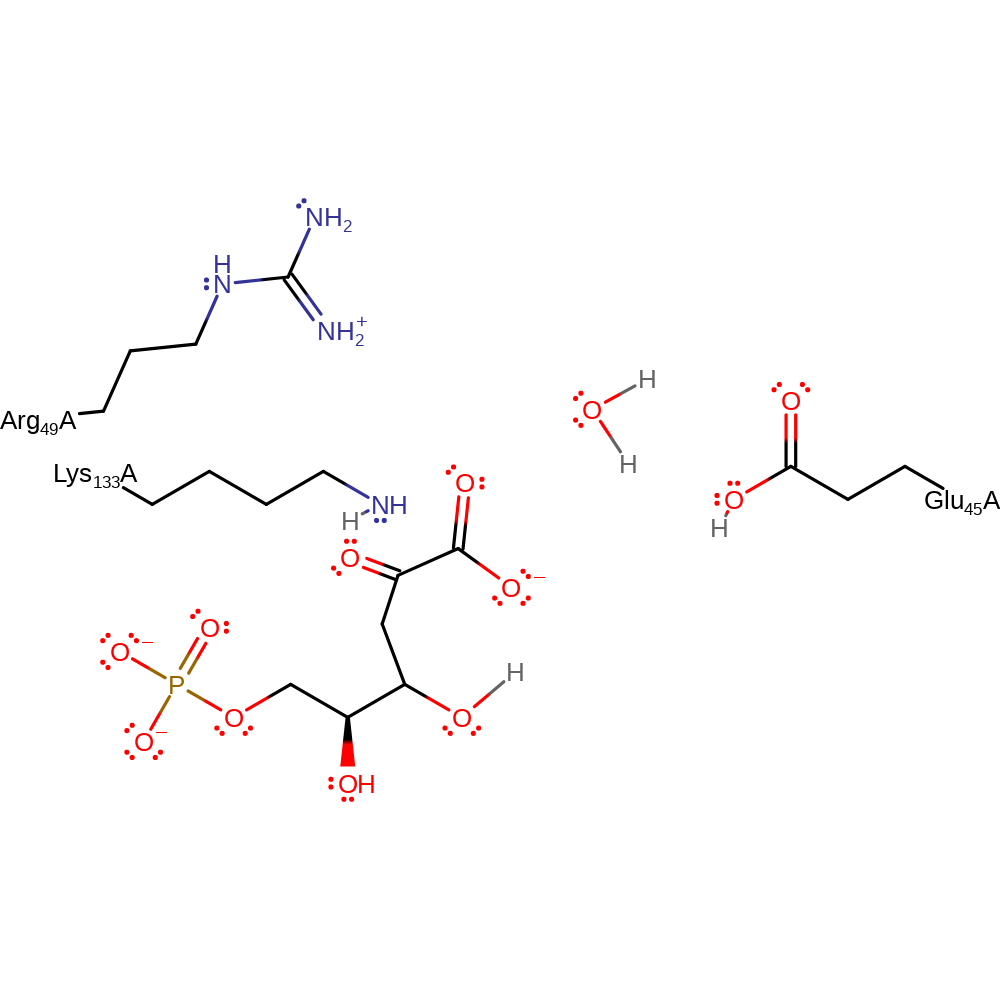 Download:
Download: