
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D:
E.C.2.5.1.60
- protein geranylgeranyltransferase type Ii.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
geranylgeranyl diphosphate + L-cysteinyl-[protein] = S-geranylgeranyl-L- cysteinyl-[protein] + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
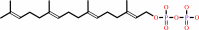 geranylgeranyl diphosphate
geranylgeranyl diphosphate
|
+
|
L-cysteinyl-[protein]
|
=
|
S-geranylgeranyl-L- cysteinyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
8:241-251
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of Rab geranylgeranyltransferase at 2.0 A resolution.
|
|
H.Zhang,
M.C.Seabra,
J.Deisenhofer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
BACKGROUND: Rab geranylgeranyltransferase (RabGGT) catalyzes the addition of two
geranylgeranyl groups to the C-terminal cysteine residues of Rab proteins, which
is crucial for membrane association and function of these proteins in
intracellular vesicular trafficking. Unlike protein farnesyltransferase (FT) and
type I geranylgeranyltransferase, which both prenylate monomeric small G
proteins or short peptides, RabGGT can prenylate Rab only when Rab is in a
complex with Rab escort protein (REP). RESULTS: The crystal structure of rat
RabGGT at 2.0 A resolution reveals an assembly of four distinct structural
modules. The beta subunit forms an alpha-alpha barrel that contains most of the
residues in the active site. The alpha subunit consists of a helical domain, an
immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain, and a leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domain. The
N-terminal region of the alpha subunit binds to the active site in the beta
subunit; residue His2alpha directly coordinates a zinc ion. The prenyl-binding
pocket of RabGGT is deeper than that in FT. CONCLUSIONS: LRR and Ig domains are
often involved in protein-protein interactions; in RabGGT they might participate
in the recognition and binding of REP. The binding of the N-terminal peptide of
the alpha subunit to the active site suggests an autoinhibition mechanism that
might contribute to the inability of RabGGT to recognize short peptides or Rab
alone as its substrate. Replacement of residues Trp102beta and Tyr154beta in FT
by Ser48beta and Leu99beta, respectively, in RabGGT largely determine the
different lipid-binding specificities of the two enzymes.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Ribbon representation of the RabGGT structure
(cyan, helical domain of the a subunit; orange, Ig-like domain;
green, LRR domain; purple, b subunit; blue, 3[10] helices of all
domains). (a) Complete structure of RabGGT. (b) The helical
domain and LRR domain of RabGGTa in a slightly different
orientation from (a). The 15 helices are numbered from a1 to
a15. (c) The Ig-like domain of RabGGTa. The strands are labelled
according to the convention in [34]. (d) The b subunit of
RabGGT, with the zinc ion shown as a red ball and the ligands
Asp238b, Cys240b and His290b in ball-and-stick representation.
The helices are numbered b1-b14.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(2000,
8,
241-251)
copyright 2000.
|
|
| |
Figure was
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.Kim,
J.Basner,
and
B.Lee
(2010).
Detecting internally symmetric protein structures.
|
| |
BMC Bioinformatics,
11,
303.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Hovlid,
R.L.Edelstein,
O.Henry,
J.Ochocki,
A.DeGraw,
S.Lenevich,
T.Talbot,
V.G.Young,
A.W.Hruza,
F.Lopez-Gallego,
N.P.Labello,
C.L.Strickland,
C.Schmidt-Dannert,
and
M.D.Distefano
(2010).
Synthesis, properties, and applications of diazotrifluropropanoyl-containing photoactive analogs of farnesyl diphosphate containing modified linkages for enhanced stability.
|
| |
Chem Biol Drug Des,
75,
51-67.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
U.T.Nguyen,
R.S.Goody,
and
K.Alexandrov
(2010).
Understanding and exploiting protein prenyltransferases.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
11,
1194-1201.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.L.Hindle,
J.Bella,
and
S.C.Lovell
(2009).
Quantitative analysis and prediction of curvature in leucine-rich repeat proteins.
|
| |
Proteins,
77,
342-358.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.N.Chan,
C.Hart,
L.Guo,
T.Nyberg,
B.S.Davies,
L.G.Fong,
S.G.Young,
B.J.Agnew,
and
F.Tamanoi
(2009).
A novel approach to tag and identify geranylgeranylated proteins.
|
| |
Electrophoresis,
30,
3598-3606.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.A.Baron,
R.Tavaré,
A.C.Figueiredo,
K.M.Blazewska,
B.A.Kashemirov,
C.E.McKenna,
F.H.Ebetino,
A.Taylor,
M.J.Rogers,
F.P.Coxon,
and
M.C.Seabra
(2009).
Phosphonocarboxylates inhibit the second geranylgeranyl addition by rab geranylgeranyl transferase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
6861-6868.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.I.Anzellotti,
and
N.P.Farrell
(2008).
Zinc metalloproteins as medicinal targets.
|
| |
Chem Soc Rev,
37,
1629-1651.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Watanabe,
H.D.Fiji,
L.Guo,
L.Chan,
S.S.Kinderman,
D.J.Slamon,
O.Kwon,
and
F.Tamanoi
(2008).
Inhibitors of protein geranylgeranyltransferase I and Rab geranylgeranyltransferase identified from a library of allenoate-derived compounds.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
9571-9579.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Pavkov,
E.M.Egelseer,
M.Tesarz,
D.I.Svergun,
U.B.Sleytr,
and
W.Keller
(2008).
The structure and binding behavior of the bacterial cell surface layer protein SbsC.
|
| |
Structure,
16,
1226-1237.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Guo,
Y.W.Wu,
D.Das,
C.Delon,
J.Cramer,
S.Yu,
S.Thuns,
N.Lupilova,
H.Waldmann,
L.Brunsveld,
R.S.Goody,
K.Alexandrov,
and
W.Blankenfeldt
(2008).
Structures of RabGGTase-substrate/product complexes provide insights into the evolution of protein prenylation.
|
| |
EMBO J,
27,
2444-2456.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Raposo,
and
M.S.Marks
(2007).
Melanosomes--dark organelles enlighten endosomal membrane transport.
|
| |
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,
8,
786-797.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Chavas,
S.Torii,
H.Kamikubo,
M.Kawasaki,
K.Ihara,
R.Kato,
M.Kataoka,
T.Izumi,
and
S.Wakatsuki
(2007).
Structure of the small GTPase Rab27b shows an unexpected swapped dimer.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
63,
769-779.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Sommerhalter,
Y.Zhang,
and
A.C.Rosenzweig
(2007).
Solution structure of the COMMD1 N-terminal domain.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
365,
715-721.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Matsushima,
T.Tanaka,
P.Enkhbayar,
T.Mikami,
M.Taga,
K.Yamada,
and
Y.Kuroki
(2007).
Comparative sequence analysis of leucine-rich repeats (LRRs) within vertebrate toll-like receptors.
|
| |
BMC Genomics,
8,
124.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Rasteiro,
and
J.B.Pereira-Leal
(2007).
Multiple domain insertions and losses in the evolution of the Rab prenylation complex.
|
| |
BMC Evol Biol,
7,
140.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.H.Gelb,
L.Brunsveld,
C.A.Hrycyna,
S.Michaelis,
F.Tamanoi,
W.C.Van Voorhis,
and
H.Waldmann
(2006).
Therapeutic intervention based on protein prenylation and associated modifications.
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
2,
518-528.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.R.Lackner,
R.M.Kindt,
P.M.Carroll,
K.Brown,
M.R.Cancilla,
C.Chen,
H.de Silva,
Y.Franke,
B.Guan,
T.Heuer,
T.Hung,
K.Keegan,
J.M.Lee,
V.Manne,
C.O'Brien,
D.Parry,
J.J.Perez-Villar,
R.K.Reddy,
H.Xiao,
H.Zhan,
M.Cockett,
G.Plowman,
K.Fitzgerald,
M.Costa,
and
P.Ross-Macdonald
(2005).
Chemical genetics identifies Rab geranylgeranyl transferase as an apoptotic target of farnesyl transferase inhibitors.
|
| |
Cancer Cell,
7,
325-336.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Pejchal,
and
M.L.Ludwig
(2005).
Cobalamin-independent methionine synthase (MetE): a face-to-face double barrel that evolved by gene duplication.
|
| |
PLoS Biol,
3,
e31.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.M.Sebti
(2005).
Protein farnesylation: implications for normal physiology, malignant transformation, and cancer therapy.
|
| |
Cancer Cell,
7,
297-300.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Enkhbayar,
M.Kamiya,
M.Osaki,
T.Matsumoto,
and
N.Matsushima
(2004).
Structural principles of leucine-rich repeat (LRR) proteins.
|
| |
Proteins,
54,
394-403.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Zhang,
W.Hu,
L.Cano,
T.D.Lee,
D.J.Chen,
and
Y.Chen
(2004).
Solution structure of the C-terminal domain of Ku80 suggests important sites for protein-protein interactions.
|
| |
Structure,
12,
495-502.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Larijani,
A.N.Hume,
A.K.Tarafder,
and
M.C.Seabra
(2003).
Multiple factors contribute to inefficient prenylation of Rab27a in Rab prenylation diseases.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
46798-46804.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Alory,
and
W.E.Balch
(2003).
Molecular evolution of the Rab-escort-protein/guanine-nucleotide-dissociation-inhibitor superfamily.
|
| |
Mol Biol Cell,
14,
3857-3867.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.S.Taylor,
T.S.Reid,
K.L.Terry,
P.J.Casey,
and
L.S.Beese
(2003).
Structure of mammalian protein geranylgeranyltransferase type-I.
|
| |
EMBO J,
22,
5963-5974.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Pylypenko,
A.Rak,
R.Reents,
A.Niculae,
V.Sidorovitch,
M.D.Cioaca,
E.Bessolitsyna,
N.H.Thomä,
H.Waldmann,
I.Schlichting,
R.S.Goody,
and
K.Alexandrov
(2003).
Structure of Rab escort protein-1 in complex with Rab geranylgeranyltransferase.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
11,
483-494.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Maurer-Stroh,
S.Washietl,
and
F.Eisenhaber
(2003).
Protein prenyltransferases.
|
| |
Genome Biol,
4,
212.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.An,
Y.Shao,
C.Alory,
J.Matteson,
T.Sakisaka,
W.Chen,
R.A.Gibbs,
I.A.Wilson,
and
W.E.Balch
(2003).
Geranylgeranyl switching regulates GDI-Rab GTPase recycling.
|
| |
Structure,
11,
347-357.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.V.Kajava,
and
B.Kobe
(2002).
Assessment of the ability to model proteins with leucine-rich repeats in light of the latest structural information.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
11,
1082-1090.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Ceulemans,
V.Vulsteke,
M.De Maeyer,
K.Tatchell,
W.Stalmans,
and
M.Bollen
(2002).
Binding of the concave surface of the Sds22 superhelix to the alpha 4/alpha 5/alpha 6-triangle of protein phosphatase-1.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
47331-47337.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.C.Evans,
D.P.Huddler,
J.Jiracek,
C.Castro,
N.S.Millian,
T.A.Garrow,
and
M.L.Ludwig
(2002).
Betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase: zinc in a distorted barrel.
|
| |
Structure,
10,
1159-1171.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Pei,
and
N.V.Grishin
(2002).
Breaking the singleton of germination protease.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
11,
691-697.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Mondragón-Palomino,
B.C.Meyers,
R.W.Michelmore,
and
B.S.Gaut
(2002).
Patterns of positive selection in the complete NBS-LRR gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana.
|
| |
Genome Res,
12,
1305-1315.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.H.Liang,
T.P.Ko,
and
A.H.Wang
(2002).
Structure, mechanism and function of prenyltransferases.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
269,
3339-3354.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Alory,
and
W.E.Balch
(2001).
Organization of the Rab-GDI/CHM superfamily: the functional basis for choroideremia disease.
|
| |
Traffic,
2,
532-543.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

