
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 94 a.a.
94 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 309 a.a.
309 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 248 a.a.
248 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 251 a.a.
251 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Ternary complex (zymogen)
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Ternary complex of procarboxypeptidase a, proproteinase e, and chymotrypsinogen c
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Procarboxypeptidase a. Chain: a. Procarboxypeptidase a. Chain: b. Proproteinase e. Chain: c. Chymotrypsinogen c. Chain: d. Synonym: tc, pcpa-tc
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Bos taurus. Cattle. Organism_taxid: 9913. Organ: pancreas. Organ: pancreas
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Tetramer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.35Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.192
|
R-free:
|
0.283
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
F.X.Gomis-Ruth,M.Gomez,W.Bode,R.Huber,F.X.Aviles
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
F.X.Gomis-Rüth
et al.
(1995).
The three-dimensional structure of the native ternary complex of bovine pancreatic procarboxypeptidase A with proproteinase E and chymotrypsinogen C.
Embo J,
14,
4387-4394.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
21-Jun-95
|
Release date:
|
27-Jan-97
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00730
(CBPA1_BOVIN) -
Carboxypeptidase A1 from Bos taurus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
419 a.a.
94 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P00730
(CBPA1_BOVIN) -
Carboxypeptidase A1 from Bos taurus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
419 a.a.
309 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.3.4.17.1
- carboxypeptidase A.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
Peptidyl-L-amino acid + H2O = peptide + L-amino acid
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
+
|
|
=
|
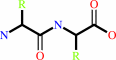
|
+
|
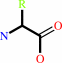
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chain D:
E.C.3.4.21.2
- chymotrypsin C.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
Preferential cleavage: Leu-|-Xaa, Tyr-|-Xaa, Phe-|-Xaa, Met-|-Xaa, Trp-|-Xaa, Gln-|-Xaa, Asn-|-Xaa.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Embo J
14:4387-4394
(1995)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The three-dimensional structure of the native ternary complex of bovine pancreatic procarboxypeptidase A with proproteinase E and chymotrypsinogen C.
|
|
F.X.Gomis-Rüth,
M.Gómez,
W.Bode,
R.Huber,
F.X.Avilés.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The metalloexozymogen procarboxypeptidase A is mainly secreted in ruminants as a
ternary complex with zymogens of two serine endoproteinases, chymotrypsinogen C
and proproteinase E. The bovine complex has been crystallized, and its molecular
structure analysed and refined at 2.6 A resolution to an R factor of 0.198. In
this heterotrimer, the activation segment of procarboxypeptidase A essentially
clamps the other two subunits, which shield the activation sites of the former
from tryptic attack. In contrast, the propeptides of both serine proproteinases
are freely accessible to trypsin. This arrangement explains the sequential and
delayed activation of the constituent zymogens. Procarboxypeptidase A is
virtually identical to the homologous monomeric porcine form. Chymotrypsinogen C
displays structural features characteristic for chymotrypsins as well as
elastases, except for its activation domain; similar to bovine chymotrypsinogen
A, its binding site is not properly formed, while its surface located activation
segment is disordered. The proproteinase E structure is fully ordered and
strikingly similar to active porcine elastase; its specificity pocket is
occluded, while the activation segment is fixed to the molecular surface. This
first structure of a native zymogen from the proteinase E/elastase family does
not fundamentally differ from the serine proproteinases known so far.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.Wu,
P.Y.Kim,
R.Manuel,
M.Seto,
M.Whitlow,
M.Nagashima,
J.Morser,
A.Gils,
P.Declerck,
and
M.E.Nesheim
(2009).
The Roles of Selected Arginine and Lysine Residues of TAFI (Pro-CPU) in Its Activation to TAFIa by the Thrombin-Thrombomodulin Complex.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
7059-7067.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Alonso-del-Rivero,
S.A.Trejo,
M.Rodríguez de la Vega,
Y.González,
S.Bronsoms,
F.Canals,
J.Delfín,
J.Diaz,
F.X.Aviles,
and
M.A.Chávez
(2009).
A novel metallocarboxypeptidase-like enzyme from the marine annelid Sabellastarte magnifica--a step into the invertebrate world of proteases.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
4875-4890.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.K.Shah,
L.P.Tripathi,
L.J.Jensen,
M.Gahnim,
C.Mason,
E.E.Furlong,
V.Rodrigues,
K.P.White,
P.Bork,
and
R.Sowdhamini
(2008).
Enhanced function annotations for Drosophila serine proteases: a case study for systematic annotation of multi-member gene families.
|
| |
Gene,
407,
199-215.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Nemoda,
and
M.Sahin-Tóth
(2006).
Chymotrypsin C (caldecrin) stimulates autoactivation of human cationic trypsinogen.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
11879-11886.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Bayés,
M.Comellas-Bigler,
M.Rodríguez de la Vega,
K.Maskos,
W.Bode,
F.X.Aviles,
M.A.Jongsma,
J.Beekwilder,
and
J.Vendrell
(2005).
Structural basis of the resistance of an insect carboxypeptidase to plant protease inhibitors.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
102,
16602-16607.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Gál,
V.Harmat,
A.Kocsis,
T.Bián,
L.Barna,
G.Ambrus,
B.Végh,
J.Balczer,
R.B.Sim,
G.Náray-Szabó,
and
P.Závodszky
(2005).
A true autoactivating enzyme. Structural insight into mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease-2 activations.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
33435-33444.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.X.Gomis-Rüth,
A.Bayés,
G.Sotiropoulou,
G.Pampalakis,
T.Tsetsenis,
V.Villegas,
F.X.Avilés,
and
M.Coll
(2002).
The structure of human prokallikrein 6 reveals a novel activation mechanism for the kallikrein family.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
27273-27281.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.L.Fink,
L.D.Cope,
E.J.Hansen,
and
J.W.Geme
(2001).
The Hemophilus influenzae Hap autotransporter is a chymotrypsin clan serine protease and undergoes autoproteolysis via an intermolecular mechanism.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
276,
39492-39500.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.X.Gomis-Rüth,
and
M.Coll
(2001).
Solving a 300 kDa multimeric protein by low-resolution MAD phasing and averaging/phase extension.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
57,
800-805.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Neurath,
and
H.Neurath
(2001).
From proteases to proteomics.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
10,
892-904.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Perera,
C.Foley,
T.A.Darden,
D.Stafford,
T.Mather,
C.T.Esmon,
and
L.G.Pedersen
(2000).
Modeling zymogen protein C.
|
| |
Biophys J,
79,
2925-2943.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.X.Gomis-Rüth,
V.Companys,
Y.Qian,
L.D.Fricker,
J.Vendrell,
F.X.Avilés,
and
M.Coll
(1999).
Crystal structure of avian carboxypeptidase D domain II: a prototype for the regulatory metallocarboxypeptidase subfamily.
|
| |
EMBO J,
18,
5817-5826.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Jing,
K.J.Macon,
D.Moore,
L.J.DeLucas,
J.E.Volanakis,
and
S.V.Narayana
(1999).
Structural basis of profactor D activation: from a highly flexible zymogen to a novel self-inhibited serine protease, complement factor D.
|
| |
EMBO J,
18,
804-814.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.T.Mkwetshana,
R.J.Naudé,
W.Oelofsen,
T.Naganuma,
and
K.Muramoto
(1999).
The isolation and partial characterization of precursor forms of ostrich carboxypeptidase.
|
| |
Int J Biochem Cell Biol,
31,
331-343.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Darnis,
N.Juge,
C.Marino,
F.X.Avilés,
A.Puigserver,
J.C.Chaix,
and
X.J.Guo
(1999).
Cloning, sequencing and functional expression of a cDNA encoding porcine pancreatic preprocarboxypeptidase A1.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
259,
719-725.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Reuter,
G.Wiegand,
R.Huber,
and
M.E.Than
(1999).
Structural analysis at 2.2 A of orthorhombic crystals presents the asymmetry of the allophycocyanin-linker complex, AP.LC7.8, from phycobilisomes of Mastigocladus laminosus.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
96,
1363-1368.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Reverter,
J.Vendrell,
F.Canals,
J.Horstmann,
F.X.Avilés,
H.Fritz,
and
C.P.Sommerhoff
(1998).
A carboxypeptidase inhibitor from the medical leech Hirudo medicinalis. Isolation, sequence analysis, cDNA cloning, recombinant expression, and characterization.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
32927-32933.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Reverter,
S.Ventura,
V.Villegas,
J.Vendrell,
and
F.X.Avilés
(1998).
Overexpression of human procarboxypeptidase A2 in Pichia pastoris and detailed characterization of its activation pathway.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
3535-3541.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Aloy,
L.Catasús,
V.Villegas,
D.Reverter,
J.Vendrell,
and
F.X.Avilés
(1998).
Comparative analysis of the sequences and three-dimensional models of human procarboxypeptidases A1, A2 and B.
|
| |
Biol Chem,
379,
149-155.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.García-Sáez,
D.Reverter,
J.Vendrell,
F.X.Avilés,
and
M.Coll
(1997).
The three-dimensional structure of human procarboxypeptidase A2. Deciphering the basis of the inhibition, activation and intrinsic activity of the zymogen.
|
| |
EMBO J,
16,
6906-6913.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Baumeister,
Z.Cejka,
M.Kania,
and
E.Seemüller
(1997).
The proteasome: a macromolecular assembly designed to confine proteolysis to a nanocompartment.
|
| |
Biol Chem,
378,
121-130.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|

| |

