 |
PDBsum entry 6gg6
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of m2 pyk in complex with serine.
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Pyruvate kinase pkm. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h. Synonym: cytosolic thyroid hormone-binding protein,cthbp,opa- interacting protein 3,oip-3,pyruvate kinase 2/3,pyruvate kinase muscle isozyme,thyroid hormone-binding protein 1,thbp1,tumor m2-pk, p58. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: pkm, oip3, pk2, pk3, pkm2. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.96Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.237
|
R-free:
|
0.252
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
I.W.Mcnae,M.Yuan,M.D.Walkinshaw
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
M.Yuan
et al.
(2018).
An allostatic mechanism for M2 pyruvate kinase as an amino-acid sensor.
Biochem J,
475,
1821-1837.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
02-May-18
|
Release date:
|
23-May-18
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P14618
(KPYM_HUMAN) -
Pyruvate kinase PKM from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
531 a.a.
510 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.1.40
- pyruvate kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
pyruvate + ATP = phosphoenolpyruvate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 pyruvate
pyruvate
|
+
|
ATP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 62.50% similarity
|
=
|
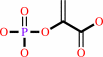 phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.10.2
- non-specific protein-tyrosine kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-tyrosyl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein] + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-tyrosyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.11.1
- non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
L-seryl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein] + ADP + H+
|
|
2.
|
L-threonyl-[protein] + ATP = O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein] + ADP + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-seryl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
O-phospho-L-seryl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-threonyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
O-phospho-L-threonyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochem J
475:1821-1837
(2018)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
An allostatic mechanism for M2 pyruvate kinase as an amino-acid sensor.
|
|
M.Yuan,
I.W.McNae,
Y.Chen,
E.A.Blackburn,
M.A.Wear,
P.A.M.Michels,
L.A.Fothergill-Gilmore,
T.Hupp,
M.D.Walkinshaw.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
We have tested the effect of all 20 proteinogenic amino acids on the activity of
the M2 isoenzyme of pyruvate kinase (M2PYK) and show that, within
physiologically relevant concentrations, phenylalanine, alanine, tryptophan,
methionine, valine, and proline act as inhibitors, while histidine and serine
act as activators. Size exclusion chromatography has been used to show that all
amino acids, whether activators or inhibitors, stabilise the tetrameric form of
M2PYK. In the absence of amino-acid ligands an apparent tetramer-monomer
dissociation Kd is estimated to be ∼0.9 µM with a slow
dissociation rate (t1/2 ∼ 15 min). X-ray
structures of M2PYK complexes with alanine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan show
the M2PYK locked in an inactive T-state conformation, while activators lock the
M2PYK tetramer in the active R-state conformation. Amino-acid binding in the
allosteric pocket triggers rigid body rotations (11°) stabilising either T or R
states. The opposing inhibitory and activating effects of the non-essential
amino acids serine and alanine suggest that M2PYK could act as a rapid-response
nutrient sensor to rebalance cellular metabolism. This competition at a single
allosteric site between activators and inhibitors provides a novel regulatory
mechanism by which M2PYK activity is finely tuned by the relative (but not
absolute) concentrations of activator and inhibitor amino acids. Such
'allostatic' regulation may be important in metabolic reprogramming and
influencing cell fate.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

