Orotate phosphoribosyltransferase
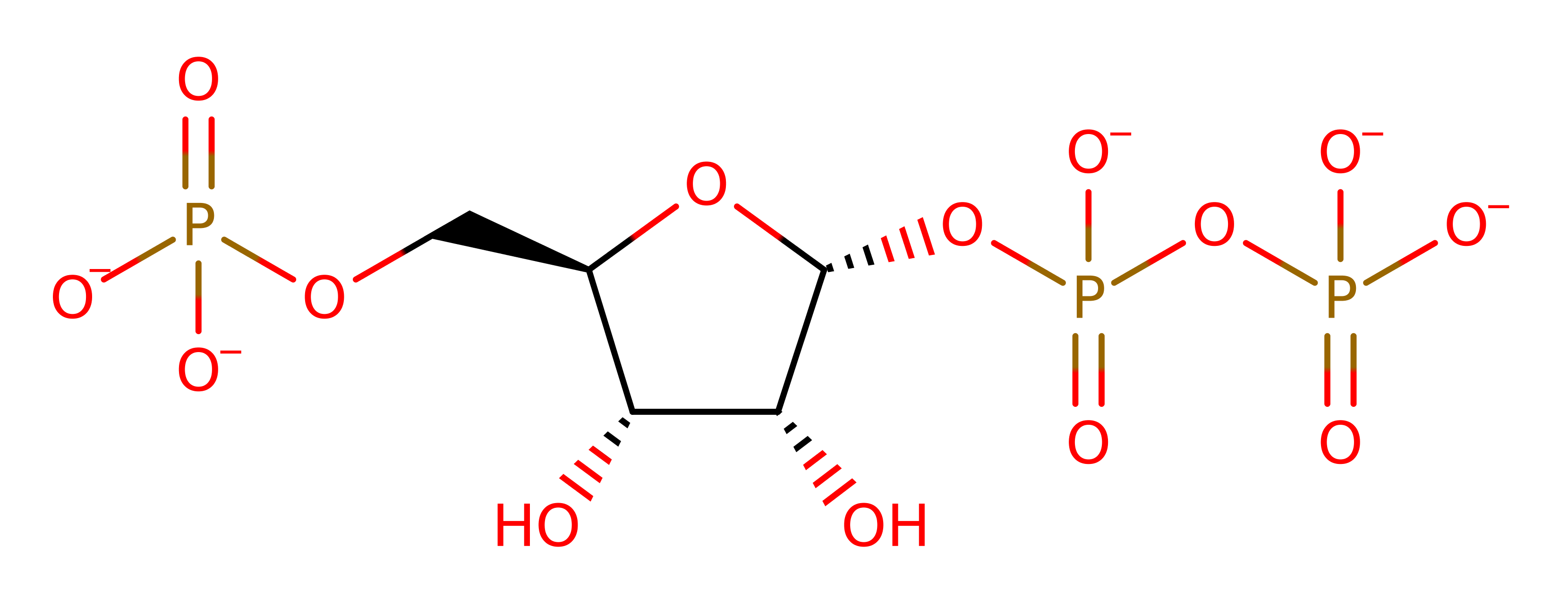
Orotate phosphoribosyltransferase (OPRTase) is involved in the biosynthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides. In the pyrimidine synthesis pathway, OPRT catalyses the reversible phosphoribosyl transfer from 5'-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1'-diphosphate (PRPP) to orotic acid (OA), forming pyrophosphate and orotidine 5'-monophosphate (OMP).
The mechanism of PRTases has been the subject of much debate over the years. However, stereochemical results argue against mechanisms which invoke a covalent enzyme-phosphoribosyl intermediate. Kinetic studies argue against a direct SN2-type displacement. Thus, a two-step, SN1-type mechanisms with oxocarbonium-like transition states or intermediates has been proposed as the most likely mechanism. However, there is still much debate as to the exact roles of the residues involved.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0A7E3
 (2.4.2.10)
(2.4.2.10)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1oro
- A FLEXIBLE LOOP AT THE DIMER INTERFACE IS A PART OF THE ACTIVE SITE OF THE ADJACENT MONOMER OF ESCHERICHIA COLI OROTATE PHOSPHORIBOSYLTRANSFERASE
(2.4 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.2020
 (see all for 1oro)
(see all for 1oro)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.4.2.10)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Although there has been much debate as to the exact mechanism of this protein, it is now thought to proceed via an SN1-type mechanism. Here, the phosphate group (activated by the divalent metal ion) dissociates, forming an oxycarbenium intermediate which is then attacked by the orotate substrate to form the OMP product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1oro) | ||
| His105 | His105A | Thought to play a direct role for His105 in binding to the alpha-phosphate, may also play a role in protonation or deprotonation of the leaving or attacking pyrophosphate, respectively. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys103 | Lys103A | Thought to act as a general acid/base. Lys103 appears poised to provide geometric stabilisation, proton transfer, and/or charge neutralisation at the transition state. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
Chemical Components
unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, overall product formed, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- González-Segura L et al. (2007), Biochemistry, 46, 14075-14086. Ternary complex formation and induced asymmetry in orotate phosphoribosyltransferase. DOI:10.1021/bi701023z. PMID:18020427.
- Donini S et al. (2017), Sci Rep, 7, 1180-. Structural investigations on orotate phosphoribosyltransferase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a key enzyme of the de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-01057-z. PMID:28446777.
- Wang GP et al. (2012), Biochemistry, 51, 4406-4415. Loop residues and catalysis in OMP synthase. DOI:10.1021/bi300082s. PMID:22531099.
- Grubmeyer C et al. (2012), Biochemistry, 51, 4397-4405. Structure of Salmonella typhimurium OMP synthase in a complete substrate complex. DOI:10.1021/bi300083p. PMID:22531064.
- Zhang Y et al. (2010), J Am Chem Soc, 132, 17023-17031. Leaving group activation and pyrophosphate ionic state at the catalytic site of Plasmodium falciparum orotate phosphoribosyltransferase. DOI:10.1021/ja107806j. PMID:21067187.
- Zhang Y et al. (2010), J Am Chem Soc, 132, 8787-8794. Pyrophosphate interactions at the transition states of Plasmodium falciparum and human orotate phosphoribosyltransferases. DOI:10.1021/ja102849w. PMID:20527751.
- Zhang Y et al. (2009), J Am Chem Soc, 131, 4685-4694. Transition states of Plasmodium falciparum and human orotate phosphoribosyltransferases. DOI:10.1021/ja808346y. PMID:19292447.
- Wang GP et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 284-295. Motional dynamics of the catalytic loop in OMP synthase. DOI:10.1021/bi982057s. PMID:9890909.
- Tao W et al. (1996), Biochemistry, 35, 14-21. Transition state structure of Salmonella typhimurium orotate phosphoribosyltransferase. DOI:10.1021/bi951898l. PMID:8555167.
- Ozturk DH et al. (1995), Biochemistry, 34, 10755-10763. Locations and functional roles of conserved lysine residues in Salmonella typhimurium orotate phosphoribosyltransferase. PMID:7545005.
- Scapin G et al. (1995), Biochemistry, 34, 10744-10754. The crystal structure of the orotate phosphoribosyltransferase complexed with orotate and alpha-D-5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate. PMID:7545004.
- Bhatia MB et al. (1993), Arch Biochem Biophys, 303, 321-325. The role of divalent magnesium in activating the reaction catalyzed by orotate phosphoribosyltransferase. DOI:10.1006/abbi.1993.1290. PMID:7685580.

Step 1. The diphosphate group dissociates from the PRPP substrate, forming an oxycarbenium ion intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys103A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His105A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall reactant used
Step 2. Lys103 (or a bound water molecule, activated by Lys103) abstracts a proton from the substrate which initiates the nucleophilic attack on the oxycarmenium ion, forming the final products.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His105A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys103A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, overall product formed, overall reactant used
Step 3. Inferred return step in which water (although it could also be the product diphosphate) abstracts the proton from Lys103.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys103A | proton donor |



 Download:
Download: