Exodeoxyribonuclease (lambda-induced)
Lambda-exonuclease from Bacteriophage lambda is a 5'->3' exonuclease. It catalyses the hydrolysis of one strand of double stranded DNA in a 5' to 3' direction, leaving single stranded DNA. This is involved in DNA replication, recombination and repair. Once started on a reaction, lambda-exonuclease will continue to hydrolyse until either the DNA strand ends, or the enzyme dissociates into monomers.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P03697
 (3.1.11.3)
(3.1.11.3)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia virus Lambda (Virus)

- PDB
-
1avq
- TOROIDAL STRUCTURE OF LAMBDA EXONUCLEASE DETERMINED AT 2.4 ANGSTROMS
(2.4 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.320.10
 (see all for 1avq)
(see all for 1avq)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (3)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.11.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The three-metal mechanism of EcoRV is the most likely mechanism for lambda-exonuclease. This is a dissociative hydrolysis mechanism where the O-P bond is broken before the nucleophilic of water upon the phosphate. The dissociation of the O-P bond is facilitated by protonation from a magnesium activated water molecule. And the nucleophilic attack is facilitated by Glu129 deprotonating a second water promoting the attack.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1avq) | ||
| Glu129 | Glu129(131)A | Activates the nucleophilic water | increase nucleophilicity, metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp109, Glu129, Glu93, Leu130 (main-C) | Asp109(111)A, Glu129(131)A, Glu93(95)A, Leu130(132)A (main-C) | Involved in coordinating the magnesium ions | metal ligand |
| Glu102 | Glu102(104)A | Stabilizes a water molecule which coordinates the magnesium ion | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys131 | Lys131(133)A | Stabilizes the nucleophilic water so its in the correct orientation to perform a nucleophilic attack | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, heterolysis, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, native state of enzyme regenerated, proton relayReferences
- Kovall RA et al. (1999), Curr Opin Chem Biol, 3, 578-583. Type II restriction endonucleases: structural, functional and evolutionary relationships. DOI:10.1016/s1367-5931(99)00012-5. PMID:10508668.
- Imhof P et al. (2009), Biochemistry, 48, 9061-9075. Catalytic mechanism of DNA backbone cleavage by the restriction enzyme EcoRV: a quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical analysis. DOI:10.1021/bi900585m. PMID:19678693.
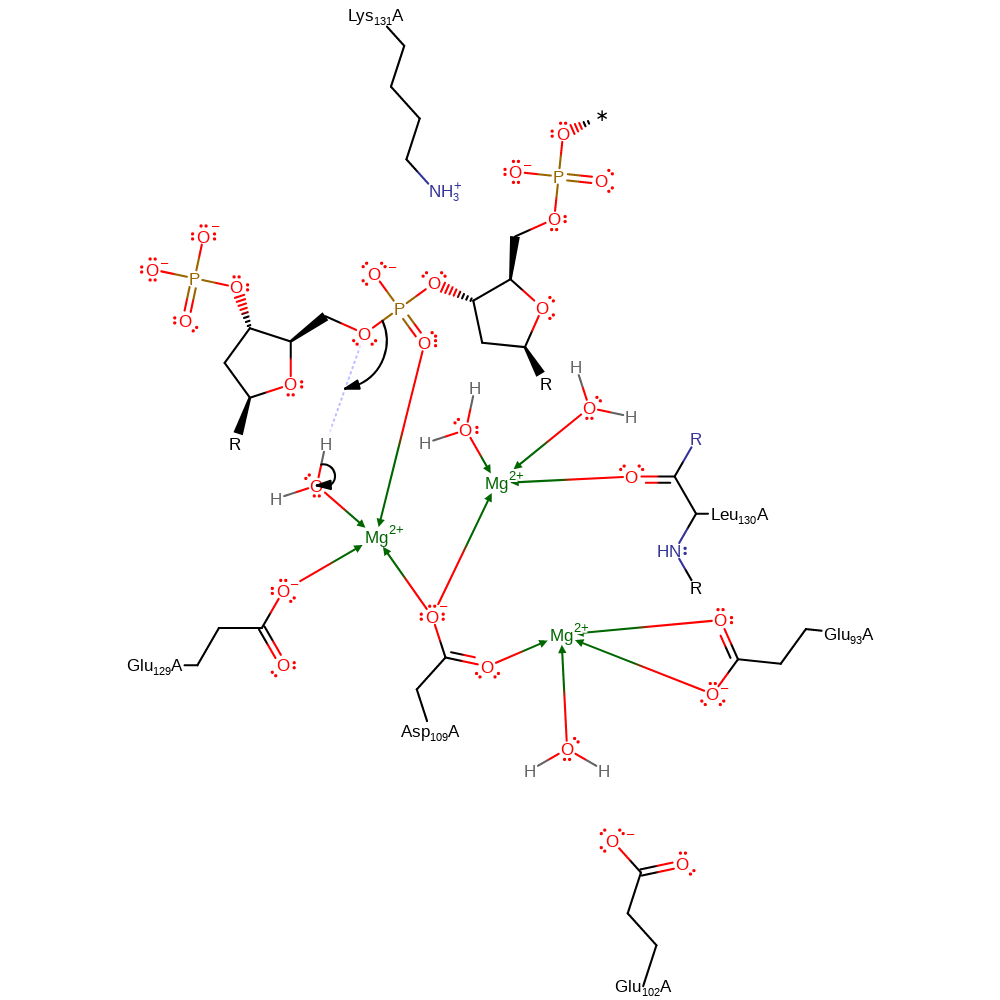
Step 1. A magnesium activated water molecule donates a proton to the 5' hydroxyl group promoting its dissociation from the phosphate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys131(133)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu93(95)A | metal ligand |
| Asp109(111)A | metal ligand |
| Glu129(131)A | metal ligand |
| Leu130(132)A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu102(104)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, heterolysis
Step 2. Glu129 rotates to become closer to a second water molecule. It then deprotonates the water molecule allowing the water to perform a nucleophilic attack on the phosphate. Lys131 is thought to be responsible for orientating the water molecule for nucleophilic attack.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu93(95)A | metal ligand |
| Asp109(111)A | metal ligand |
| Glu129(131)A | metal ligand |
| Leu130(132)A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu102(104)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu129(131)A | increase nucleophilicity |
| Lys131(133)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu129(131)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer
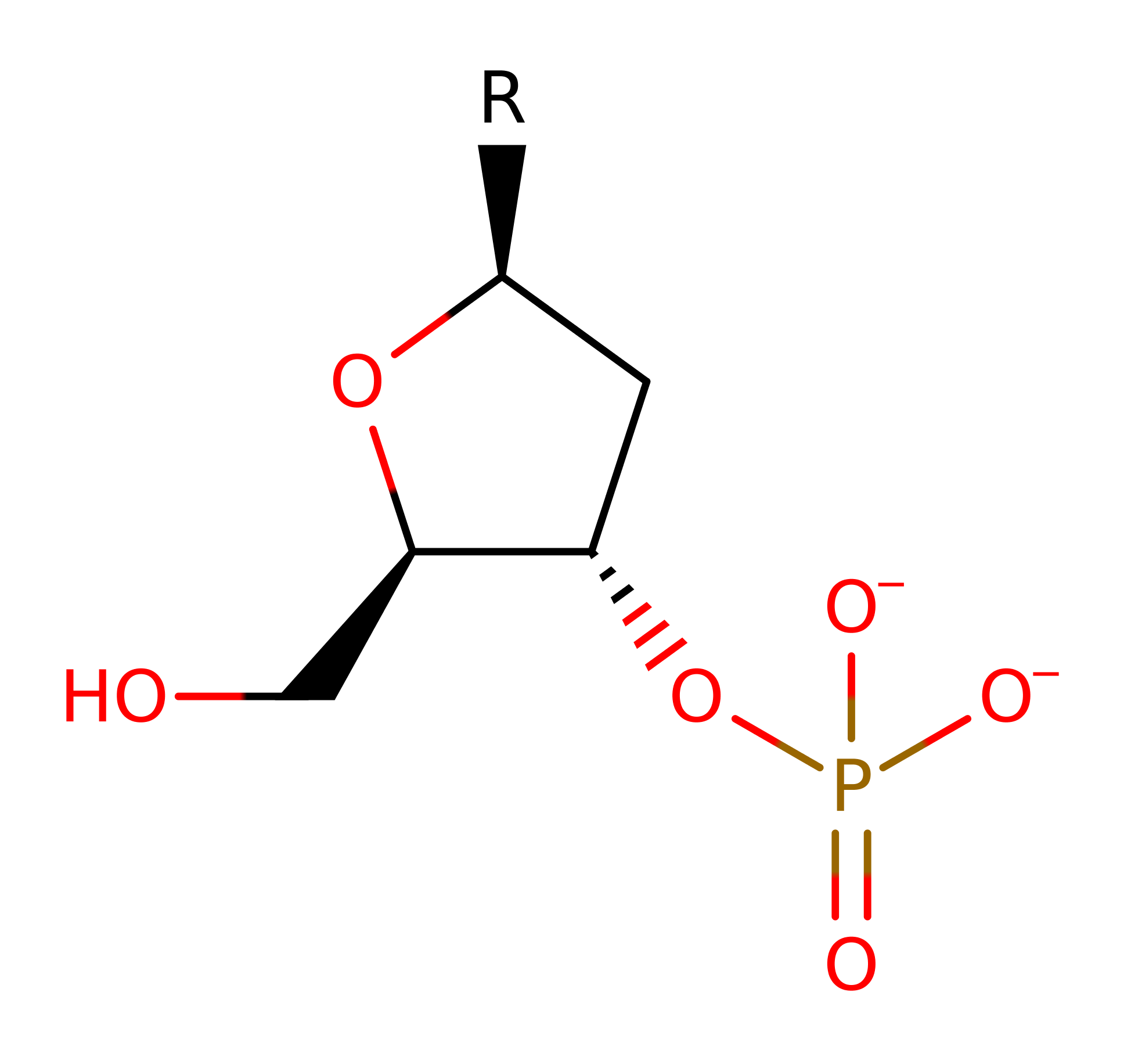
Step 3. Glu129 donates a proton to a phosphate oxygen regenrating the residue in its native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu93(95)A | metal ligand |
| Asp109(111)A | metal ligand |
| Glu129(131)A | metal ligand |
| Leu130(132)A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu102(104)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys131(133)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu129(131)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, native state of enzyme regenerated
Step 4. The leaving group hydroxyl acts as a proton relay deprotonating the phosphate group and protonating the metal coordinated hydroxide ion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu93(95)A | metal ligand |
| Asp109(111)A | metal ligand |
| Glu129(131)A | metal ligand |
| Leu130(132)A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu102(104)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys131(133)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton relay, overall product formedIntroduction
In this associative mechanism Glu129 activates a water molecule for nucleophilic attack on the scissile phosphate. A penta-covalent intermediate is formed which collapses to form the products and restore the enzyme to its native state. See other mechanism for the references.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1avq) | ||
| Glu129 | Glu129(131)A | Activates the water molecule for nucleophilic attack by deprotonating it. | metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp109, Glu93, Leu130 (main-C) | Asp109(111)A, Glu93(95)A, Leu130(132)A (main-C) | Coordinate the magnesium ion. | metal ligand |
| Glu102 | Glu102(104)A | Stabilizes a magnesium coordinating water molecule. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys131 | Lys131(133)A | Orientate the water molecule for nucleophillic attack. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, decoordination from a metal ion, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, overall product formed, coordination to a metal ion, heterolysis, native state of enzyme regenerated, proton relayReferences
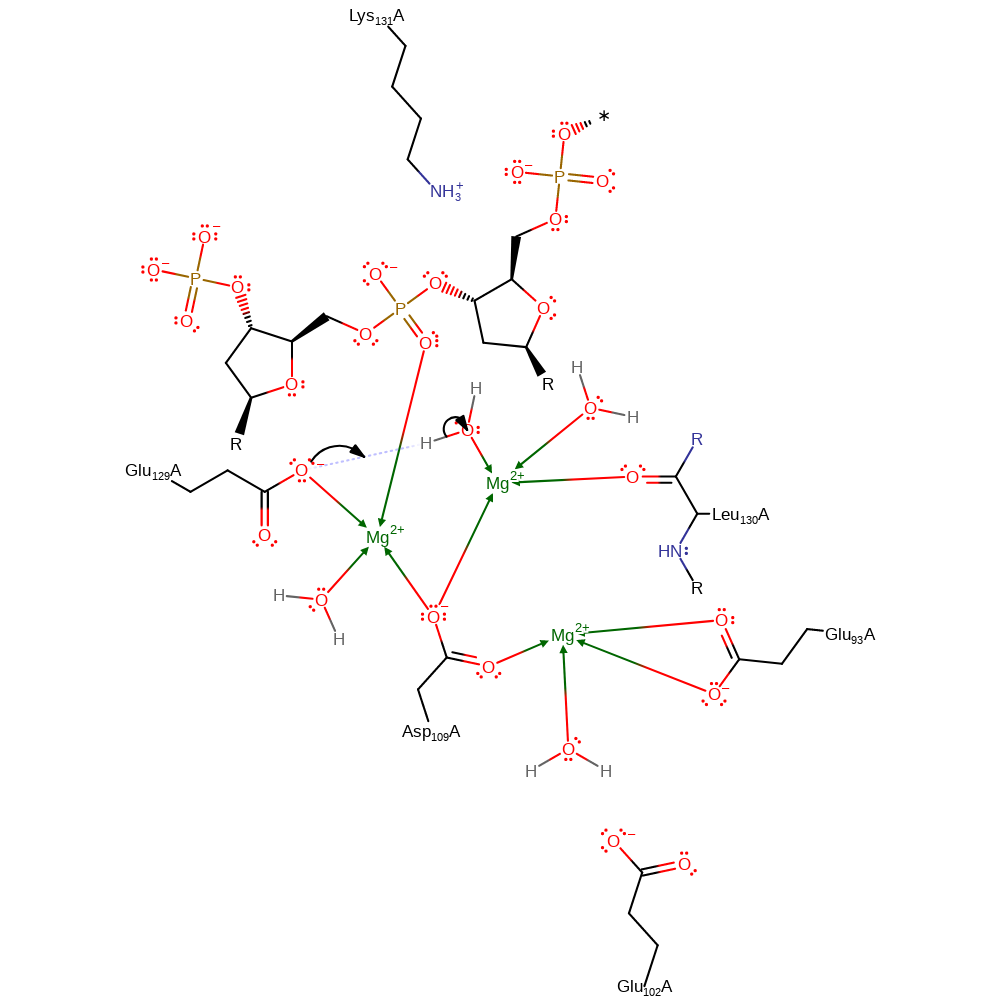
Step 1. Glu129 deprotonates a water molecule this will activate it for nucleophillic attack. The deprotonating oxygen of Glu129 and the hydroxide will decoordinate from the magnesium ions after the proton transfer has occurred.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu102(104)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Leu130(132)A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu129(131)A | metal ligand |
| Asp109(111)A | metal ligand |
| Glu93(95)A | metal ligand |
| Lys131(133)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu129(131)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, decoordination from a metal ion
Step 2. The activated hydroxide ion performs a nucleophillic on the phosphate group forming a penta-covalent intermediate. Lys131 acts to orientate the hydroxide ion for the nucleophilic attack.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu93(95)A | metal ligand |
| Asp109(111)A | metal ligand |
| Leu130(132)A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu102(104)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys131(133)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used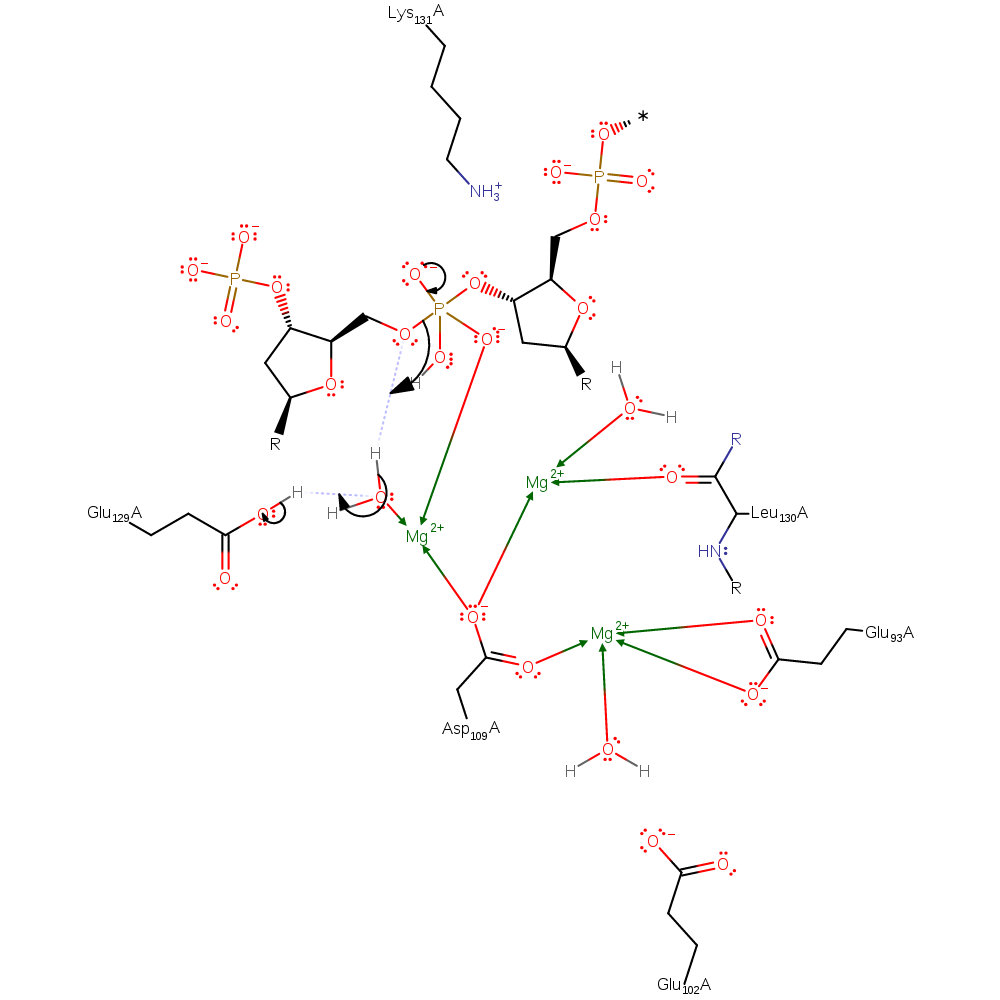
Step 3. The intermediate collapses forming the products. This is facilitated by the leaving group hydroxyl accepting a proton from a water molecule with the concomitant deprotonation of Glu129 by the same water molecule. Glu129 can now re-coordinate to the magnesium ion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu93(95)A | metal ligand |
| Asp109(111)A | metal ligand |
| Leu130(132)A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu102(104)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys131(133)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu129(131)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
overall product formed, coordination to a metal ion, heterolysis, native state of enzyme regenerated, proton transfer, proton relayIntroduction
This is another dissociative mechanism where the first step is identical to the first proposal. These mechanisms differ because in this proposal Lys131 acts as a proton relay to activate the water molecule for nucleophilic attack. See first mechanism for the references.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1avq) | ||
| Asp109, Glu129, Glu93, Leu130 (main-C) | Asp109(111)A, Glu129(131)A, Glu93(95)A, Leu130(132)A (main-C) | Coordinate the magnesium ion | metal ligand |
| Glu102 | Glu102(104)A | Stabilizes a water molecule coordinated to the magnesium ion. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys131 | Lys131(133)A | Acts as a proton relay to activate the water mole clue for nucleophilic attack. | proton relay, proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, overall product formed, overall reactant used, proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton relayReferences

Step 1. A magnesium activated water molecule donates a proton to the 5' hydroxyl group promoting its dissociation from the phosphate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu102(104)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Leu130(132)A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu129(131)A | metal ligand |
| Asp109(111)A | metal ligand |
| Glu93(95)A | metal ligand |
| Lys131(133)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, overall product formed, overall reactant used, proton transfer
Step 2. Lys131 acts as a proton relay to promote the nucleophilic attack of a water molecule on to the phosphate group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu93(95)A | metal ligand |
| Asp109(111)A | metal ligand |
| Glu129(131)A | metal ligand |
| Leu130(132)A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu102(104)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys131(133)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys131(133)A | proton relay |
| Lys131(133)A | proton donor, proton acceptor |

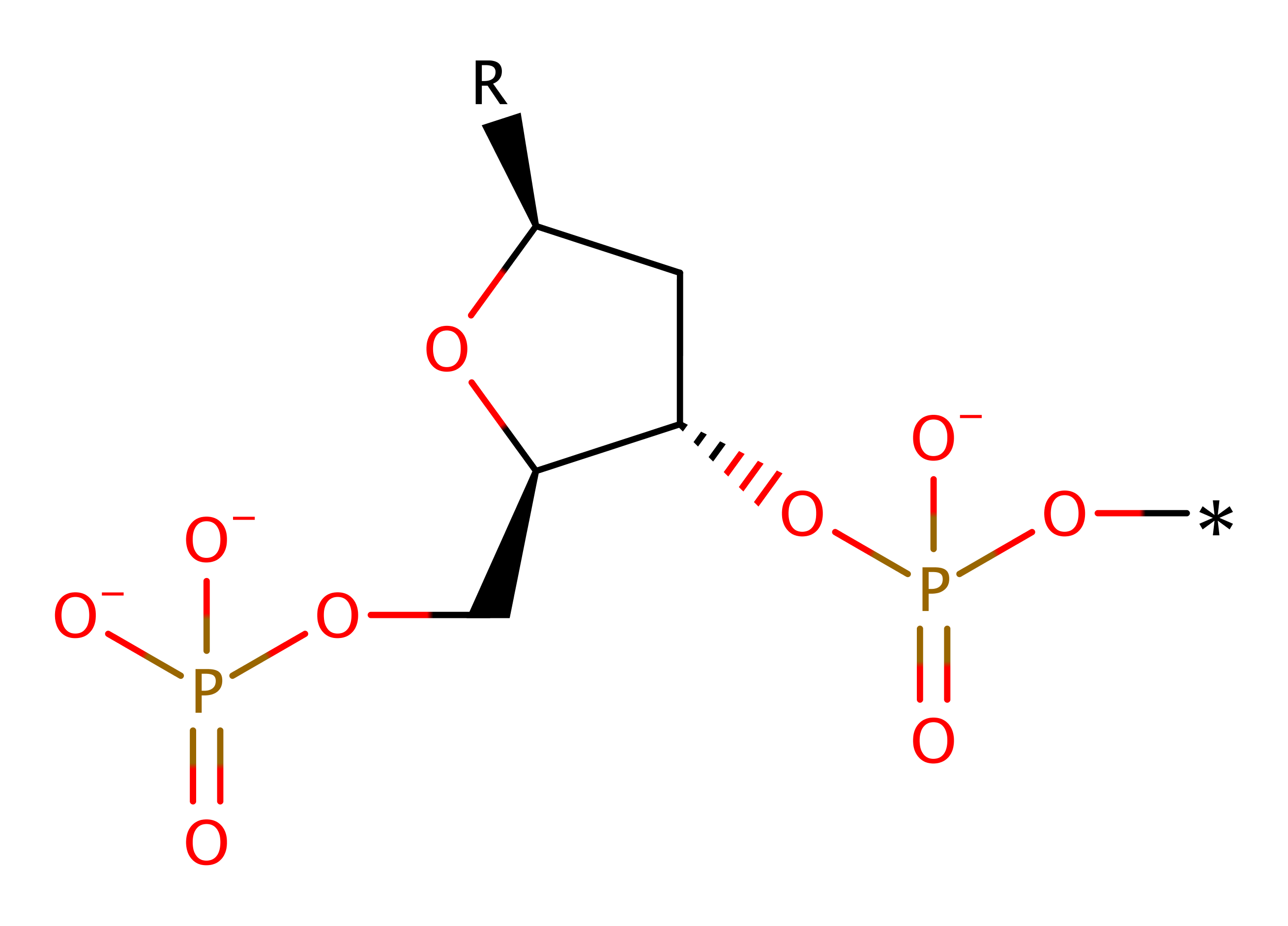

 Download:
Download:  Download:
Download: 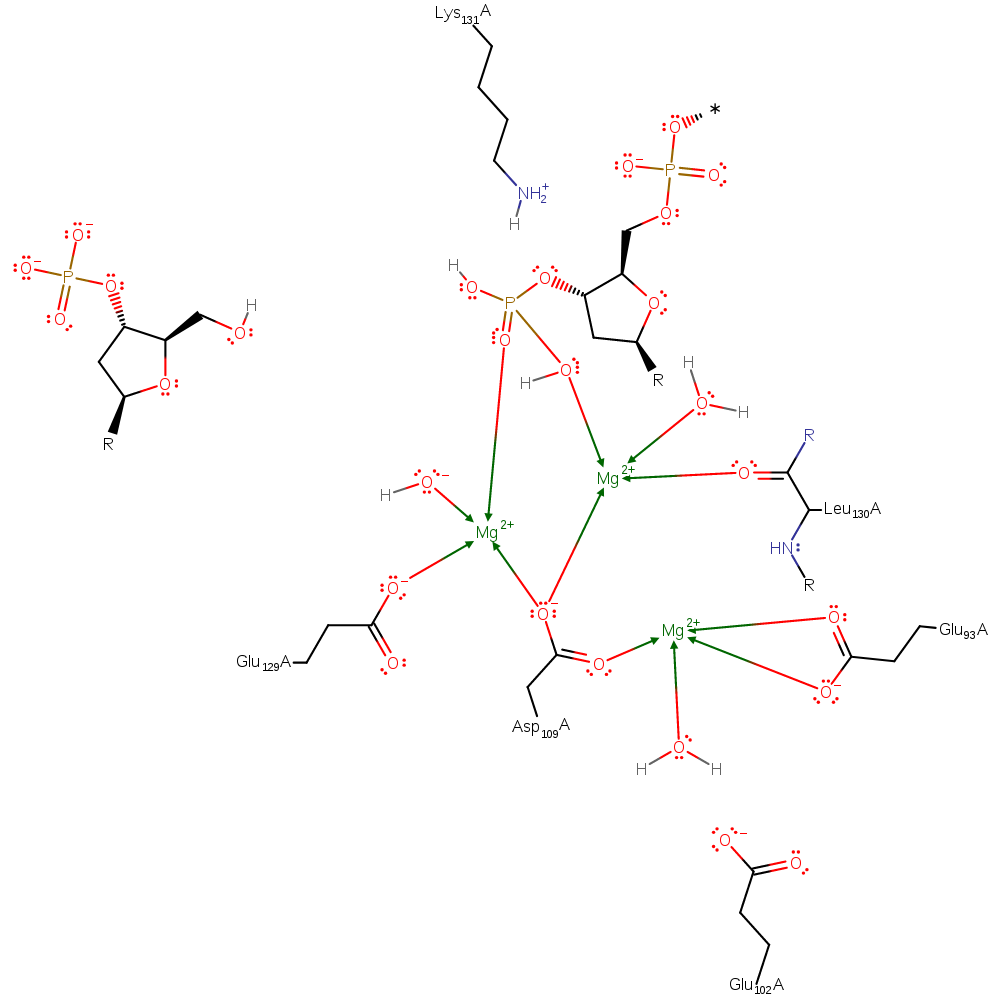 Download:
Download: