Cathepsin S
Cathepsin S is a cysteine proteinase of the papain superfamily and is involved in generation of a major histocompatability complex class II restricted T-cell response by antigen-presenting cells. Expression is almost exclusively restricted to cells of lymphoid origin. This enzyme is therefore important for study in reference to immune-related disorders.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P25774
 (3.4.22.27)
(3.4.22.27)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1glo
- Crystal Structure of Cys25Ser mutant of human cathepsin S
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.70.10
 (see all for 1glo)
(see all for 1glo)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Cathepsin S is a cysteine protease. The resting state contains a thioloate-imidazolium pair (Cys 25 and His 164) that is stabilised by Asn 184. Cys 25 attacks the peptide carbonyl nucleophilically, having been activated by deprotonation by His 164 which is in turn activated to act as a base by Asn 184, to form an acyl enzyme intermediate, with His 164 protonating the departing amine. Negative charge that accumulates on the substrate carbonyl oxygen during the reaction is stabilised by an 'oxyanion-hole' involving the side chain of Gln 19 and the backbone NH of Cys 25. The thioester intermediate is then hydrolysed by a water molecule that is deprotonated by His 164 acting as a general base.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1glo) | ||
| His278 | His164A | Acts as a general acid/base catalyst to activate Cys 25 and a water molecule for nucleophilic attack, and to facilitate loss of the leaving groups by proton donation. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asn298 | Asn184A | Activates and stabilises His 164 to allow it to act as a general acid/base catalyst. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys139 | Ser25A | Acts as a nucleophile in the attack of the scissile bond. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Gln133, Cys139 (main-N) | Gln19A, Ser25A (main-N) | Forms part of the oxyanion hole to stabilise the development of negative charge in the transition state. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Turkenburg JP et al. (2002), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 58, 451-455. Structure of a Cys25→Ser mutant of human cathepsin S. DOI:10.1107/s0907444901021825. PMID:11856830.
- Kaulmann G et al. (2006), Protein Sci, 15, 2619-2629. The crystal structure of a Cys25 -> Ala mutant of human procathepsin S elucidates enzyme-prosequence interactions. DOI:10.1110/ps.062401806. PMID:17075137.
- Pauly TA et al. (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 3203-3213. Specificity determinants of human cathepsin s revealed by crystal structures of complexes. DOI:10.1021/bi027308i. PMID:12641451.

Step 1. His164 deprotonates Cys25, activating it so that it can nucleophilically attack the carbon of the scissille bond which produces the oxyanion intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln19A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn184A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser25A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser25A | proton donor, nucleophile |
| His164A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used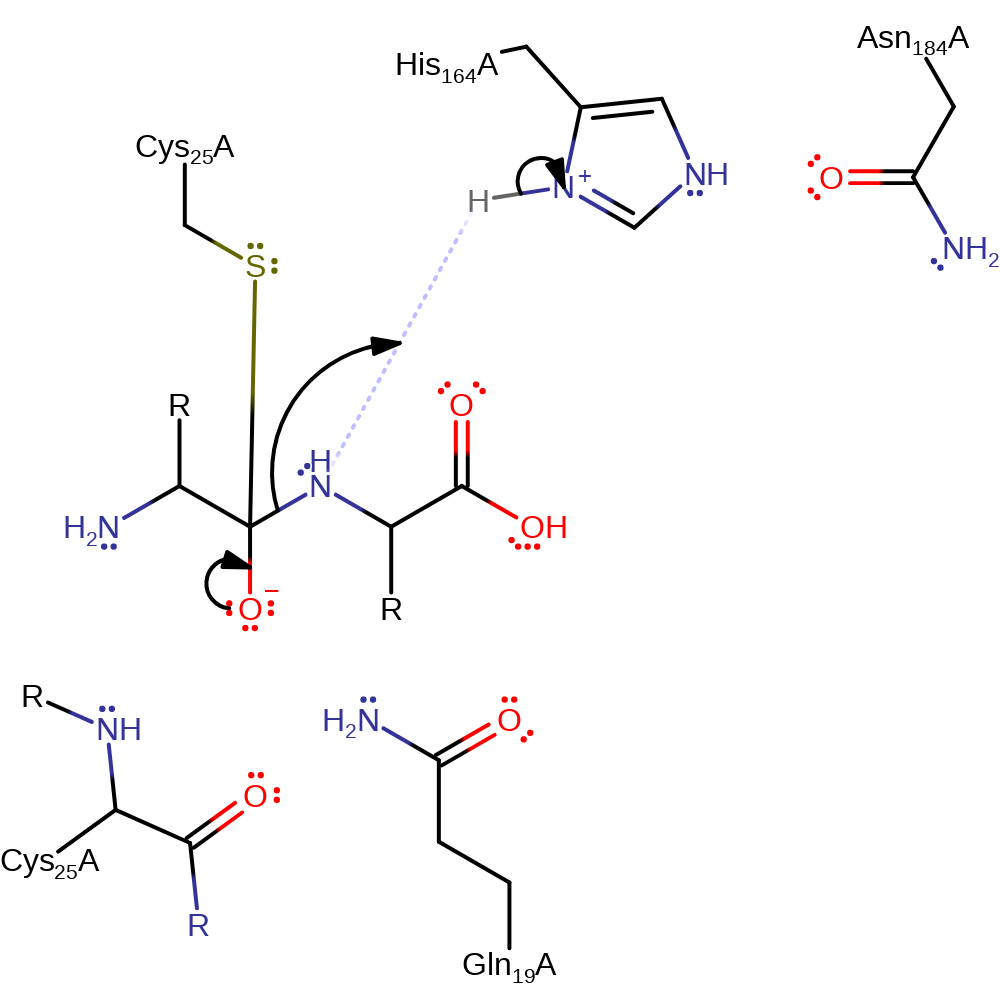
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates an elimantion resulting in the cleavage of the scissille bond. The amino group of the N-terminal product then accepts a proton from His164 which prevents reformation of the peptide bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln19A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser25A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn184A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His164A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, overall product formed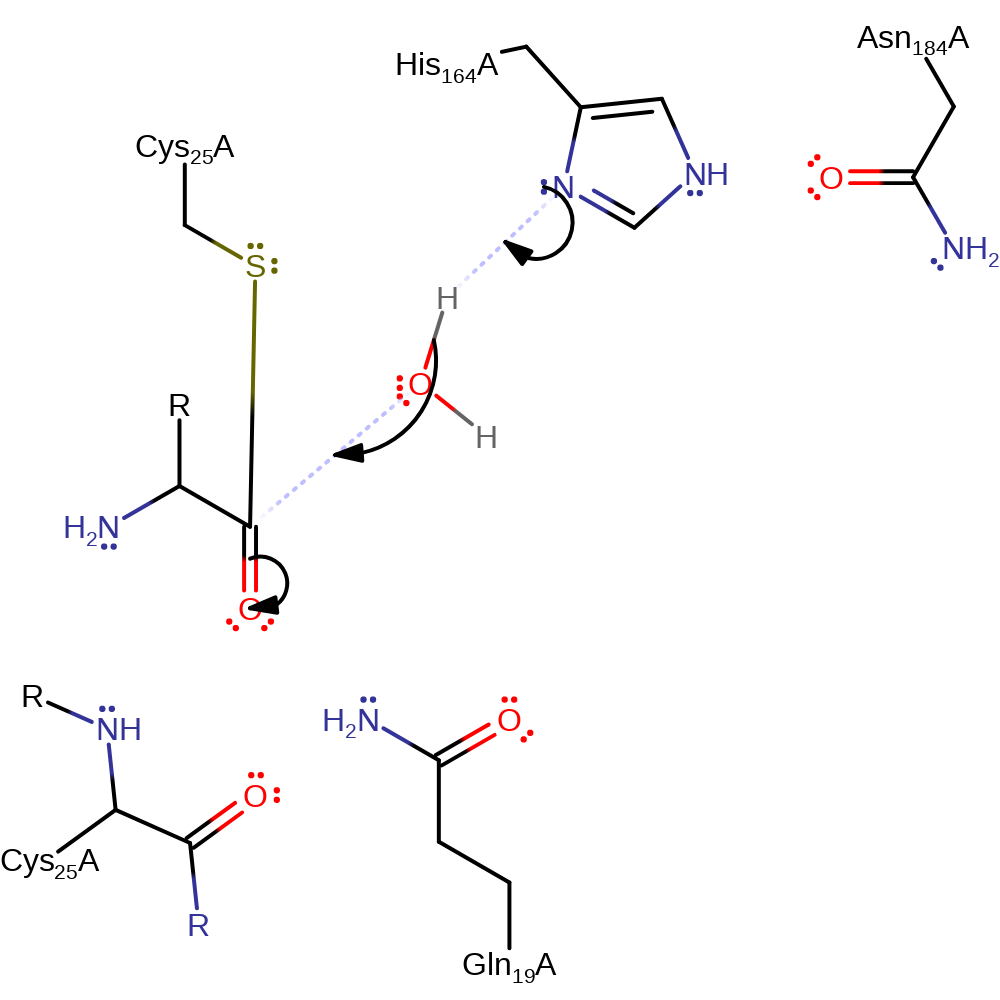
Step 3. His164 abstracts a proton from water resulting in the activation of it so that it can go on to attack the carbon of the thioester bond in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln19A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser25A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn184A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His164A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used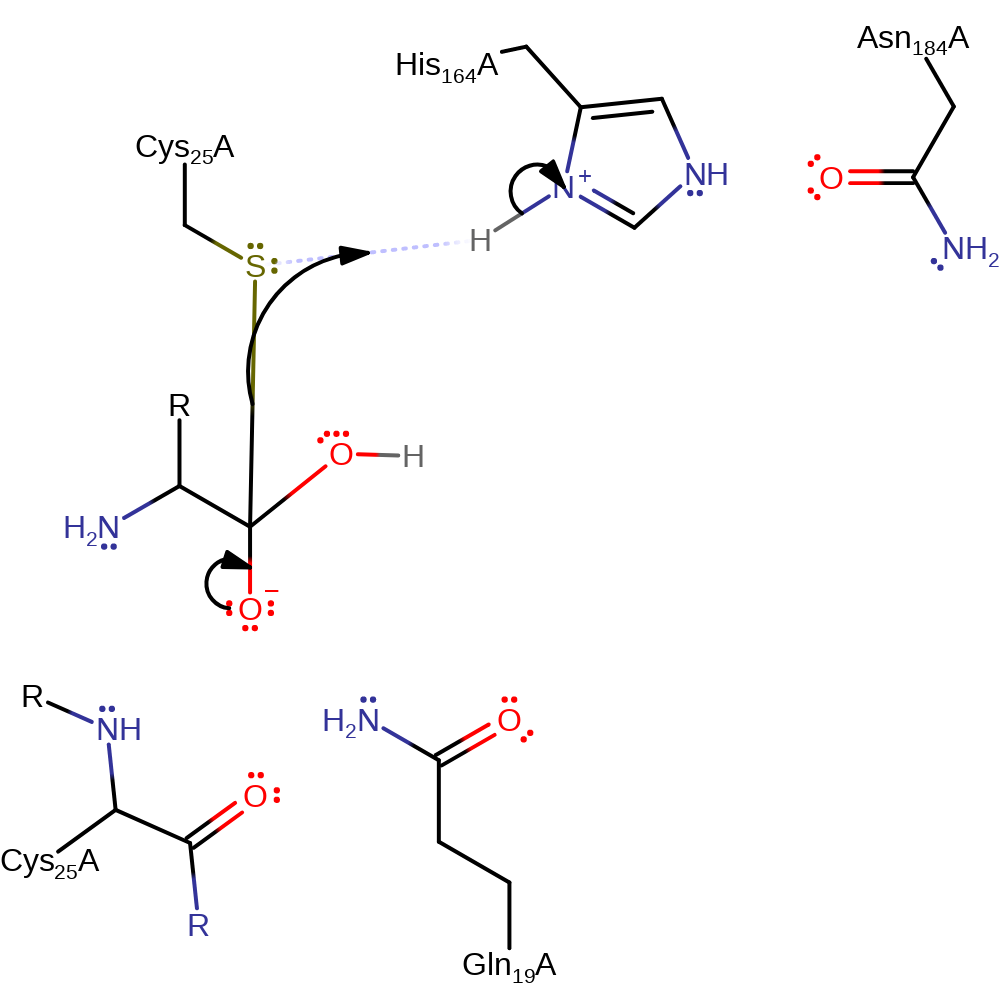
Step 4. The oxyanion initiates another elimination resulting in the cleavage of the thioester bond. The released Cys25 can now accept a proton from His164 resulting in the regeneration of the native state of the enzyme.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln19A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser25A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn184A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser25A | nucleofuge |
| His164A | proton donor |
| Ser25A | proton acceptor |



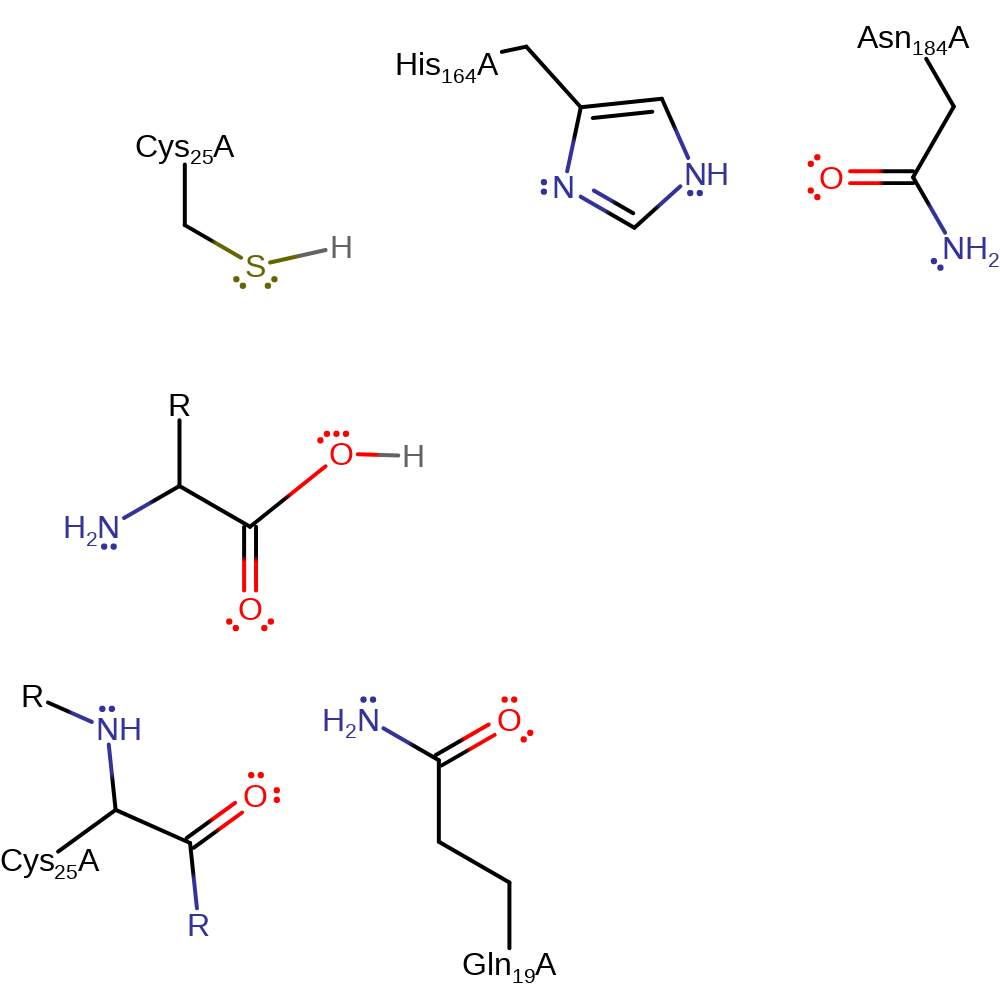 Download:
Download: