Nicotinate-nucleotide diphosphorylase (carboxylating) (type II)
Quinolinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase from Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (Mt-QAPRTase) is required for the de novo biosynthesis of NAD in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes (equivalent enzyme). The enzyme catalyses the reaction between quinolinic acid (QA) and 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP), to yield nicotinic acid mononucleotide (NAMN), pyrophosphate and CO2, the latter resulting from decarboxylation at position 2 of the quinolinate ring.
QAPRTase has been grouped with other phosphoribosyltransferases, (PRTases) that catalyse chemically similar phosphoribosyl transfer reactions using the substrate PRPP. The PRTases are involved in de novo and salvage reactions of nucleotide synthesis, as well as in histidine and tryptophan biosynthesis [PMID:9016724]. To date, crystal structures have been determined for several PRTase enzymes and all show a common 'PRTase fold' (the 'type I' fold) composed of a central beta sheet, of five beta strands, surrounded by alpha helices. The fold contains a common recognition motif of thirteen residues which is critical for PRPP binding and catalysis. However, as type II enzymes like Mt-QAPRTase lack the type I PRPP-binding motif and have TIM barrel-like structure, it becomes possible that there might be at least two different types of PRTase fold [PMID:9016724]. Despite their structural differences, it has been suggested TI and TII indeed still have the same catalytic mechanism but more work is needed to understand this fully.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P9WJJ7
 (2.4.2.19)
(2.4.2.19)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1qpr
- QUINOLINATE PHOSPHORIBOSYLTRANSFERASE (QAPRTASE) FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS IN COMPLEX WITH PHTHALATE AND PRPCP
(2.45 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.70
 3.90.1170.20
3.90.1170.20  (see all for 1qpr)
(see all for 1qpr)
- Cofactors
- Manganese(2+) (1), Manganese(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.4.2.19)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Phosphoribosyl transfer has been proposed to proceed via a unimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN1 reaction) involving an oxycarbonium-like intermediate. In a rate-limiting step, the pyrophosphate group of PRPP is protonated and cleaved to yield an oxycarbonium of ribosylphosphate. The formation of the anticipated intermediate may be facilitated by the electron-withdrawing power of the metal ions and the C3-exo pucker of the ribosyl ring. Subsequently, the nucleophilic N1 of QA combines with the oxycarbonium in a diffusion-controlled reaction to form quinolinic acid mononucleotide (QAMN) [PMID:9862811].
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1qpr) | ||
| Glu201 | Glu201(200)A | Acts as a general acid/base abstracting a proton from the 3'-OH of the substrate. It is returned to its original protonation state by the ribose product. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Lys140 | Lys140(139)A | Helps stabilise the negatively charged intermediates. | repulsive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Arg105 | Arg105(104)B | Binds and helps stabilise the pyridine substrate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys172 | Lys172(171)A | Acts as a general acid base having a proton abstracted by the pyridine intermediate during the decarboxylation step. It is returned to its initial protonation step by water in an inferred return step. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Asp222 | Asp222(221)A | Acts to stabilise the carbenium (positively charged) intermediate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton transfer, heterolysis, overall product formed, bond polarisation, dephosphorylation, intermediate collapse, rate-determining step, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, decarboxylation, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme is not regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Sharma V et al. (1998), Structure, 6, 1587-1599. Crystal structure of quinolinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a potential TB drug target. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(98)00156-7. PMID:9862811.
- Bello Z et al. (2010), Biochemistry, 49, 1388-1395. Roles for Cationic Residues at the Quinolinic Acid Binding Site of Quinolinate Phosphoribosyltransferase. DOI:10.1021/bi9018225. PMID:20047306.
- di Luccio E et al. (2008), Biochemistry, 47, 4039-4050. Comprehensive X-ray Structural Studies of the Quinolinate Phosphoribosyl Transferase (BNA6) fromSaccharomyces cerevisiae‡. DOI:10.1021/bi7020475. PMID:18321072.
- Eads JC et al. (1997), Structure, 5, 47-58. A new function for a common fold: the crystal structure of quinolinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(97)00165-2. PMID:9016724.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys172(171)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg105(104)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu201(200)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton transfer
Step 2. The ribose intermediate undergoes an elimination reaction, with concomitant deprotonation of an unidentified base, represented here as a hydronium ion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg105(104)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys140(139)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu201(200)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, proton transfer, overall product formed, bond polarisation, dephosphorylation, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, rate-determining step
Step 3. The nitrogen of the pyridine initiates a nucleophilic attack on the ribose in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu201(200)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp222(221)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg105(104)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys140(139)A | repulsive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 4. The pyridine intermediate decarboxylates with concomitant deprotonation of Lys172. Proton transfer to nicotinamide carbon is inferred.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg105(104)B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys140(139)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys172(171)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, overall product formed, decarboxylation, intermediate formation, intermediate collapseCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys140(139)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu201(200)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme is not regenerated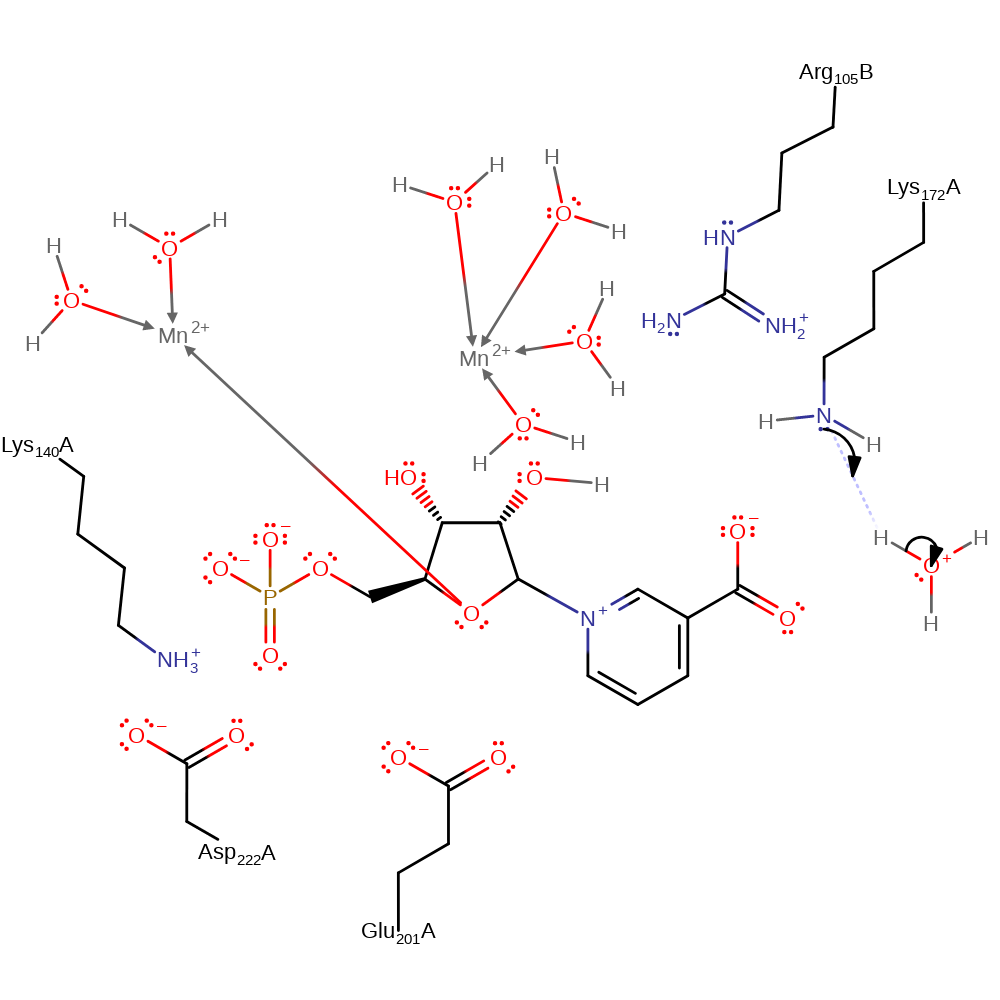
Step 6. Inferred return step. Lys172 returns to its positive state via a water molecule.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys172(171)A | proton acceptor |
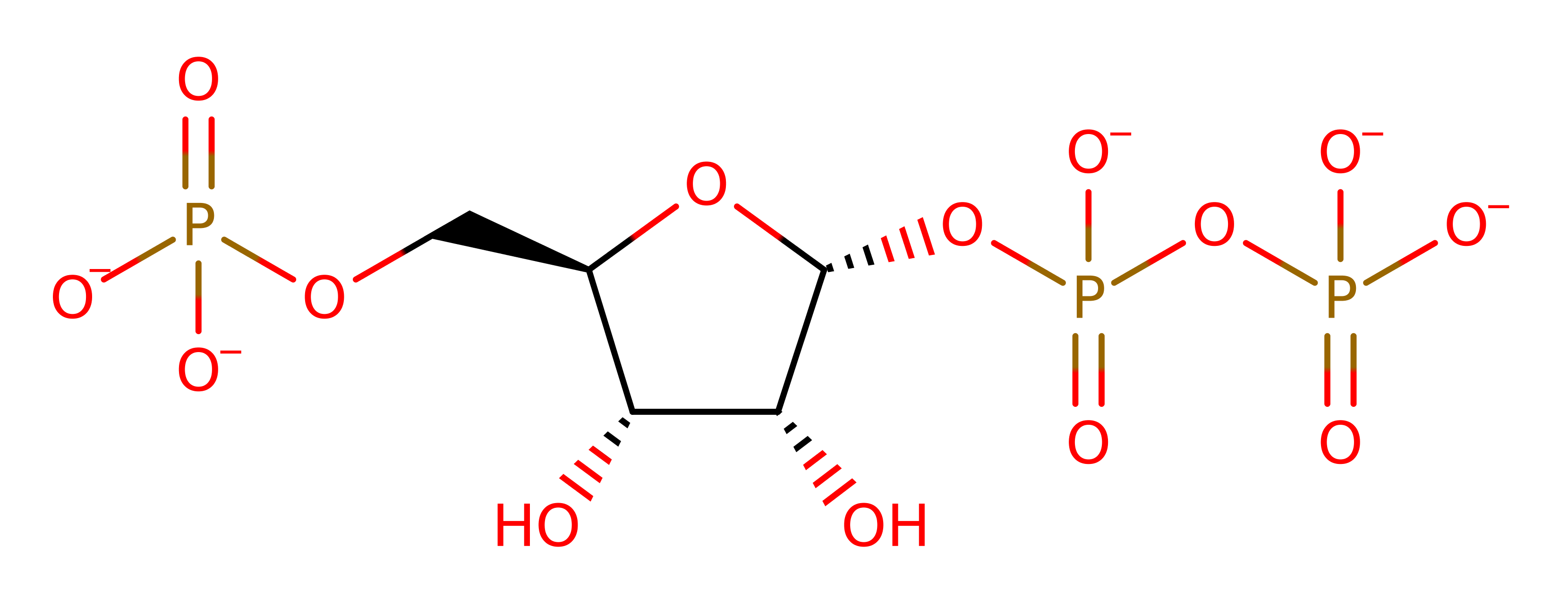







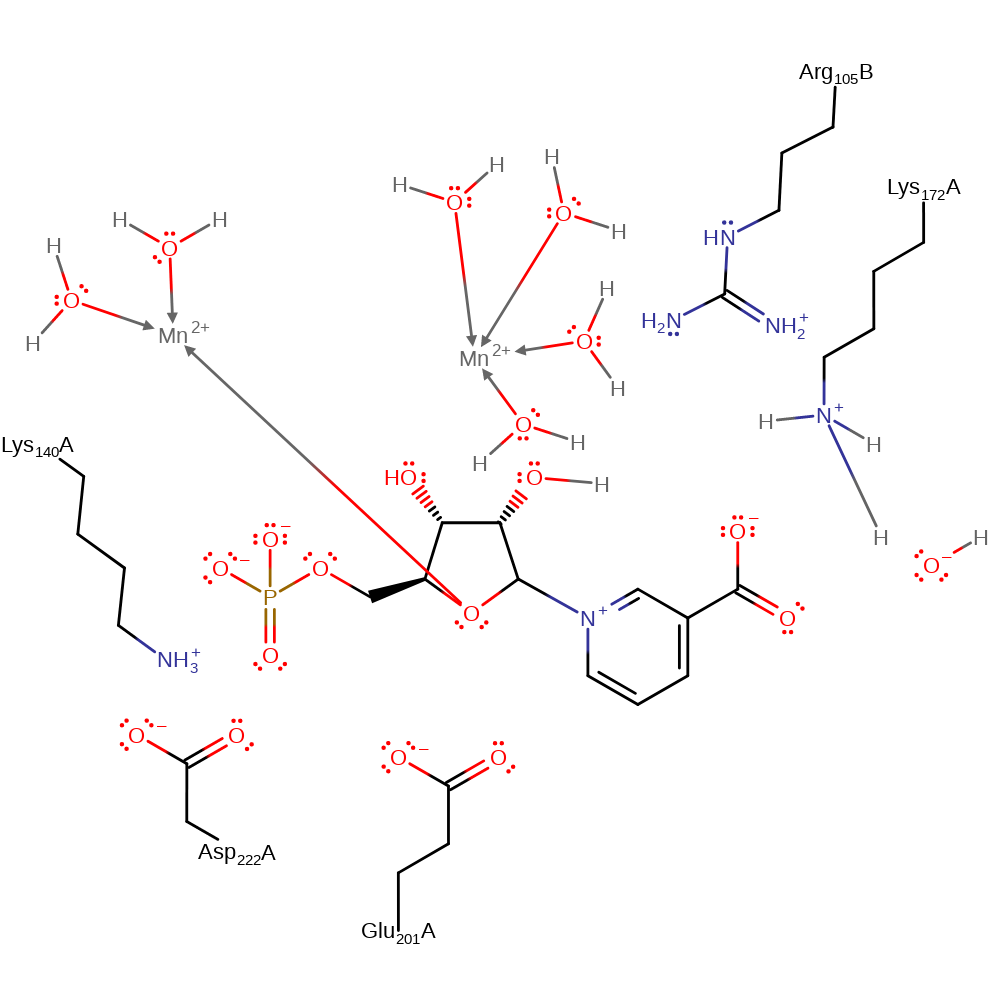 Download:
Download: