DNA-directed RNA polymerase
DNA-dependent RNA polymerases bind to promoter DNA in transcription initiation, opens the duplex strands, and can convert from initiation to elongation phase conformation. More specifically, RNA polymerase II transcribes mRNA in the nucleus of eukaryotes, with closely related enzymes in bacteria and some viruses. RNA synthesis occurs through cycles of repeated ribonucleotide incorporation. While RNAPII is apart of a family containing multiple subunits, there are also single subunit RNAPs such as in the T7 bacteriophage which display high similarity to DNA polymerases.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P04050
 (2.7.7.6)
(2.7.7.6)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c (Baker's yeast)

- PDB
-
2e2h
- RNA polymerase II elongation complex at 5 mM Mg2+ with GTP
(3.95 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.40.40.20
 2.40.270.10
2.40.270.10  (see all for 2e2h)
(see all for 2e2h)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (2)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.7.7.6)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
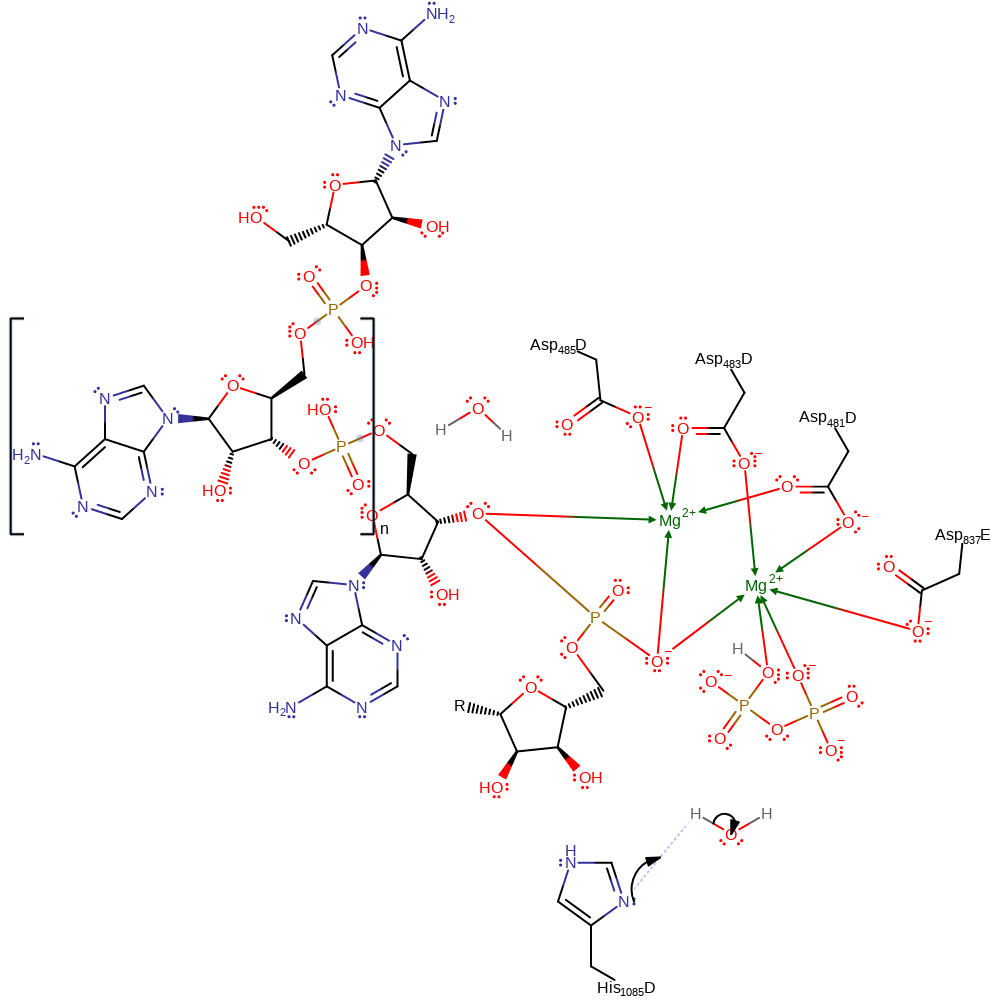
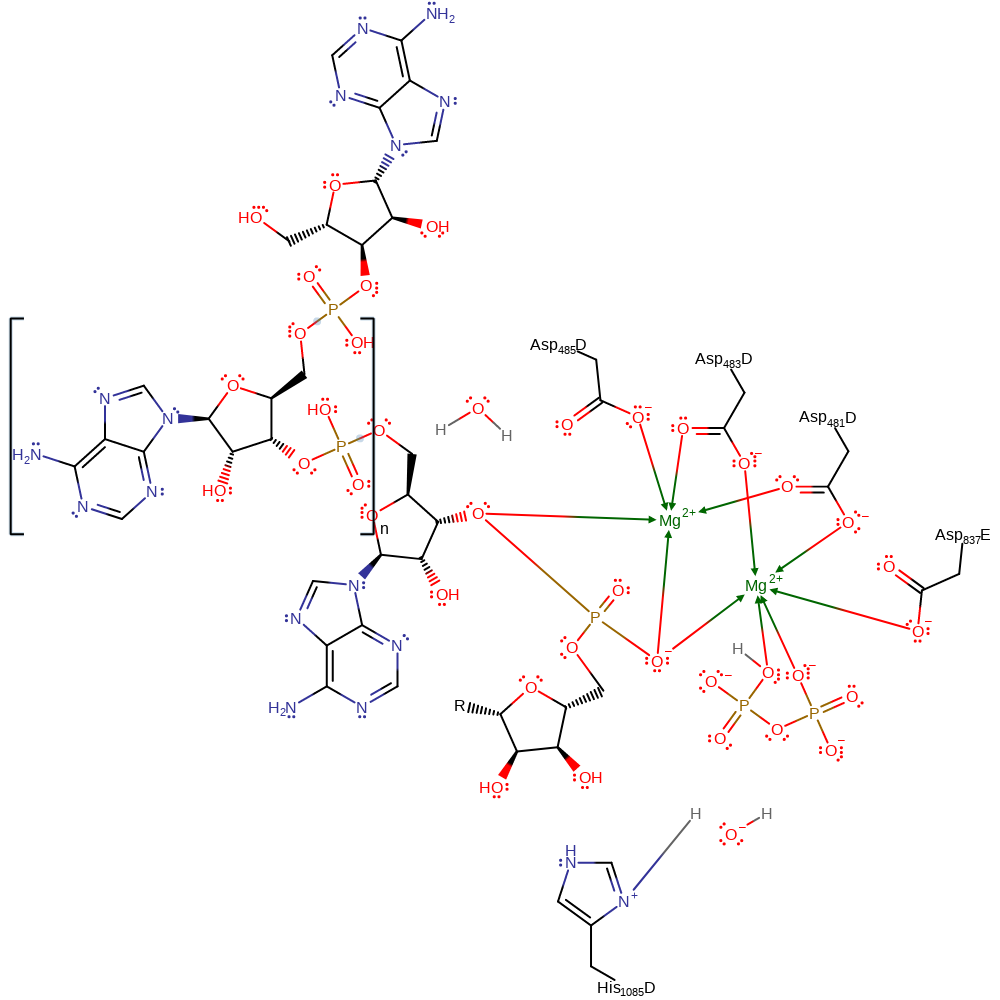
RNA polymerases catalyse the nucleophilic attack of a bound nucleoside 5'-triphosphate by the 3'-hydroxyl of an RNA primer, resulting in the incorporation of a nucleoside monophosphate into RNA and the release of pyrophosphate. This is thought to occur using two-metal catalysis. In RNA polymerase II, two magnesium ions are coordinated by four aspartates (3'OH of RNA also proposed to weakly coordinate to Mg2+A). Mg2+A is proposed to lower the pKa around the attacking hydroxyl while Mg2+B is there to stabilise the negative charges during transition state. More recently, computational evidence suggests the reaction proceeds by nucleophilic attack by a recently deprotonated 3' OH group (by a solvent hydroxide ion), on the alpha NTP phosphate. The leaving group, pyrophosphate is also protonated by His1085. There has however been evidence to rule out His1085 acting as a general acid (and a nearby Arginine), where another residue that remains unknown carries out this function.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2e2h) | ||
| His1085 | His1085A(D) | Proposed to act as a general acid to protonate the leaving group, pyrophosphate. However, there has been a recent paper disproving it's role as an acid-base catalyst and instead involved in a positional catalyst. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp485, Asp483, Asp481, Asp837 | Asp485A(D), Asp483A(D), Asp481A(D), Asp837B(E) | Coordinates to the two magnesium metal ions. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall product formed, overall reactant used, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Carvalho AT et al. (2011), J Chem Theory Comput, 7, 1177-1188. The Catalytic Mechanism of RNA Polymerase II. DOI:10.1021/ct100579w. PMID:26606364.
- Mishanina TV et al. (2017), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 114, E5103-E5112. Trigger loop of RNA polymerase is a positional, not acid-base, catalyst for both transcription and proofreading. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1702383114. PMID:28607053.
- Svetlov V et al. (2013), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1829, 20-28. Basic mechanism of transcription by RNA polymerase II. DOI:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.08.009. PMID:22982365.
- Wang D et al. (2006), Cell, 127, 941-954. Structural basis of transcription: role of the trigger loop in substrate specificity and catalysis. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.023. PMID:17129781.

Step 1. Free hydroxyl from bulk sulvent acts as a general base and deprotonates the ribose sugar's 3' OH. This increases the 3'OH nucleophilicity to attack the alpha phosphate on the NTP. The pyrophosphate leaving group is protonated by His1085.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp481A(D) | metal ligand |
| Asp483A(D) | metal ligand |
| Asp485A(D) | metal ligand |
| Asp837B(E) | metal ligand |
| His1085A(D) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall product formed, overall reactant usedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His1085A(D) | proton acceptor |




 Download:
Download: