NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase
ADP-ribosyltransferase is a eukaryotic DNA binding protein that participates in cell recovery after DNA damage, particularly in base excision repair. After activation by binding to DNA strand-breaks it modifies itself (automodification) and other nuclear proteins (heteromodification) involved in chromatin architecture and DNA metabolism by covalent attachment of ADP-ribose units of NAD+ forming extended and branched polymers.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P26446
 (2.4.2.-, 2.4.2.30)
(2.4.2.-, 2.4.2.30)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Gallus gallus (Chicken)

- PDB
-
1a26
- THE CATALYTIC FRAGMENT OF POLY(ADP-RIBOSE) POLYMERASE COMPLEXED WITH CARBA-NAD
(2.25 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.228.10
 (see all for 1a26)
(see all for 1a26)
- Cofactors
- Water (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.4.2.30)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Glutamate deprotonates the 2' OH of the ADP-D-ribosyl-acceptor. The oxyanion then initiates a nucleophilic attack on the ribose carbon of ADP covalently attacked to the nicotinamide ring in a substitution reaction, eliminating nicotinamide with concomitant deprotonation of Glu988
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1a26) | ||
| Tyr904 | Tyr907(254)A | Has a non-polar interaction with the donor's pyridine ring and a hydrogen bond to the 3' OH of the acceptor - these are important for positioning the substrates to prevent attack in the wrong position. The 3' OH of the adenine-ribose is known to be required for full elongation. | van der waals interaction, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu985 | Glu988(335)A | Deprotonates incoming acceptor and increases its nucleophilicity, and polarises the donor and acceptor by hydrogen bonding. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser901 | Ser904(251)A | Stabilises and binds the nicotinamide portion of the substrate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, overall product formedReferences
- Ruf A et al. (1998), J Mol Biol, 278, 57-65. The mechanism of the elongation and branching reaction of Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase as derived from crystal structures and mutagenesis. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1998.1673. PMID:9571033.
- Salmas RE et al. (2016), J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem, 31, 112-120. In silicoinvestigation of PARP-1 catalytic domains inholoandapostates for the design of high-affinity PARP-1 inhibitors. DOI:10.3109/14756366.2015.1005011. PMID:26083304.
- Halder AK et al. (2015), J Biomol Struct Dyn, 33, 1756-1779. Stepwise development of structure–activity relationship of diverse PARP-1 inhibitors through comparative and validatedin silico modeling techniques and molecular dynamics simulation. DOI:10.1080/07391102.2014.969772. PMID:25350685.
- Langelier MF et al. (2013), Curr Opin Struct Biol, 23, 134-143. PARP-1 mechanism for coupling DNA damage detection to poly(ADP-ribose) synthesis. DOI:10.1016/j.sbi.2013.01.003. PMID:23333033.
- Wang Y et al. (2011), J Biomol Struct Dyn, 28, 881-893. The Key Residues of Active Sites on the Catalytic Fragment for Paclitaxel Interacting with Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase. DOI:10.1080/07391102.2011.10508615. PMID:21469749.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr907(254)A | hydrogen bond donor, van der waals interaction |
| Glu988(335)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser904(251)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu988(335)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation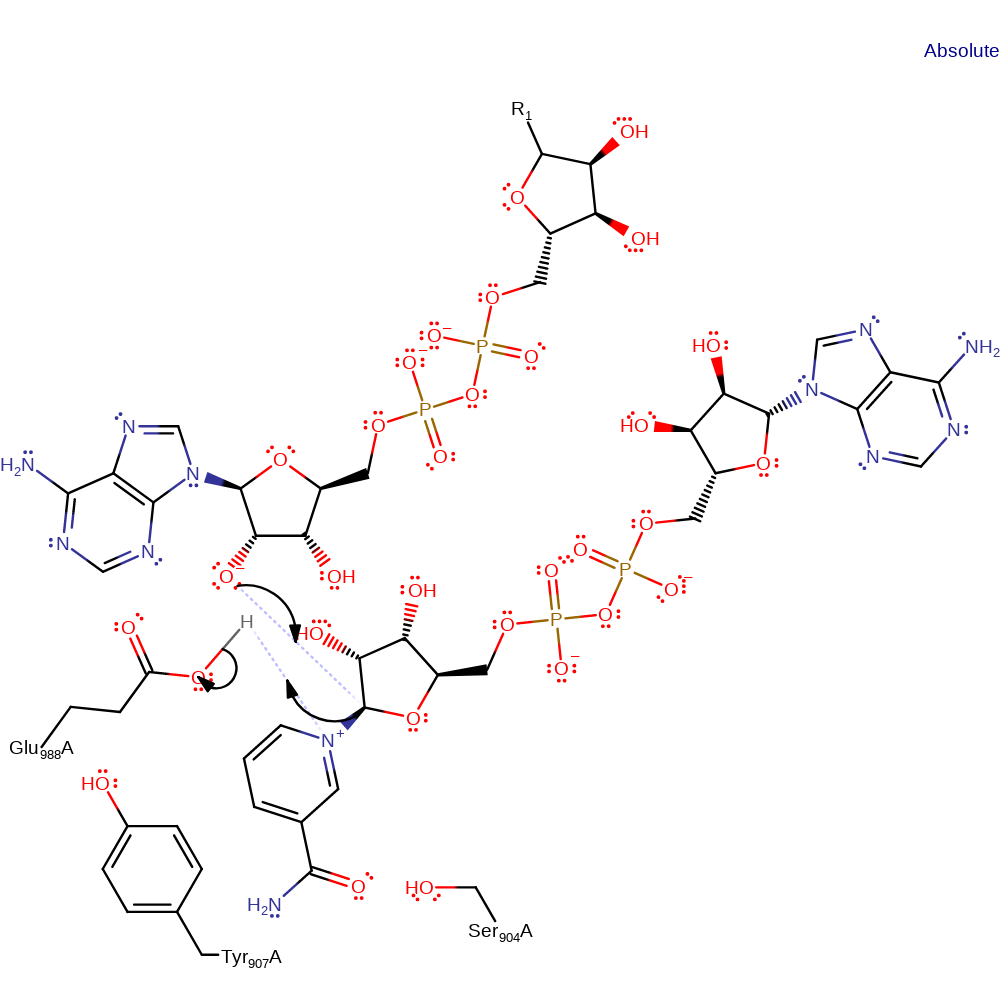
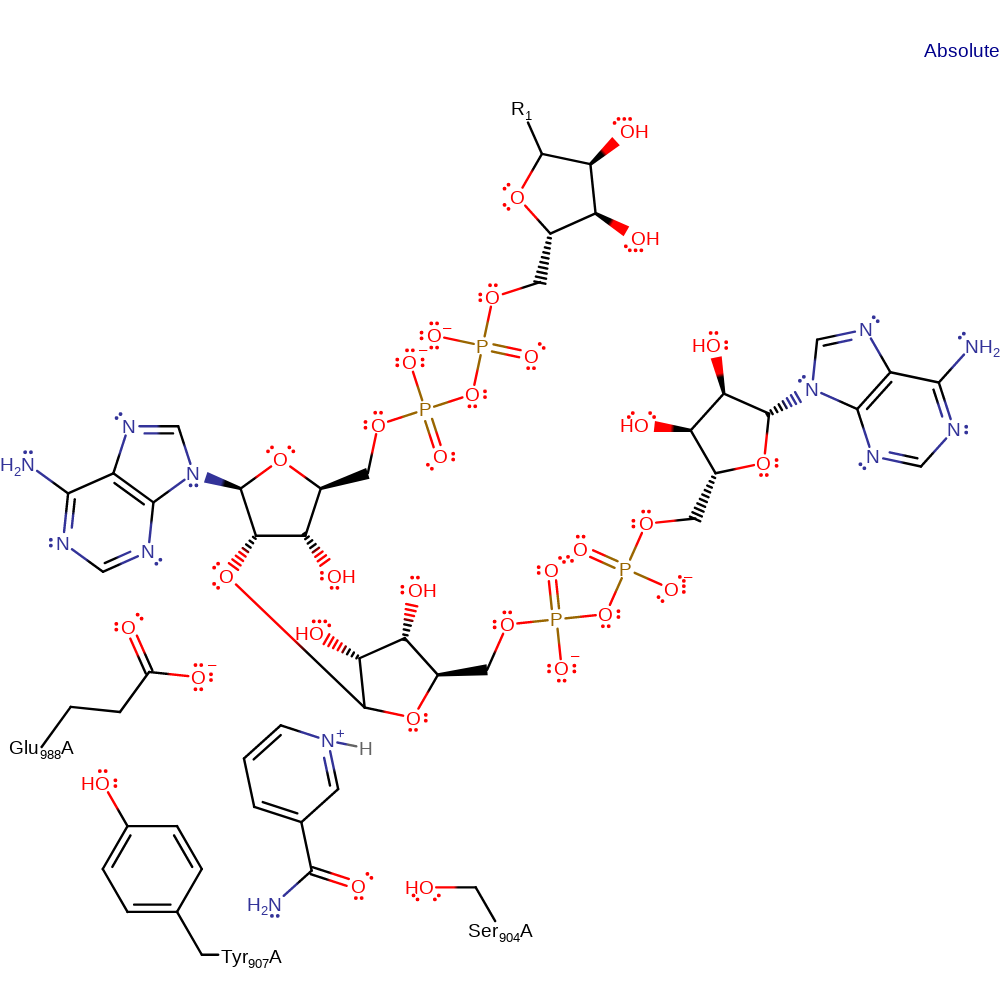
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates a nucleophilic attack on the ribose carbon of ADP covalently attacked to the nicotinamide ring in a substitution reaction, eliminating nicotinamide with concomitant deprotonation of Glu988.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr907(254)A | hydrogen bond donor, van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu988(335)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser904(251)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu988(335)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, overall product formed
Step 3. In an inferred step, the nicotinamide loses a proton to the solvent, and the final product is generated.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|






 Download:
Download: