Mannose-6-phosphate isomerase
Several aerobic crenarcheaons, including Pyrobaculum aerophilum, contain an isomerase that converts both glucose-6-phosphate and mannose-6-phosphate (G6P and M6P, which are C2 epimers) into fructose-6-phosphate. Most organisms contain only highly specific phosphoglucose and phosphomannose isomerases (PGIs and PMIs), which only accept either glucose or mannose as a substrate.
These dual specificity isomerases share very low sequence identity with 'conventional' PGIs or PMIs, but structure is conserved, especially at the active site, supporting a common mechanism. They belong to the larger PGI superfamily.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q8ZWV0
 (5.3.1.8, 5.3.1.9)
(5.3.1.8, 5.3.1.9)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Pyrobaculum aerophilum str. IM2 (Archaea)

- PDB
-
1x9h
- Crystal structure of phosphoglucose/phosphomannose isomerase from Pyrobaculum aerophilum in complex with fructose 6-phosphate
(1.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.10490
 (see all for 1x9h)
(see all for 1x9h)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.3.1.8)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Lys 248 is deprotonates the C1 hydroxyl group. This leads to concomitant ring opening and protonation of the ring oxygen by His 219. Rotation takes place around the C3-C4 bond, and also C2-C3 for the M6P mechanism (this is forbidden in conventional PGIs by a glutamate residue). Glu 203 abstracts the C2 proton, leading to cis-enediolate formation. In the PGI mechanism, this cis-enediolate is stabilised by Arg 135. The C1 enolate oxygen deprotonates the C2 enol. Glu 203 protonates C1, reducing the C1=C2 bond while the C2 hydroxyl is oxidised to a carbonyl. Rotation about the C3-C4 bond occurs. His 219 deprotonates the C5 hydroxyl (formerly the ring oxygen). This is concomitant with the attack of the C5 hydroxyl oxygen on the new C2 carbonyl, which is protonated by Lys 248 (ring closure). The product is fructose-6-phosphate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1x9h) | ||
| Glu203 | Glu203A | Glu 203 abstracts the C2 proton, which leads to enolisation to give a enediolate. After bond rotation, Glu 203 then returns the proton to the other side of the enediolate. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Arg135 | Arg135A | In the PGI mechanism, Arg 135 stabilises the charge on the enediolate and the transition states leading to and from the intermediate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His219 | His219B | His 219 protonates the ring oxygen in the first, ring opening, step in the mechanism. His 219 later abstracts the same proton in the last, ring closing, step. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Lys298 | Lys298A | Lys 298 deprotonates the C2 hydroxyl group in the first, ring opening, step in the mechanism. The proton is later redonated to the C2 carbonyl in the last, ring closing, step. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, decyclisation, overall reactant used, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, native state of enzyme regenerated, cyclisation, overall product formed, intramolecular nucleophilic additionReferences
- Swan MK et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 14088-14095. Structural Basis for Phosphomannose Isomerase Activity in Phosphoglucose Isomerase fromPyrobaculum aerophilum: A Subtle Difference between Distantly Related Enzymes†. DOI:10.1021/bi048608y. PMID:15518558.
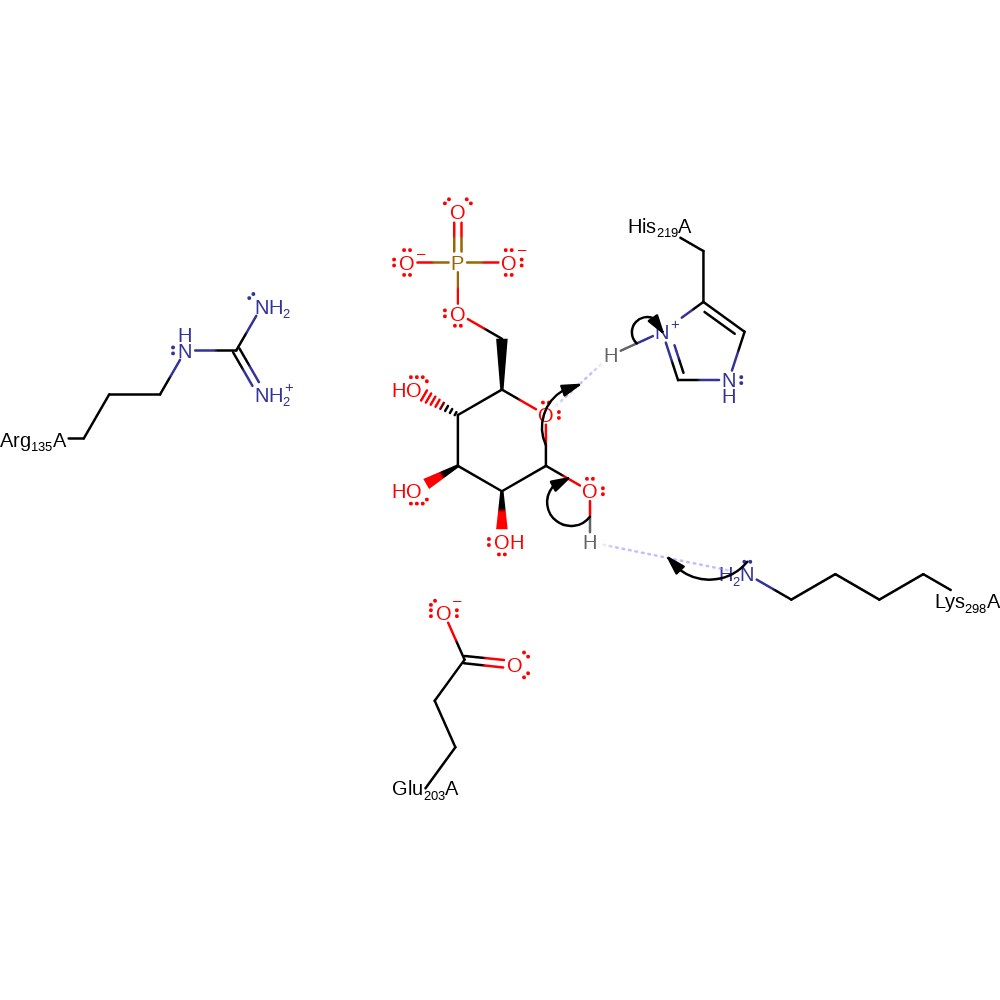
Step 1. Lys 298 accepts a proton from the C1 hydroxyl. The ring oxygen accepts a proton from His 219. This leads to the ring opening. Following this step there is a 180 degree rotation about the C3-C4 bond followed by rotation about the C2-C3 bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His219B | proton donor |
| Lys298A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, decyclisation, overall reactant used
Step 2. Glu 203 accepts a proton from C2. This leads to the formation of a cis-enediolate intermediate stabilized by Arg 135. Following this step there is rotation about the C2-C3 bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg135A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu203A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation
Step 3. The C=C bond of the enediolate intermediate accepts a proton from Glu 203. Simultaneously, there is an intramolecular proton transfer where C1 oxygen accepts a proton from the C2 hydroxyl. These proton transfers lead to a second tautomerization, forming a keto group on C2 and a hydroxyl group on C1. Following this step there is a 180 degree rotation about the C3-C4 bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg135A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu203A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, native state of enzyme regenerated
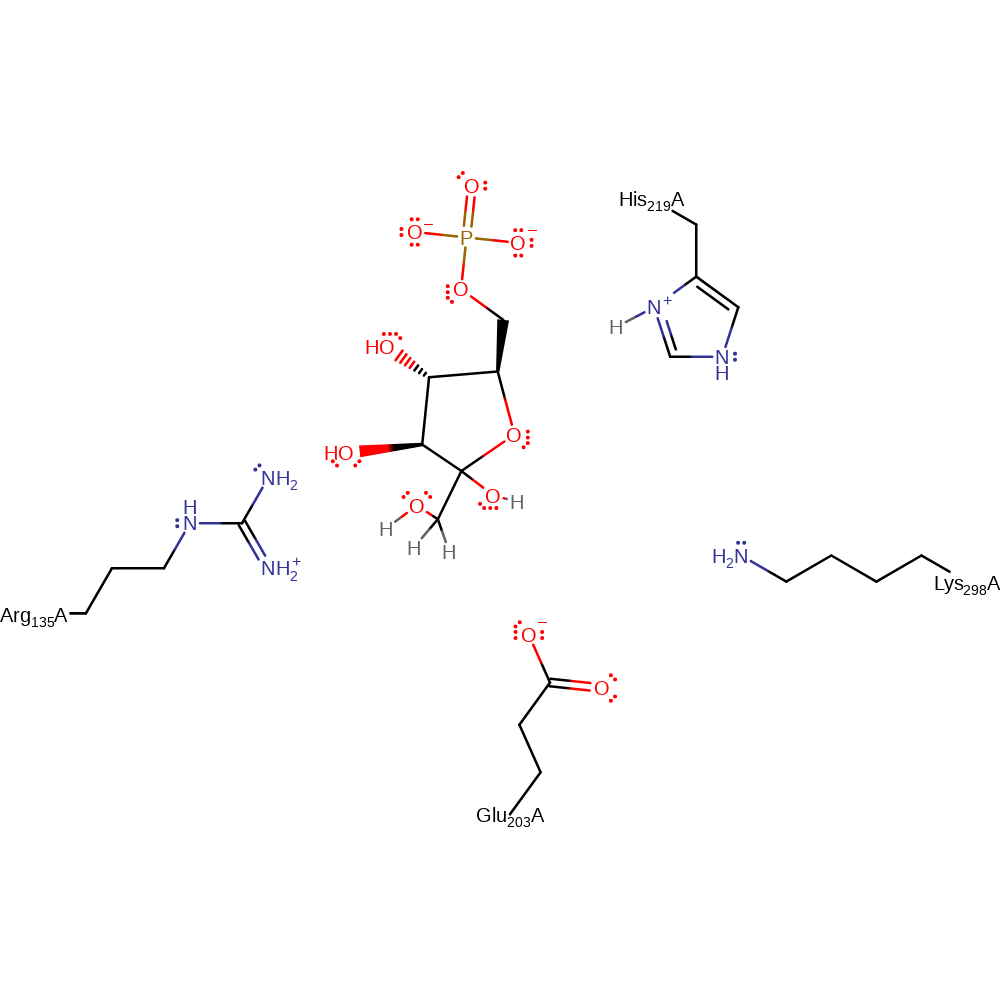
Step 4. The ring closes in the reverse process of step 1. This creates the final product: D-fructose 6-phosphate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys298A | proton donor |
| His219B | proton acceptor |


 Download:
Download: