5'-nucleotidase (bacterial)
5'-nucleotidase is a zinc-containing enzyme involved in ATP hydrolysis and is bound to the membrane as an extracellular nucleotidase, or ectonucleotidase. Bacterial 5'-nucleotidases show a significant sequence homology to animal counterparts suggesting a common evolutionary origin. It is also related to 2',3'-cyclic phosphodiesterases and apyrases, all being part of the superfamily of metallophosphoesterases which also includes the Ser/Thr protein phosphatases and the purple acid phosphatases. The enzyme also has a UDP-sugar hydrolase activity which catalyses the periplasmic degradation of external UDP-glucose to uridine, glucose-1-phosphate and phosphate.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P07024
 (3.1.3.5, 3.6.1.45)
(3.1.3.5, 3.6.1.45)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1ush
- 5'-NUCLEOTIDASE FROM E. COLI
(1.73 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.60.21.10
 3.90.780.10
3.90.780.10  (see all for 1ush)
(see all for 1ush)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (2)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.3.5)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
5'-nucleotidase catalyses the hydrolytic cleavage of 5'-mononucleotides to nucleoside and phosphate by nucleophilic attack of a water molecule on the phosphorous. A water ligand is coordinated to the di-zinc centre. The phosphate group of the substrate binds with one oxygen atom to a metal ion. The metal-bound water attacks the phosphorous nucleophilically, with the proton transferred to His 117. The pentahedral transition state is stabilised by both metal ions, Asn 116, Arg 375, Arg 379, Arg 410 and His 117. After expulsion of the leaving group the tetrahedral phosphate ion remains bound to the dimetal centre.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ush) | ||
| Asn116 | Asn116A | Stabilises the pentacoordinate transition state. | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp41, Asp84, His217, His252, Gln254, His43, Asn116 | Asp41A, Asp84A, His217A, His252A, Gln254A, His43A, Asn116A | Coordinate the metal ions. | metal ligand |
| His117 | His117A | Facilitates proton transfer from water and acts to stabilise the pentacoordinate transition state. | proton acceptor, increase nucleophilicity, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp120 | Asp120A | Activates the His 117 to allow it to act as a general base. | increase basicity, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg375 | Arg375A | Contributes to positive potential at the active site and stabilise transition state. | increase electrophilicity, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| Arg379, Arg375, Arg410 | Arg379A, Arg375A, Arg410A | Contributes to the distinct positive potential at the active site and stabilises the pentacoordinate transition state. | increase electrophilicity, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, heterolysis, overall product formed, decoordination from a metal ion, coordination to a metal ionReferences
- Knöfel T et al. (2001), J Mol Biol, 309, 239-254. Mechanism of hydrolysis of phosphate esters by the dimetal center of 5′-nucleotidase based on crystal structures. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4656. PMID:11491293.
- Mitić N et al. (2006), Chem Rev, 106, 3338-3363. The catalytic mechanisms of binuclear metallohydrolases. DOI:10.1021/cr050318f. PMID:16895331.
- Knöfel T et al. (1999), Nat Struct Biol, 6, 448-453. X-ray structure of the Escherichia coli periplasmic 5'-nucleotidase containing a dimetal catalytic site. DOI:10.1038/8253. PMID:10331872.

Step 1. His117/Asp120 dyad and the two zinc ions activate a water molecule to perform a nucleophiliic attack on the phosphate group. This forms a penta-covalent intermediate stabilized by the arginine residues. The bridging water is thought to be the nucleophile as it has the lowest pKa out of the potential water molecules.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg375A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp120A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg410A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg379A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp41A | metal ligand |
| His43A | metal ligand |
| Asp84A | metal ligand |
| Asn116A | metal ligand |
| His117A | metal ligand |
| His217A | metal ligand |
| His252A | metal ligand |
| Gln254A | metal ligand |
| Asp120A | increase basicity |
| His117A | increase nucleophilicity |
| Arg375A | increase electrophilicity |
| Arg379A | increase electrophilicity |
| Arg410A | increase electrophilicity |
| Asn116A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His117A | electrostatic stabiliser, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition
Step 2. Since no acidic residues are positioned to protonate the leaving group this role is thought to be performed by a solvent water molecule. This leaves a tetrahedral phosphate bound to the zinc ions.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg375A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg379A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg410A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp41A | metal ligand |
| His43A | metal ligand |
| Asp84A | metal ligand |
| Asn116A | metal ligand |
| His217A | metal ligand |
| His252A | metal ligand |
| Gln254A | metal ligand |
| Arg375A | increase acidity |
| Arg379A | increase acidity |
| Arg410A | increase acidity |
| Asn116A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His117A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, proton transfer, overall product formed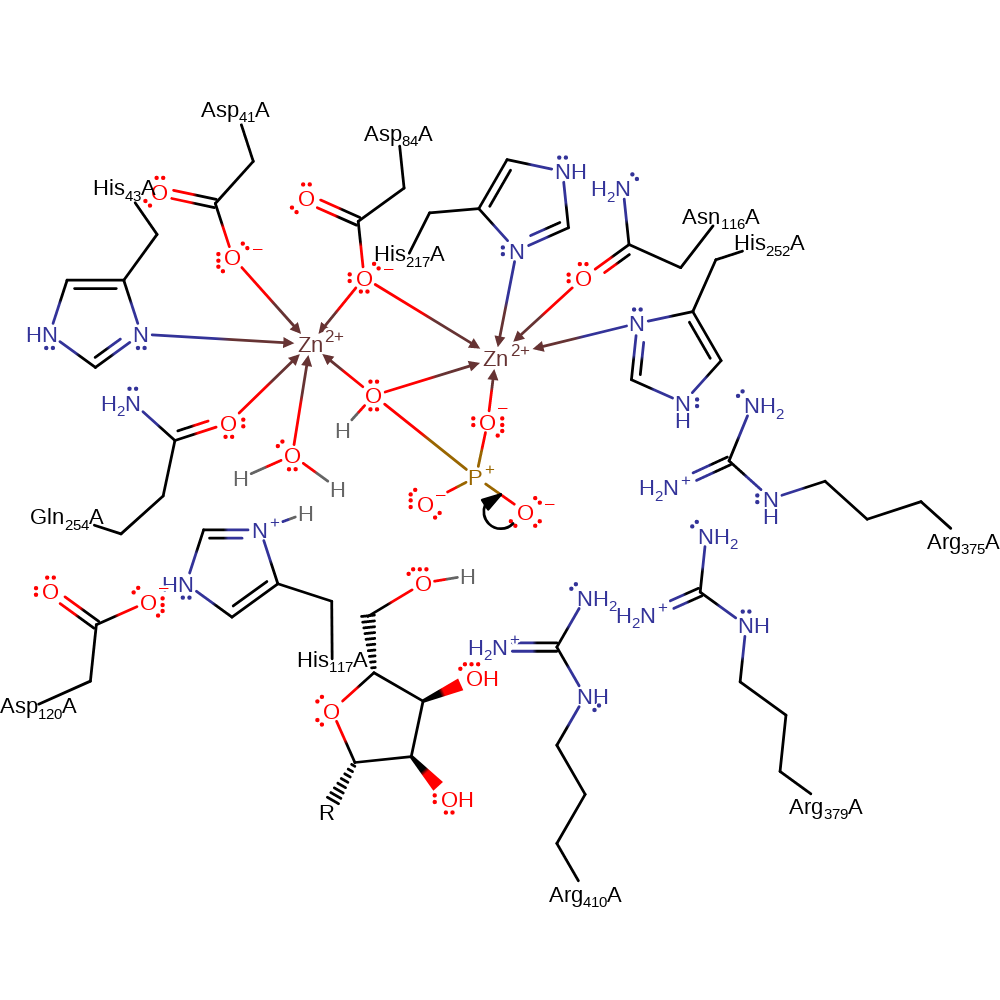
Step 3. Phosphate leaves the active site and the active site transitions to its resting state with each zinc ion being 5 coordinate and no terminal water molecules coordianted.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp41A | metal ligand |
| His43A | metal ligand |
| Asp84A | metal ligand |
| Asn116A | metal ligand |
| His217A | metal ligand |
| His252A | metal ligand |
| Gln254A | metal ligand |
| Arg375A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg379A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg410A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn116A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His117A | electrostatic stabiliser |




 Download:
Download: