Carboxy-cis,cis-muconate cyclase
Eukaryote 3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate lactonizing enzyme is an eukaryote muconate lactonizing enzyme(MLE), converting cis,cis-muconates to muconlactones. It is in the class of CyclicMLE among the three classes of muconate lactonizing enzymes. The other 2 classes are bacterial CyclicMLE and bacterial MLE. The three classes of MLE are structurally very different but catalyse an analogous reaction, i.e. convergent functional evolution occurred.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P38677
 (5.5.1.5)
(5.5.1.5)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Neurospora crassa OR74A (Fungus)

- PDB
-
1jof
- Neurospora crassa 3-carboxy-cis,cis-mucoante lactonizing enzyme
(2.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.130.10.10
 (see all for 1jof)
(see all for 1jof)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.5.1.5)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The mechanism is a general acid/base catalysis, where His 148 deprotonates C5 and Glu 212 donates a proton to the C6 carboxylate. This causes a tautomerization to take place forming an eneolate intermediate, stabilized by Arg 274 and 196 via hydrogen bonding. Intramolecular nucleophilic attack from the C6 enolate to C4 via the C=C bond causes the enolate to tautomerize back into a carboxylate and for the 5 member ring to be opened, forming another carboxylate group on C1. The Arg residues act to increase nucleophilicity of the enolate via hydrogen bonding, allowing the product to be formed in this step.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1jof) | ||
| Arg197 | Arg196A | Hydrogen bonded to the substrate C6 carboxylate group oxygen to increase the nucleophilicity of the group | increase nucleophilicity, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu213 | Glu212A | Donates a proton to the C6 carboxylate in the initial tautomerization step. | proton donor |
| Arg275 | Arg274A | Hydrogen bonded to the substrate C6 carboxylate group oxygen to increase its nucleophilicity. | increase nucleophilicity, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His149 | His148A | Acts as a base to deprotonate C5 in the initial tautomerization. | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step, keto-enol tautomerisation, intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall product formedReferences
- Kajander T et al. (2002), Structure, 10, 483-492. The Structure of Neurospora crassa 3-Carboxy-cis,cis-Muconate Lactonizing Enzyme, a β Propeller Cycloisomerase. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(02)00744-x. PMID:11937053.
- Yang J et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 10424-10434. Crystal structure of 3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate lactonizing enzyme from Pseudomonas putida, a fumarase class II type cycloisomerase: enzyme evolution in parallel pathways. DOI:10.1021/bi036205c. PMID:15301541.

Step 1. His 148 deprotonates C5, simultaneously Glu 212 donates a proton to the C6 carboxylate. This causes a tautomerization to take place forming an eneolate which is stabilized by the Arg residues via hydrogen bonding.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg274A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg196A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His148A | proton acceptor |
| Glu212A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step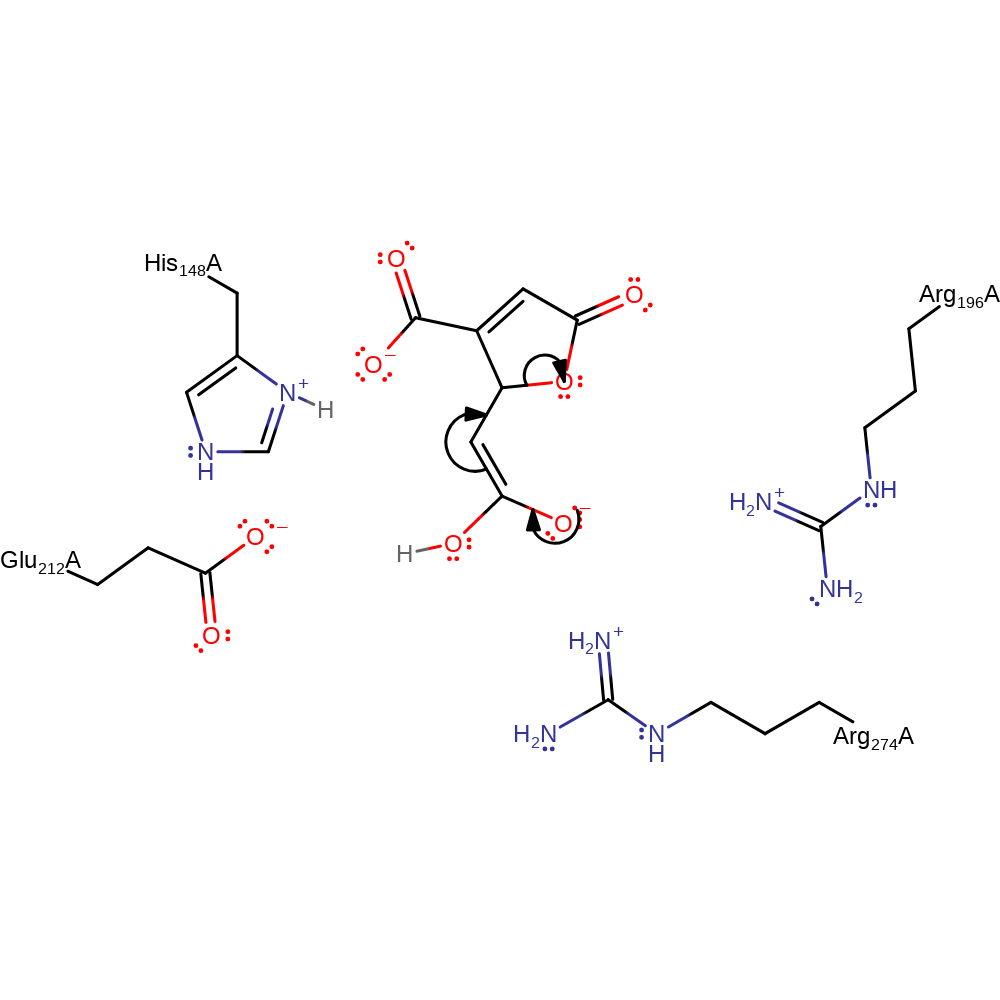
Step 2. Intramolecular nucleophilic attack from the C6 enolate to C4 via the C=C bond causes the enolate to tautomerize back into a carboxylate and for the 5 member ring to be opened, forming another carboxylate group on C1. The Arg residues act to increase nucleophilicity of the enolate via hydrogen bonding.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg196A | increase nucleophilicity |
| Arg274A | increase nucleophilicity |
| Arg196A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg274A | electrostatic stabiliser |


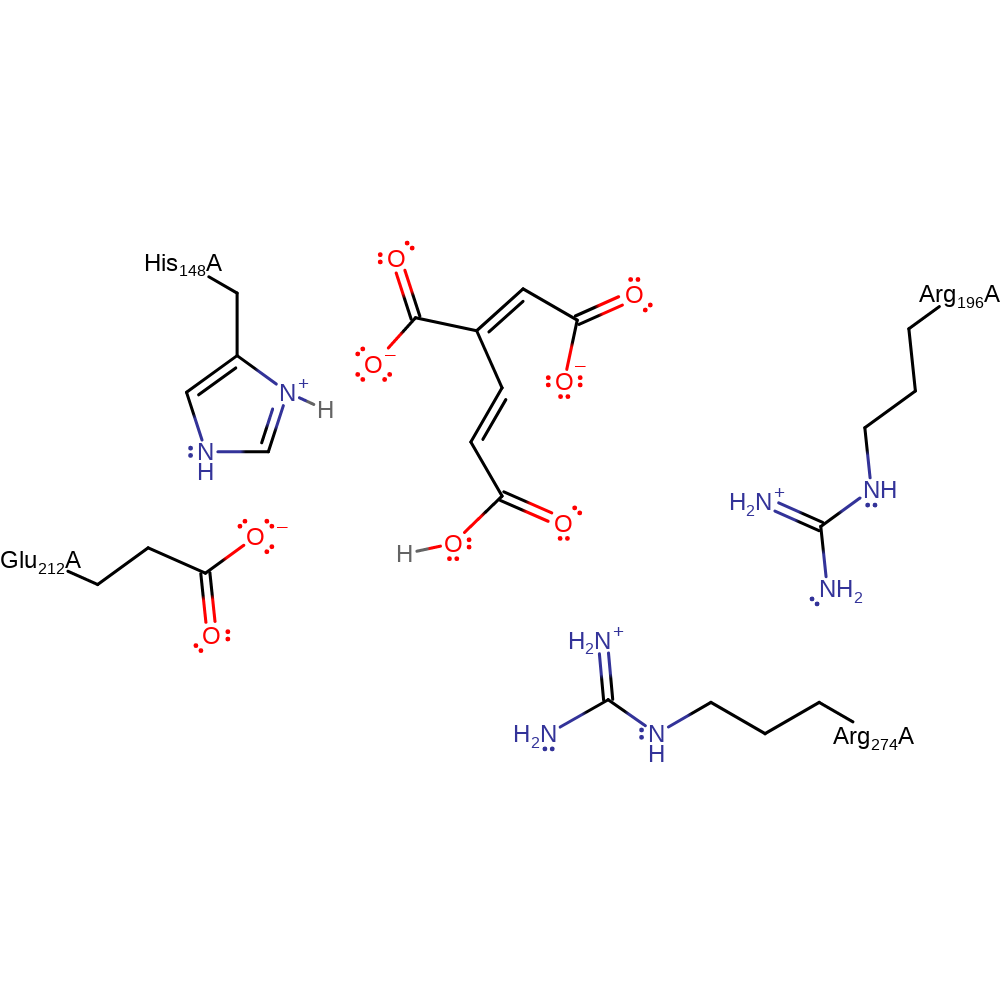 Download:
Download: