 |
PDBsum entry 1jof

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Neurospora crassa 3-carboxy-cis,cis-mucoante lactonizing enzyme
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Carboxy-cis,cis-muconate cyclase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h. Synonym: 3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate lactonizing enzyme. Cmle. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Neurospora crassa. Organism_taxid: 5141. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Tetramer (from
)
Tetramer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.50Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.212
|
R-free:
|
0.251
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
T.Kajander,M.C.Merckel,A.Thompson,A.M.Deacon,P.Mazur,J.W.Kozarich, A.Goldman
|
Key ref:

|
 |
T.Kajander
et al.
(2002).
The structure of Neurospora crassa 3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate lactonizing enzyme, a beta propeller cycloisomerase.
Structure,
10,
483-492.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
28-Jul-01
|
Release date:
|
12-Apr-02
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P38677
(CMLE_NEUCR) -
Carboxy-cis,cis-muconate cyclase from Neurospora crassa (strain ATCC 24698 / 74-OR23-1A / CBS 708.71 / DSM 1257 / FGSC 987)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
366 a.a.
365 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.5.1.5
- carboxy-cis,cis-muconate cyclase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Muconate Cycloisomerase
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
3-carboxy-2,5-dihydro-5-oxofuran-2-acetate = 3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
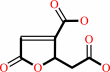 3-carboxy-2,5-dihydro-5-oxofuran-2-acetate
3-carboxy-2,5-dihydro-5-oxofuran-2-acetate
|
=
|
 3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate
3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
10:483-492
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The structure of Neurospora crassa 3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate lactonizing enzyme, a beta propeller cycloisomerase.
|
|
T.Kajander,
M.C.Merckel,
A.Thompson,
A.M.Deacon,
P.Mazur,
J.W.Kozarich,
A.Goldman.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Muconate lactonizing enzymes (MLEs) convert cis,cis-muconates to muconolactones
in microbes as part of the beta-ketoadipate pathway; some also dehalogenate
muconate derivatives of xenobiotic haloaromatics. There are three different MLE
classes unrelated by evolution. We present the X-ray structure of a eukaryotic
MLE, Neurospora crassa 3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate lactonizing enzyme (NcCMLE) at
2.5 A resolution, with a seven-bladed beta propeller fold. It is related neither
to bacterial MLEs nor to other beta propeller enzymes, but is structurally
similar to the G protein beta subunit. It reveals a novel metal-independent
cycloisomerase motif unlike the bacterial metal cofactor MLEs. Together, the
bacterial MLEs and NcCMLE structures comprise a striking structural example of
functional convergence in enzymes for 1,2-addition-elimination of carboxylic
acids. NcCMLE and bacterial MLEs may enhance the reaction rate differently: the
former by electrophilic catalysis and the latter by electrostatic stabilization
of the enolate.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 7.
Figure 7. Alignment of the MLE and CMLE Active SitesThe MLE
(cyan) and CMLE (dark gold) active site residues around the
docked substrates are shown, with the reactive substrate double
bonds aligned, indicating the different binding modes with
respect to the positive charge in the two active sites and the
conserved hydrophobic pockets between the active sites.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(2002,
10,
483-492)
copyright 2002.
|
|
| |
Figure was
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.DiGuistini,
Y.Wang,
N.Y.Liao,
G.Taylor,
P.Tanguay,
N.Feau,
B.Henrissat,
S.K.Chan,
U.Hesse-Orce,
S.M.Alamouti,
C.K.Tsui,
R.T.Docking,
A.Levasseur,
S.Haridas,
G.Robertson,
I.Birol,
R.A.Holt,
M.A.Marra,
R.C.Hamelin,
M.Hirst,
S.J.Jones,
J.Bohlmann,
and
C.Breuil
(2011).
Genome and transcriptome analyses of the mountain pine beetle-fungal symbiont Grosmannia clavigera, a lodgepole pine pathogen.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
108,
2504-2509.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Kim,
J.Basner,
and
B.Lee
(2010).
Detecting internally symmetric protein structures.
|
| |
BMC Bioinformatics,
11,
303.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Morar,
and
G.D.Wright
(2010).
The genomic enzymology of antibiotic resistance.
|
| |
Annu Rev Genet,
44,
25-51.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Tarighi,
Q.Wei,
M.Cámara,
P.Williams,
M.P.Fletcher,
T.Kajander,
and
P.Cornelis
(2008).
The PA4204 gene encodes a periplasmic gluconolactonase (PpgL) which is important for fitness of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
|
| |
Microbiology,
154,
2979-2990.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Gaudermann,
I.Vogl,
E.Zientz,
F.J.Silva,
A.Moya,
R.Gross,
and
T.Dandekar
(2006).
Analysis of and function predictions for previously conserved hypothetical or putative proteins in Blochmannia floridanus.
|
| |
BMC Microbiol,
6,
1.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.P.Kloer,
S.Ruch,
S.Al-Babili,
P.Beyer,
and
G.E.Schulz
(2005).
The structure of a retinal-forming carotenoid oxygenase.
|
| |
Science,
308,
267-269.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.C.Thomason,
D.L.Court,
A.R.Datta,
R.Khanna,
and
J.L.Rosner
(2004).
Identification of the Escherichia coli K-12 ybhE gene as pgl, encoding 6-phosphogluconolactonase.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
186,
8248-8253.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Anantharaman,
L.Aravind,
and
E.V.Koonin
(2003).
Emergence of diverse biochemical activities in evolutionarily conserved structural scaffolds of proteins.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
7,
12-20.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

