3,2-trans-enoyl-CoA isomerase (mitochondrial)
Delta3-delta2-enoyl CoA isomerase (enoyl-CoA isomerase) is a mitochondrial enzyme, in this case from human, catalyses the conversion of 3-cis-enoyl-CoA or 3-trans-enoyl-CoA into 2-trans-enoyl-CoA. This is involved in an auxiliary pathway of fatty acid degradation, and the product is subsequently metabolised further by other enzymes of the pathway.
Enoyl-CoA isomerases use fatty acyl substrates with side-chains ranging from C6 to C16. The reaction used as example uses a C12 compund as substrate
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P42126
 (5.3.3.8)
(5.3.3.8)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1sg4
- Crystal structure of human mitochondrial delta3-delta2-enoyl-CoA isomerase
(1.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.226.10
 (see all for 1sg4)
(see all for 1sg4)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.3.3.8)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This reaction proceeds via an E1cb mechanism in which Glu136 deprotonates the C2 atom of the substrate, forming the conjugate base. The thioester oxygen atom holds the negative charge, and is stabilised by the presence of an oxyanion hole formed by the amide groups of Leu77 and Gly111. As the carbonyl is reformed, the C4 atom of the product is protonated by Glu136.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1sg4) | ||
| Leu108 (main-N), Gly153 (main-N) | Leu66A (main-N), Gly111A (main-N) | Forms the oxyanion hole that stabilises the negatively charged tetrahedral intermediate. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu178 | Glu136A | Acts as a general acid/base. | proton donor, proton acceptor, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Asn177 | Asn135A | Activates Glu136 through hydrogen bonding, modifying its pKa so that it will be a better general acid/base. | modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Partanen ST et al. (2004), J Mol Biol, 342, 1197-1208. The 1.3Å Crystal Structure of Human Mitochondrial Δ3-Δ2-Enoyl-CoA Isomerase Shows a Novel Mode of Binding for the Fatty Acyl Group. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.07.039. PMID:15351645.
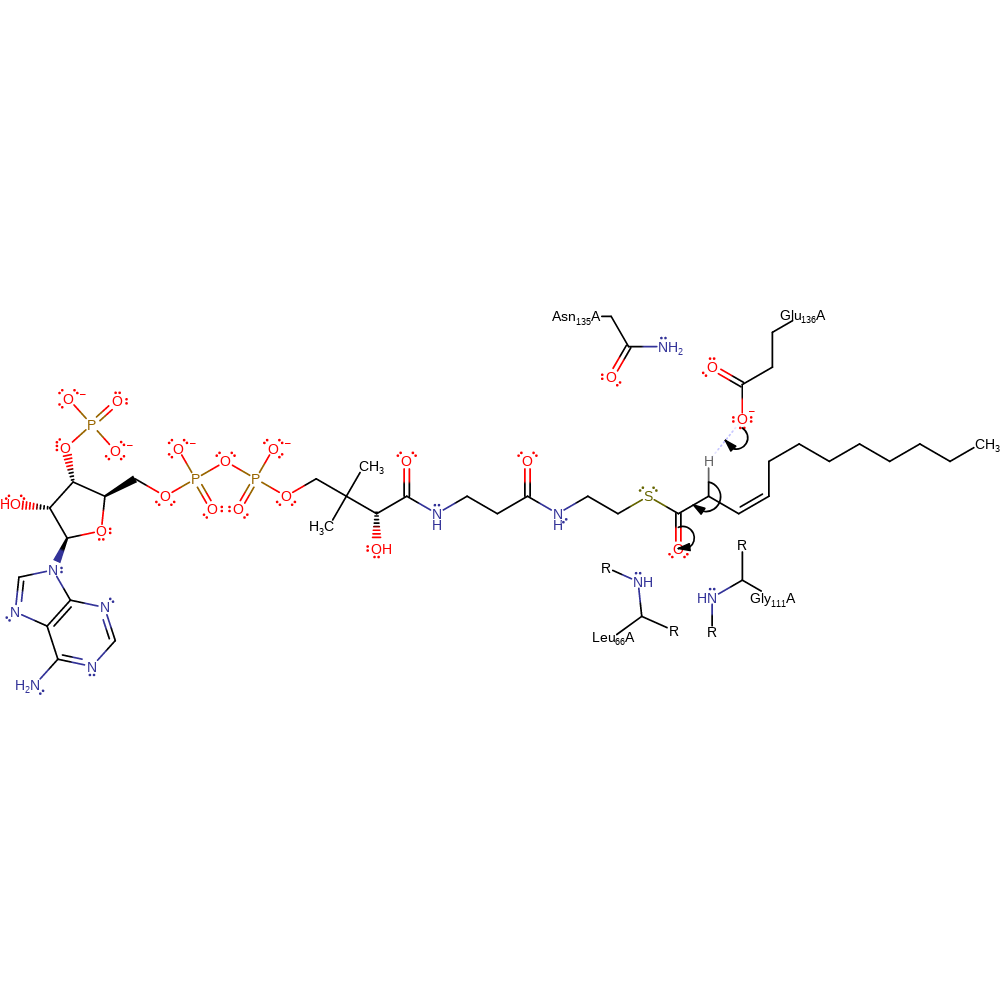
Step 1. Glu136A deprotonates the substrate with concomitant tautomerisation to the enolate form, which is stabilised by an oxyanion hole composed of the main chain amides of Leu66A and Gly111A
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Leu66A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu136A | polar/non-polar interaction |
| Gly111A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn135A | modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu136A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation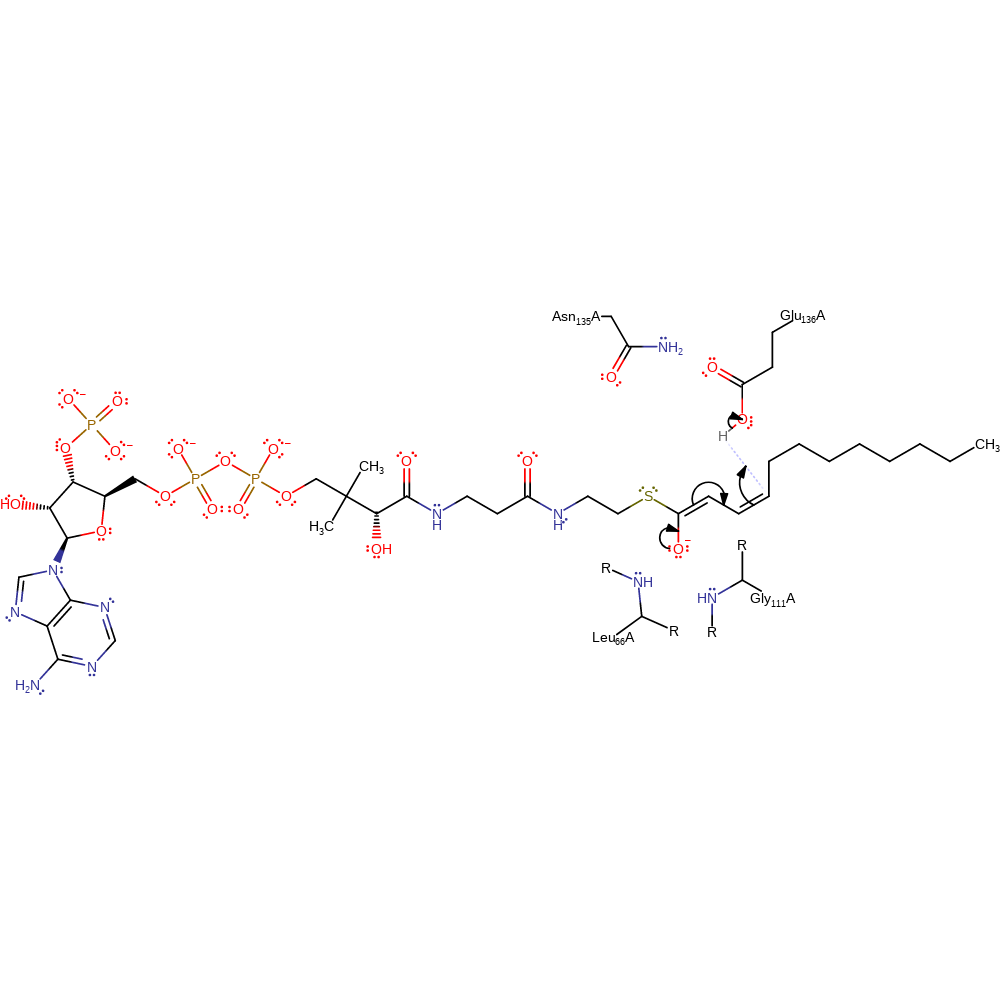
Step 2. The oxyanion intermediate tautomerises to give product with the help of a proton donated by Glu136
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Leu66A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu136A | polar/non-polar interaction |
| Gly111A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn135A | modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu136A | proton donor |


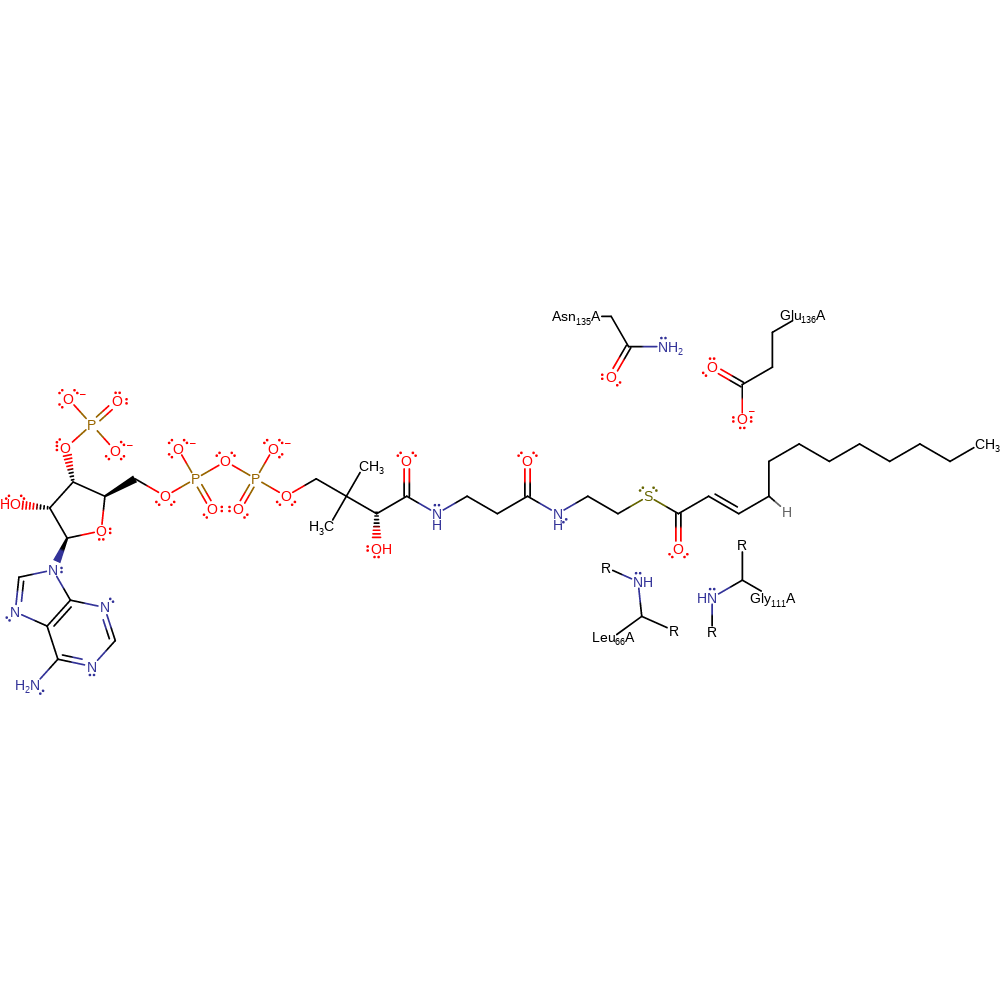 Download:
Download: