D-alanine-(R)-lactate ligase
D-alanine--D-alanine ligase (EC:6.3.2.4) is a bacterial enzyme involved in cell-wall biosynthesis. The product of this enzyme, the depsipeptide D-alanyl-(R)-lactate, can be incorporated into the peptidoglycan pentapeptide instead of the usual D-alanyl-D-alanine dipeptide. The resulting peptidoglycan does not bind the glycopeptide antibiotics vancomycin and teicoplanin, conferring resistance on the bacteria.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P25051
 (6.1.2.1)
(6.1.2.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Enterococcus faecium (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1e4e
- D-alanyl-D-lacate ligase
(2.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.20
 3.30.470.20
3.30.470.20  (see all for 1e4e)
(see all for 1e4e)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (2) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The D-lactate substrate attacks the terminal phosphate of ATP in a concerted mechanism to form ADP and phosphorylated D-lactate. D-alanine attacks the alpha phosphate of the D-lactate phosphate adduct, forming a tetrahedral intermediate. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, eliminating inorganic phosphate and forming the D-alanyl-D-lactate adduct.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1e4e) | ||
| His244 | His244A | His224 is responsible for pushing the equilibrium between D-lactate and D-alanyl binding in favour of the anionic D-lactate, with the positively charged imidazole group of His224 repelling the cationic amine groups of D-alanyl [PMID:10908650, PMID:18320587]. | attractive charge-charge interaction, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly311 (main-N), Arg290, His99 | Gly311A (main-N), Arg290A, His99A | Act to stabilise the negatively charged intermediates and transition states formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr315, Glu250, Lys22 | Tyr315A, Glu250A, Lys22A | Forms a hydrogen bonding network that ensures His244 is in the correct protonation state. | increase basicity, hydrogen bond donor |
| Val19 | Val19A | Ensures the correct stereoisomers are utilised. | electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Wu D et al. (2008), Proteins, 72, 1148-1160. Enzymatic characterization and crystal structure analysis of the D-alanine-D-alanine ligase from Helicobacter pylori. DOI:10.1002/prot.22009. PMID:18320587.
- Roper DI et al. (2000), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 97, 8921-8925. The molecular basis of vancomycin resistance in clinically relevant Enterococci: Crystal structure of D-alanyl-D-lactate ligase (VanA). DOI:10.1073/pnas.150116497. PMID:10908650.
- Marshall CG et al. (1998), J Bacteriol, 180, 5792-5795. DdlN from vancomycin-producing Amycolatopsis orientalis C329.2 is a VanA homologue with D-alanyl-D-lactate ligase activity. PMID:9791137.

Step 1. The D-lactate substrate attacks the terminal phosphate of ATP in a concerted mechanism to form ADP and phosphorylated D-lactate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly311A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys22A | hydrogen bond donor, increase basicity |
| His244A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, attractive charge-charge interaction |
| Val19A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu250A | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase basicity |
| Arg290A | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His99A | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr315A | hydrogen bond donor, increase basicity |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed
Step 2. D-alanine attacks the alpha phosphate of the D-lactate phosphate adduct, forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly311A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys22A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Val19A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg290A | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His244A | hydrogen bond donor, attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu250A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His99A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, attractive charge-charge interaction |
| Tyr315A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used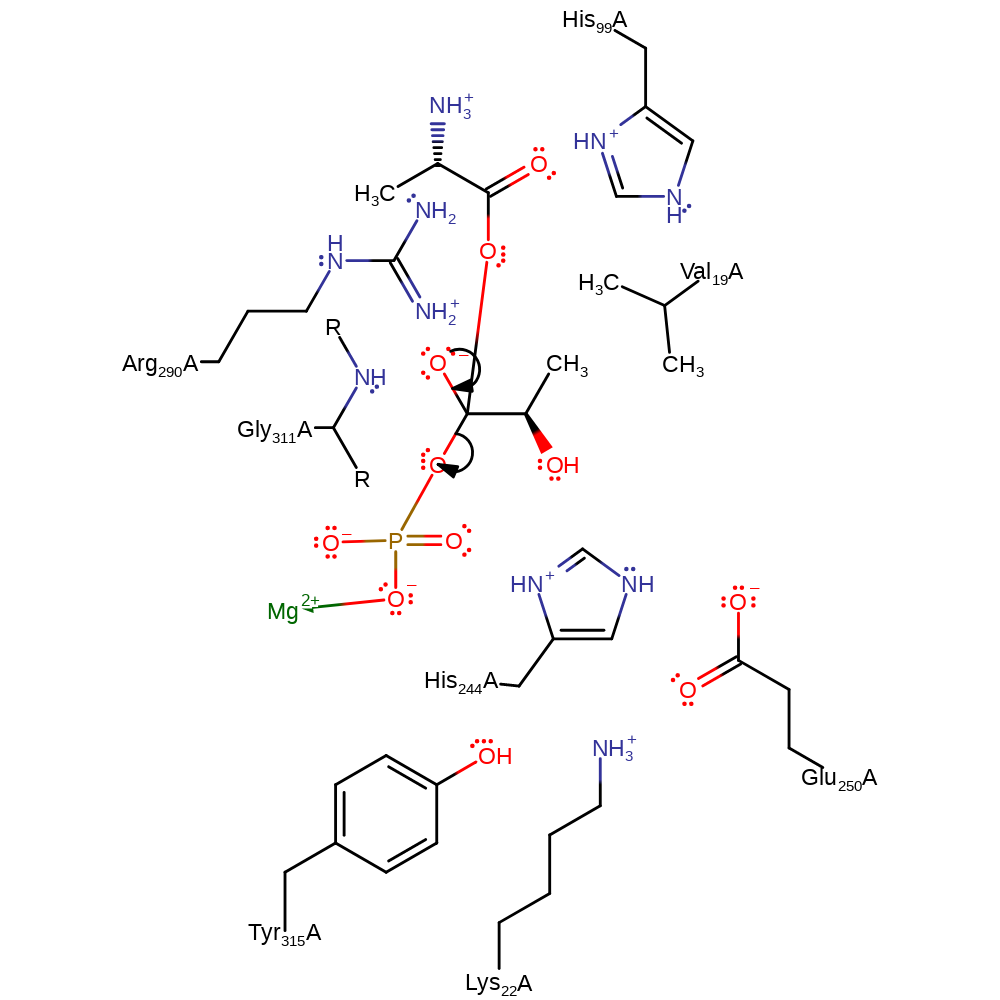
Step 3. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, eliminating inorganic phosphate and forming the D-alanyl-D-lactate adduct.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly311A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys22A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Val19A | steric role |
| Arg290A | attractive charge-charge interaction |
| His244A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu250A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His99A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr315A | hydrogen bond donor |






 Download:
Download: