Epi-isozizaene synthase
epi-isozizaene synthase is a member of the the Isoprenoid Synthase Type I superfamily. It catalyses the cyclisation of farnesyl diphosphate (FPP) to the sesquiterpene epi-isozizaene which is part of the sesquiterpene biosynthesis pathway.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9K499
 (4.2.3.37)
(4.2.3.37)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
3kb9
- Epi-isozizaene synthase: Complex with Mg, inorganic pyrophosphate and benzyl triethyl ammonium cation
(1.598 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.600.10
 (see all for 3kb9)
(see all for 3kb9)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (3) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The binding of the substrate causes a conformation change in the active site, which promotes the elimination of the pyrophosphate. The pyrophosphate attacks the C3 cationic carbon in a nucleophilic addition reaction. Intramolecular electrophilic addition across the C1-C6 bond to form the six-membered ring with concomitant elimination of the pyrophosphate and initiates a 1,2-Hydride shift. Spirocyclisation occurs to form the five and six membered ring intermediate. Intramolecular electrophilic addition to form the second six-membered ring which then contracts to a five membered ring. The pyrophosphate deprotonates the substrate, which initiates the final methyl migration.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (3kb9) | ||
| Phe95, Phe96, Phe198 | Phe95(116)A, Phe96(117)A, Phe198(219)A | Act to stabilise the positive carbocations formed during the course of the reaction. Also involved in ensuring the correct stereoisomers are formed. | polar/non-polar interaction, steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg338 | Arg338(359)A | Forms hydrogen bond with D219 that facilitates active site closure; Hydrogen bonds to PPi anion | promote heterolysis, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
intramolecular elimination, charge delocalisation, dephosphorylation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intramolecular electrophilic substitution, cyclisation, hydride transfer, intramolecular rearrangement, intramolecular electrophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Aaron JA et al. (2010), Biochemistry, 49, 1787-1797. Structure of Epi-Isozizaene Synthase fromStreptomyces coelicolorA3(2), a Platform for New Terpenoid Cyclization Templates,. DOI:10.1021/bi902088z. PMID:20131801.
- Rabe P et al. (2016), Chembiochem, 17, 1333-1337. Position-Specific Mass Shift Analysis: A Systematic Method for Investigating the EI-MS Fragmentation Mechanism of epi-Isozizaene. DOI:10.1002/cbic.201600237. PMID:27123899.
- Lin X et al. (2006), J Am Chem Soc, 128, 6022-6023. Genome Mining inStreptomycescoelicolor: Molecular Cloning and Characterization of a New Sesquiterpene Synthase. DOI:10.1021/ja061292s. PMID:16669656.

Step 1. The binding of the substrate causes a conformation change in the active site, which promotes the elimination of the pyrophosphate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg338(359)A | electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis, hydrogen bond donor |
| Phe95(116)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe96(117)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe198(219)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, charge delocalisation, dephosphorylation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 2. The pyrophosphate attacks the C3 cationic carbon in a nucleophilic addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg338(359)A | electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis, hydrogen bond donor |
| Phe95(116)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe96(117)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe198(219)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, charge delocalisation, intermediate formation
Step 3. Rotation about the newly formed C2-C3 bond generates the correpsonding cicoid conformer, which readily undergoes ionisation and cyclisation (across the C1-C6 bond) to form the bisabolyl cation [PMID:16669656] with concomitant dephosphorylation.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg338(359)A | electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis, hydrogen bond donor |
| Phe95(116)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe96(117)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe198(219)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular electrophilic substitution, intermediate formation, cyclisation, dephosphorylationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg338(359)A | electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis, hydrogen bond donor |
| Phe95(116)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe96(117)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe198(219)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, intramolecular rearrangement, intermediate formation
Step 5. Spirocyclisation to form the five and six membered ring acorenyl intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg338(359)A | electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis, hydrogen bond donor |
| Phe95(116)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe96(117)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe198(219)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
Chemical Components
intramolecular rearrangement, intermediate formation, cyclisation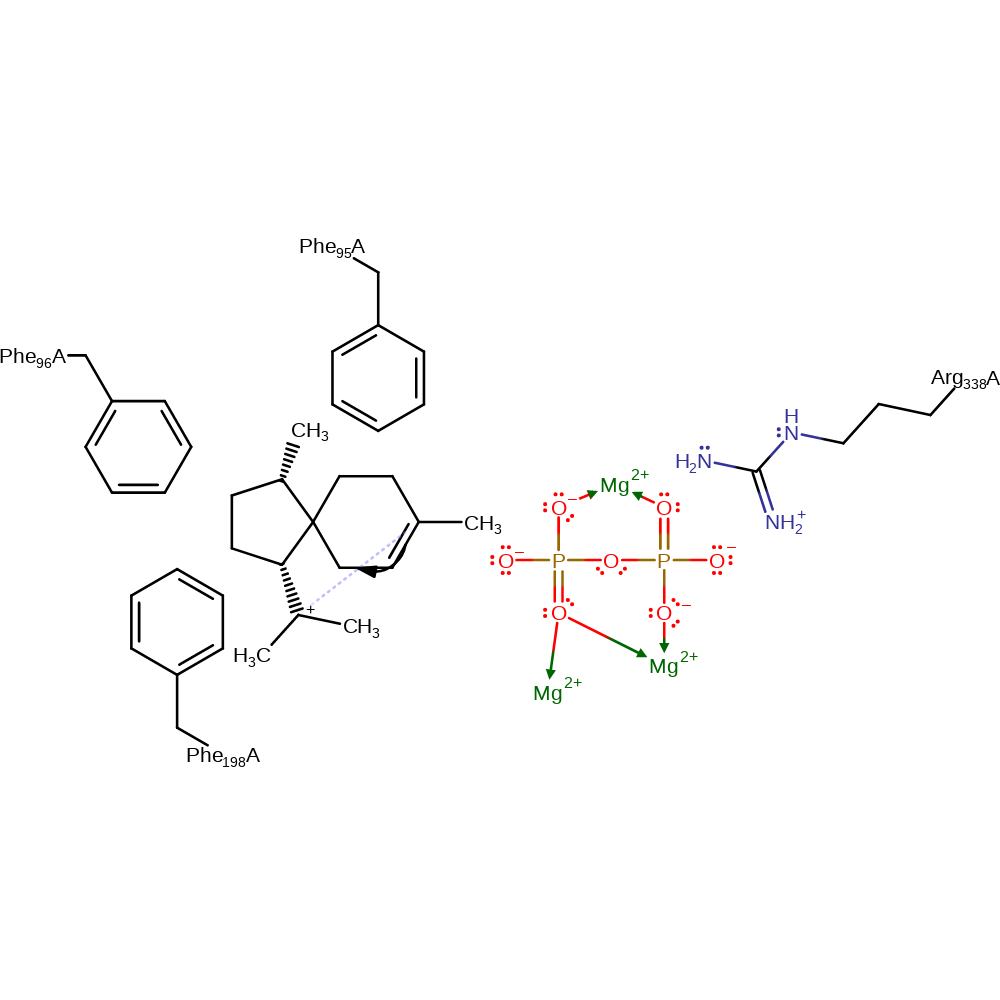
Step 6. Intramolecular electrophilic addition to form the second six-membered ring.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg338(359)A | electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis, hydrogen bond donor |
| Phe95(116)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe96(117)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe198(219)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular electrophilic addition, intermediate formation, cyclisationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg338(359)A | electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis, hydrogen bond donor |
| Phe95(116)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe96(117)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe198(219)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
Chemical Components
intramolecular rearrangement, intermediate formation
Step 8. The pyrophosphate deprotonates the substrate, which initiates the final methyl migration.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg338(359)A | electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis, hydrogen bond donor |
| Phe95(116)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe96(117)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Phe198(219)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, polar/non-polar interaction |





 Download:
Download: