Beta-lactamase (Class C)
This protein is a class C serine beta-lactamase with a substrate specificity for cephalosporins.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P05364
 (3.5.2.6)
(3.5.2.6)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Enterobacter cloacae (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1xx2
- Refinement of P99 beta-lactamase from Enterobacter cloacae
(1.88 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.710.10
 (see all for 1xx2)
(see all for 1xx2)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.5.2.6)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Tyr150 deprotonates the alcohol of Ser64, which initiates a nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl group of the beta-lactam ring. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, cleaving the C-N bond, which deprotonates Tyr150. Tyr150 deprotonates water, which attacks the carbonyl carbon of the covalently attached intermediate in a nucleophilic addition. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, eliminating Ser64, which reprotonates from Tyr150, producing the product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1xx2) | ||
| Ser84 (main-N), Ser338 (main-N) | Ser64A (main-N), Ser318A (main-N) | Forms the oxyanion hole. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser84 | Ser64A | Acts as the catalytic nucleophile. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Lys335, Glu292, Lys87 | Lys315A, Glu272A, Lys67A | Activates and stabilises Tyr150. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| Tyr170 | Tyr150A | Acts as the general acid/base that activates Ser64. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, decyclisation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Lamotte-Brasseur J et al. (2000), Proteins, 40, 23-28. pKa calculations for class C ?-lactamases: The role of tyr-150. DOI:10.1002/(sici)1097-0134(20000701)40:1<23::aid-prot40>3.0.co;2-7. PMID:10813827.
- Awasthi S et al. (2018), J Phys Chem B, 122, 4299-4308. Mechanism and Kinetics of Aztreonam Hydrolysis Catalyzed by Class-C β-Lactamase: A Temperature-Accelerated Sliced Sampling Study. DOI:10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b01287. PMID:29553742.
- Oefner C et al. (1990), Nature, 343, 284-288. Refined crystal structure of β-lactamase from Citrobacter freundiiindicates a mechanism for β-lactam hydrolysis. DOI:10.1038/343284a0. PMID:2300174.

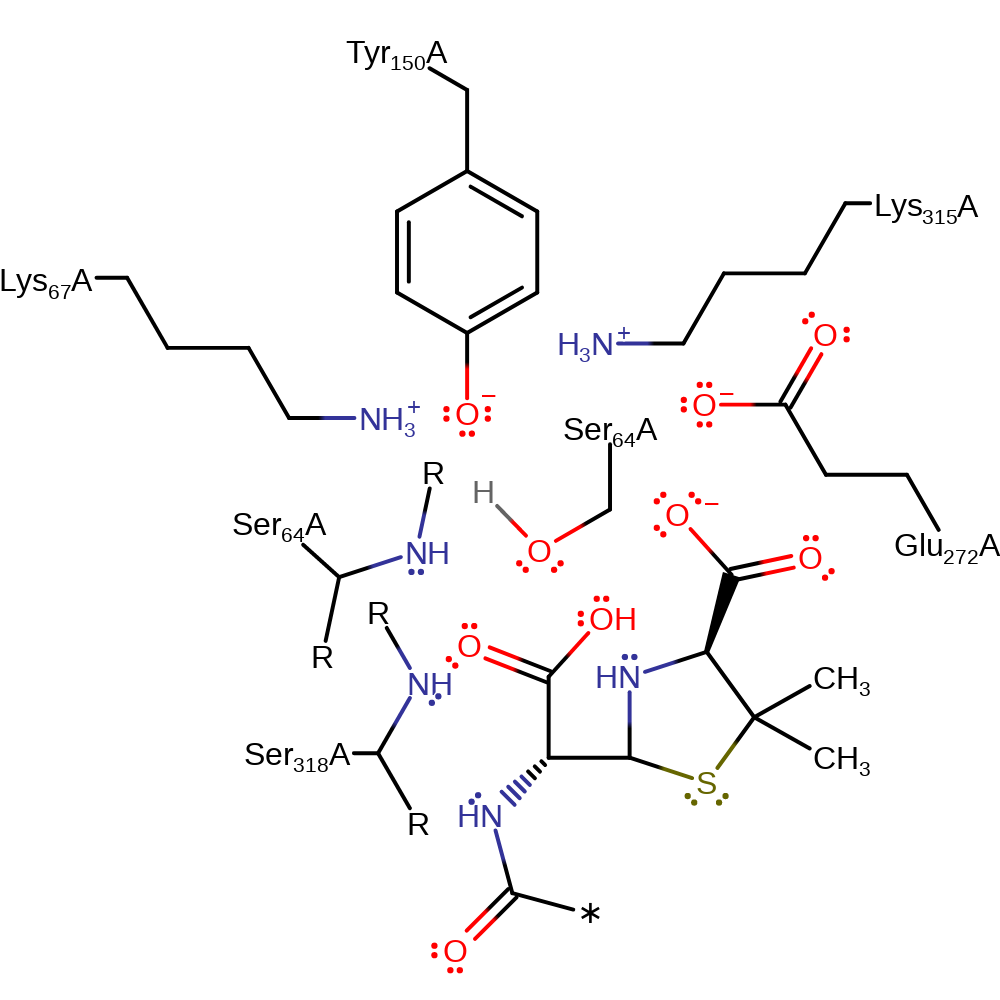
Step 1. Tyr150 deprotonates the alcohol of Ser64, which initiates a nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl group of the betalactam ring.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser64A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr150A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser318A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys67A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys315A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu272A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser64A | nucleophile |
| Tyr150A | proton acceptor |
| Ser64A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used
Step 2. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, cleaving the C-N bond, which deprotonates Tyr150.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser64A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr150A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser318A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys67A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| Lys315A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| Glu272A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser64A | covalently attached |
| Tyr150A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate formation, decyclisation
Step 3. Tyr150 deprotonates water, which attacks the carbonyl carbon of the covalently attached intermediate in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser64A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr150A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser318A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys67A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys315A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu272A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser64A | covalently attached |
| Tyr150A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 4. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, eliminating Ser64, which reprotonates from Tyr150, producing the product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser64A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr150A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser318A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys67A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| Lys315A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| Glu272A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr150A | proton donor |
| Ser64A | proton acceptor, nucleofuge |



 Download:
Download: