Methylated-DNA--[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase
Human O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase (AGT) acts to repair cytotoxic lesions in DNA by transfering the O6-alkyl groups to an active site cysteine. This mechanism for preserving genomic integrity limits the effectiveness of certain alkylating anticancer reagents, and therefore AGT is an active anticancer drug target. This enzyme catalyses only one turnover and therefore is not strictly catalytic.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P16455
 (2.1.1.63)
(2.1.1.63)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1eh6
- HUMAN O6-ALKYLGUANINE-DNA ALKYLTRANSFERASE
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.10.10
 (see all for 1eh6)
(see all for 1eh6)
- Cofactors
- Water (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.1.1.63)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
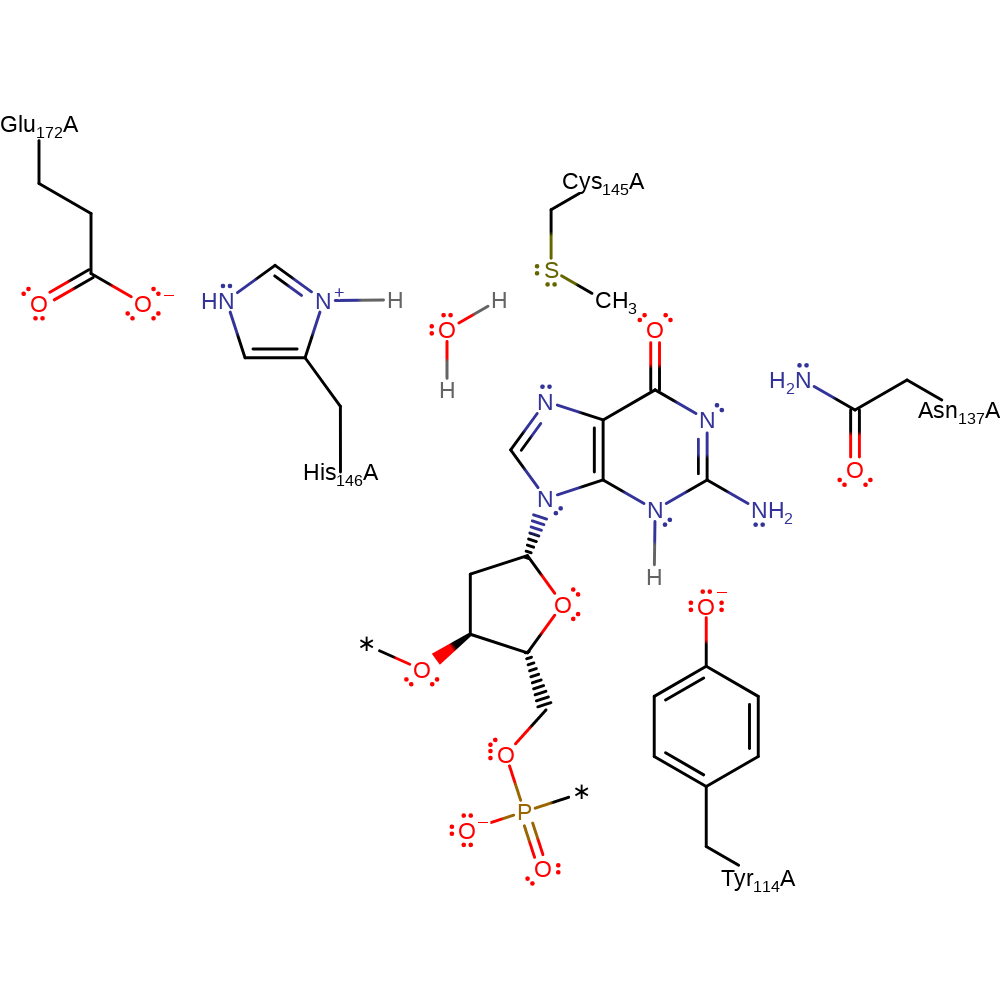
Initially His146 acts as a water mediated general base towards Cys145, deprotonating the residue to enhance its nucleophilicity, which then attacks the O6-alkyl carbon with concominant protonation of N3 of the substrate by Tyr144. This releases the DNA product, without the O6-alkyllguanine, and protein S-alkyl-L-cysteine.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1eh6) | ||
| Tyr114 | Tyr114A | The residue acts as a general acid towards the substrate, protonating N3. | hydrogen bond donor, proton donor |
| Cys145 | Cys145A | The residue is activated towards nucleophilic attack at the substrate by deprotonation through acid base interactions with a water molecule. The residue is irreversibly modified to an S-alkyl derivative during the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, proton donor |
| His146 | His146A | The residue is unprotonated within a hydrophobic environment, and is free to act as a base towards a water molecule, which in turn deprotonates the nucleophilic residue Cys 145. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor |
| Glu172 | Glu172A | Modifies the pKa of His146. | increase basicity, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asn137 | Asn137A | Binds and stabilises the DNA substrate in the active site. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton relay, overall reactant used, overall product formed, native state of enzyme is not regenerated, rate-determining stepReferences
- Daniels DS et al. (2000), EMBO J, 19, 1719-1730. Active and alkylated human AGT structures: a novel zinc site, inhibitor and extrahelical base binding. DOI:10.1093/emboj/19.7.1719. PMID:10747039.
- Miggiano R et al. (2013), J Bacteriol, 195, 2728-2736. Biochemical and structural studies of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis O6-methylguanine methyltransferase and mutated variants. DOI:10.1128/JB.02298-12. PMID:23564173.
- Walport LJ et al. (2012), Curr Opin Chem Biol, 16, 525-534. Mechanisms of human histone and nucleic acid demethylases. DOI:10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.09.015. PMID:23063108.
- Georgieva P et al. (2008), Chem Phys Lett, 463, 214-218. Density functional theory study of the reaction mechanism of the DNA repairing enzyme alkylguanine alkyltransferase. DOI:10.1016/j.cplett.2008.08.043.
- Spratt TE et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 6801-6806. Reaction and Binding of Oligodeoxynucleotides Containing Analogues ofO6-Methylguanine with Wild-Type and Mutant HumanO6-Alkylguanine-DNA Alkyltransferase†. DOI:10.1021/bi982908w. PMID:10346901.
- Goodtzova K et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 12489-12495. Investigation of the Role of Tyrosine-114 in the Activity of HumanO6-Alkylguanine-DNA Alkyltranferase†. DOI:10.1021/bi9811718. PMID:9730821.
- Moore MH et al. (1994), EMBO J, 13, 1495-1501. Crystal structure of a suicidal DNA repair protein: the Ada O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase from E. coli. PMID:8156986.
- Myers LC et al. (1992), Biochemistry, 31, 4541-4547. Zinc binding by the methylation signaling domain of the Escherichia coli Ada protein. DOI:10.1021/bi00134a002. PMID:1581309.
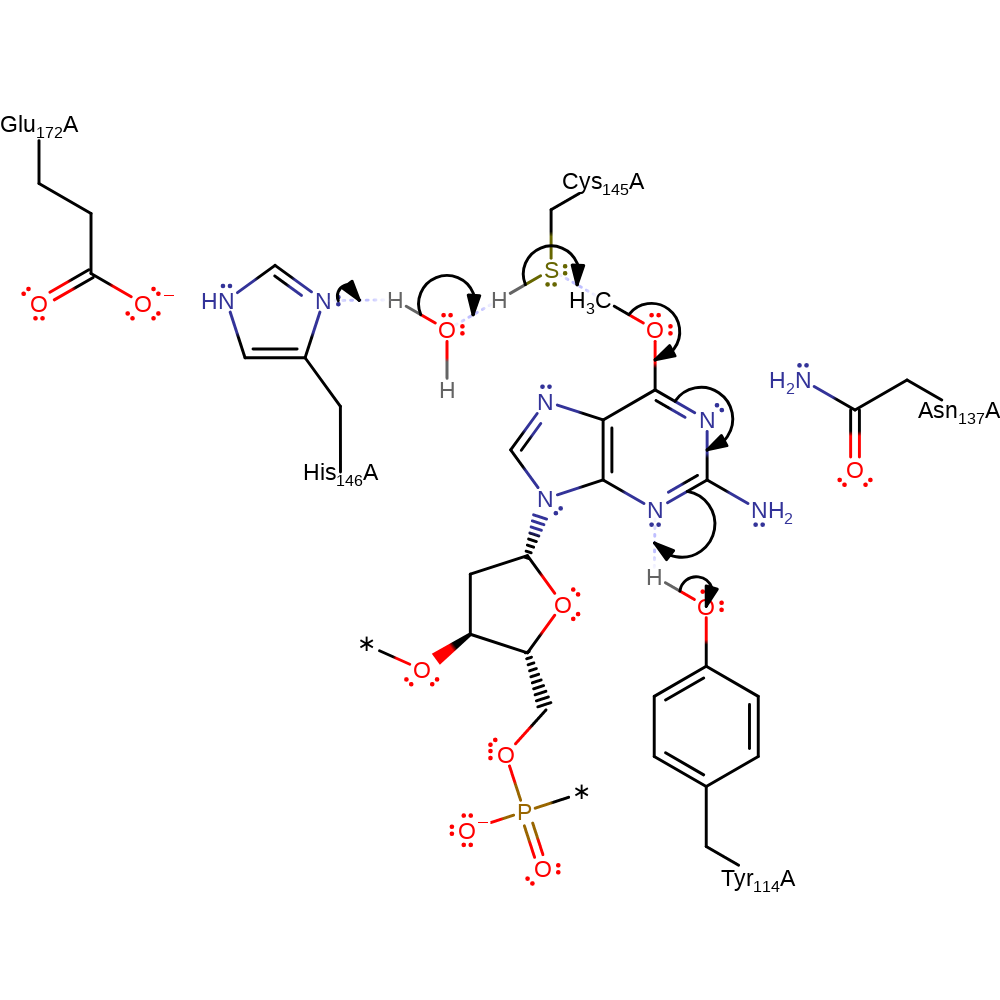
Step 1. His146 deprotonates water, which in turn deprotonates Cys145. Cys145 then initiates a nucleophilic attack upon the methylated DNA in a substitution reaction. The DNA base then undergoes double bond rearrangement, resulting in the deprotonation of Tyr114.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu172A | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase basicity |
| His146A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys145A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn137A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr114A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys145A | proton donor |
| His146A | proton acceptor |
| Cys145A | nucleophile |
| Tyr114A | proton donor |




 Download:
Download: