GDP-L-fucose synthase
GDP-4-keto-6-deoxy-D-mannose epimerase/reductase (GMER) is a bifunctional enzyme, catalysing the last two steps, epimerisation and reduction, in the biosynthesis of GDP-L-fucose, the substrate of fucosyl transferases. In bacteria, fucose is a component of the capsular polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides which function as antigenic determinants. In humans, fucose is a Lewis system antigen. It is a ligand to selectin and is involved in leukocytes and tumour cell adhesion to the endothelium. Human deficient in the biosynthesis of GDP fucose suffer from immune disorder adhesion deficiency type II, which can lead to serious symptoms, for instance, immunodeficiency and psychomotor retardation
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P32055
 (1.1.1.271)
(1.1.1.271)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1e6u
- GDP 4-keto-6-deoxy-D-mannose epimerase reductase
(1.45 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.25.10
 3.40.50.720
3.40.50.720  (see all for 1e6u)
(see all for 1e6u)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.1.1.271)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This mechanism proposal involves and ordered sequence of epimerisations, both catalysed by the same residues. In the first epimerisation Cys109 deprotonates C3 of the substrate to form an enolate which is then reprotonated on the opposite face by His179. In the second epimerisation Cys109 deprotonates C5 of the substrate. The resulting enolate is reprotonated by His179 on the opposite face. The final step involves the reduction of the carbonyl at C4 by NADPH. This is catalysed by Tyr136 of the conserved catalytic triad.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1e6u) | ||
| His179 | His179A | Protonated His179 acts as an acid in the epimerisation steps of the mechanism. | proton donor |
| Tyr136 | Tyr136A | Involved in the reduction of C4 in the final step of the mechanism. | proton relay, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Lys140 | Lys140A | Lowers the pKa of Tyr136 by electrostatic effects. | increase acidity |
| Ser107 | Ser107A | Acts as a proton shuttle between the sugar and the phenolic side chain of Tyr 136. | proton donor |
| Ser108 | Ser108A | Activates and stabilises Ser107, allowing it to act as a general acid/base. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys109 | Cys109A | Acts as a base to deprotonate C3 then C5 of the substrate in the epimerisation steps of the mechanism. | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, hydride transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, aromatic unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, intermediate collapseReferences
- Lau ST et al. (2008), J Am Chem Soc, 130, 17593-17602. Mechanism and active site residues of GDP-fucose synthase. DOI:10.1021/ja807799k. PMID:19053199.
- Rosano C et al. (2000), J Mol Biol, 303, 77-91. Probing the catalytic mechanism of GDP-4-keto-6-deoxy-d-mannose epimerase/reductase by kinetic and crystallographic characterization of site-specific mutants. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2000.4106. PMID:11021971.

Step 1. Cys109 acts as a base to deprotonate C3 of the substrate, forming an enolate intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys109A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 2. His179 acts as an acid, protonating the opposite face and completing the first epimerisation.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His179A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation
Step 3. In the second epimerisation Cys109 deprotonates C5 of the intermediate to form an enolate intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys109A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer
Step 4. His179 reprotonates the enolate intermediate on the opposite face.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His179A | proton donor |
Chemical Components

Step 5. In the final step the carbonyl at C4 is reduced by NADPH and while the resulting alkoxide is protonated by Tyr136. Tyr136 is protonated by Ser107 which is then reprotonated by water following this step.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys140A | increase acidity |
| Ser108A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr136A | proton acceptor |
| Ser107A | proton donor |
| Tyr136A | proton relay, proton donor |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, ingold: aromatic unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, intermediate collapse, proton transferIntroduction
Epimerisation of GDP-4-keto-6-deoxy-D-mannose occurs at C3 and C5 of the sugar. The mechanism involves the formation of a enolate intermediate from the keto substrate. Tyr136 acts as a general acid/base catalyst. With its pKa lowered by Lys140, it transiently protonates C4-keto group of the sugar to promote the formation of the enolate intermediate and also stabilise it. C3 or C5 of the enolate intermediate is then deprotonate by a base and reprotonate again from the opposite face of the sugar ring. Based on crystal structure and site-directed mutagenesis studies, both Cys109 and His179 can play the role of this base in abstracting a proton from C3 or C5 of the sugar ring.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1e6u) | ||
| His179 | His179A | Deprotonates C3 or C5 of the enolate intermediate and reprotonates it again from the opposite face of the sugar ring | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Tyr136 | Tyr136A | Acts as a general acid to protonate the C4 oxygen in concomitant to hydride transfer to C4 from NADPH. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys140 | Lys140A | Lowers the pKa of Tyr 136 by electrostatic effects. | increase basicity, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| Ser107 | Ser107A | Acts as a proton shuttle between the sugar and the phenolic side chain of Tyr 136. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity, increase basicity |
| Ser108 | Ser108A | Activates and stabilises Ser107, allowing it to act as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys109 | Cys109A | Has also been suggested to deprotonates C3 or C5 of the enolate intermediate and reprotonates it again from the opposite face of the sugar ring. In this proposal, it forms a hydrogen bonding network with Ser108 and Ser107, activating Ser107 to act as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, hydride transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate terminated, proton relay, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Rosano C et al. (2000), J Mol Biol, 303, 77-91. Probing the catalytic mechanism of GDP-4-keto-6-deoxy-d-mannose epimerase/reductase by kinetic and crystallographic characterization of site-specific mutants. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2000.4106. PMID:11021971.
- Somers WS et al. (1998), Structure, 6, 1601-1612. GDP-fucose synthetase from Escherichia coli: structure of a unique member of the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase family that catalyzes two distinct reactions at the same active site. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(98)00157-9. PMID:9862812.

Step 1. His179 initiates a keto-enol tautomerisation by removing the C3 proton of the substrate, forming an enolic intermediate and resulting in concomitant protonation of the C4 oxygen by Tyr136.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser107A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| Ser108A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys109A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr136A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys140A | increase acidity, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| His179A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr136A | proton donor |
| His179A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 2. Tyr136 initiates a keto-enol tautomerisation by removing the O4 proton, forming the keto form and protonation of C3 by His179 completes the epimerisation of the substrate, i.e. the proton is added to the opposite side of the ring from which it was removed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser107A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase basicity |
| Ser108A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys109A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr136A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys140A | increase basicity, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| His179A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr136A | proton acceptor |
| His179A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 3. His179 removes the C5 proton leading to the formation of an enolic intermediate and protonation of the C4 oxygen by Tyr136.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser107A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| Ser108A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys109A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr136A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys140A | increase acidity, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| His179A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr136A | proton donor |
| His179A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 4. Tyr136 deprotonates the substrate at O4 leading to the formation of the keto form and protonation of C5 by His179. This proton is added on the opposite side of the ring from which it was removed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser107A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase basicity |
| Ser108A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys109A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr136A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys140A | increase basicity, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| His179A | hydrogen bond donor, proton donor |
| Tyr136A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, intermediate formation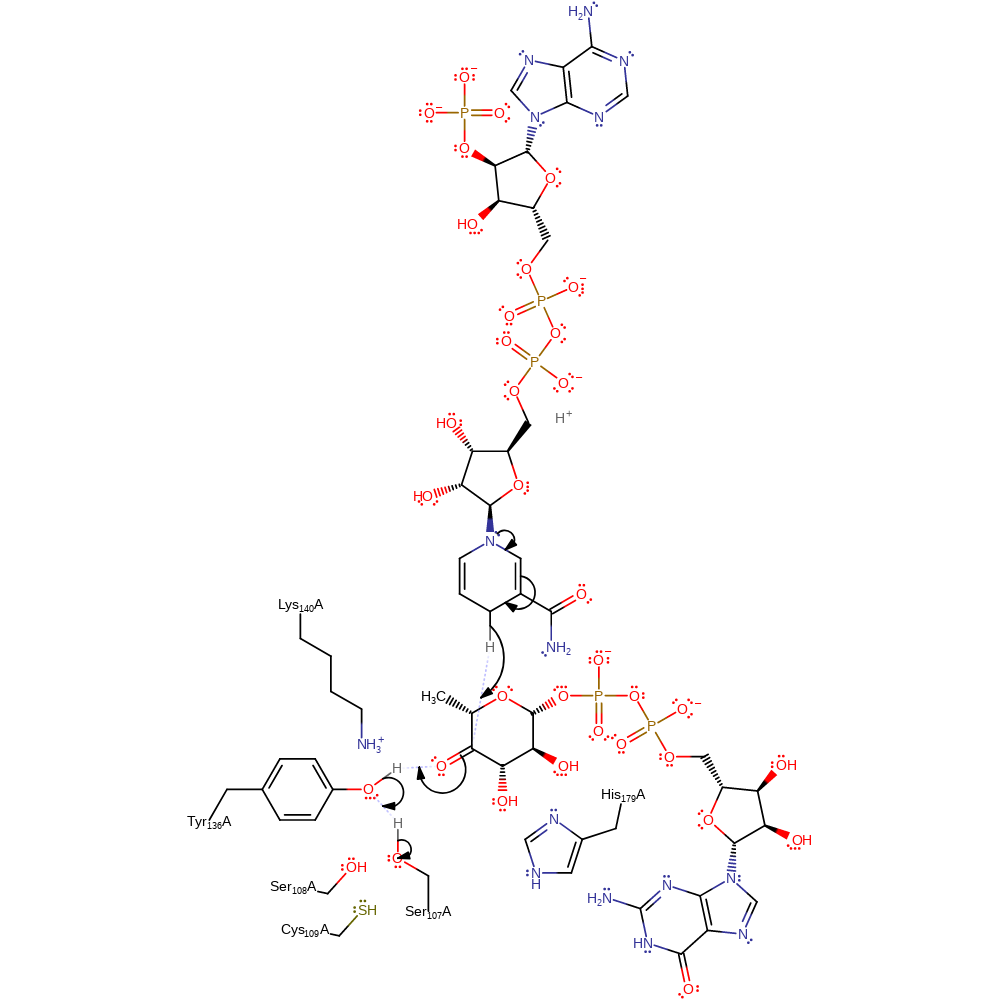
Step 5. NADPH transfers a hydride from its C4 position to the C4 position of the sugar. The resulting alkoxide is protonated by Tyr136, which is in turn protonated by Ser107.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser107A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser108A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys109A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr136A | proton relay, hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys140A | increase acidity, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| His179A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr136A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Ser107A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, proton relay, overall reactant used, overall product formed
Step 6. Inferred return step in which Ser107 is re-protonated by water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser107A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr136A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys140A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser107A | proton acceptor |





 Download:
Download:  Download:
Download: