Adenosine kinase
Toxoplasma gondii adenosine kinase catalyses the transfer of phosphoryl group from ATP to adenosine to yield AMP and ADP. It belongs to the family of carbohydrate kinases. Like all parasitic protozoans, Toxoplasma gondii cannot synthesise purine bases de novo, so enzymes of the Toxoplasma gondii purine salvage pathway are required for parasite survival. Adenosine Kinase is one of the most important enzymes involved in this pathway. Therefore it represents an attractive target for drugs which attack this highly dangerous parasite.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9TVW2
 (2.7.1.20)
(2.7.1.20)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Toxoplasma gondii (Protozoan)

- PDB
-
1lij
- STRUCTURE OF T. GONDII ADENOSINE KINASE BOUND TO PRODRUG 2 7-IODOTUBERCIDIN AND AMP-PCP
(1.86 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.1190.20
 3.30.1110.10
3.30.1110.10  (see all for 1lij)
(see all for 1lij)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Upon adenosine binding, a conserved dipeptide Gly68-Gly69 at the active site triggers a rigid-body rotation of 30 degrees of the lid domain, resulting in occlusion of the adenosine and the gamma-phosphate of ATP from the solvent. The reaction is ordered with adenosine binding first. This binding results in structural changes which are required in order for ATP to bind. The binding of ATP induces the formation of an anion hole, which completes the structural requirements for catalysis [PMID:10801355]. Asn223 and Glu226 are important in magnesium ion and phosphate binding.
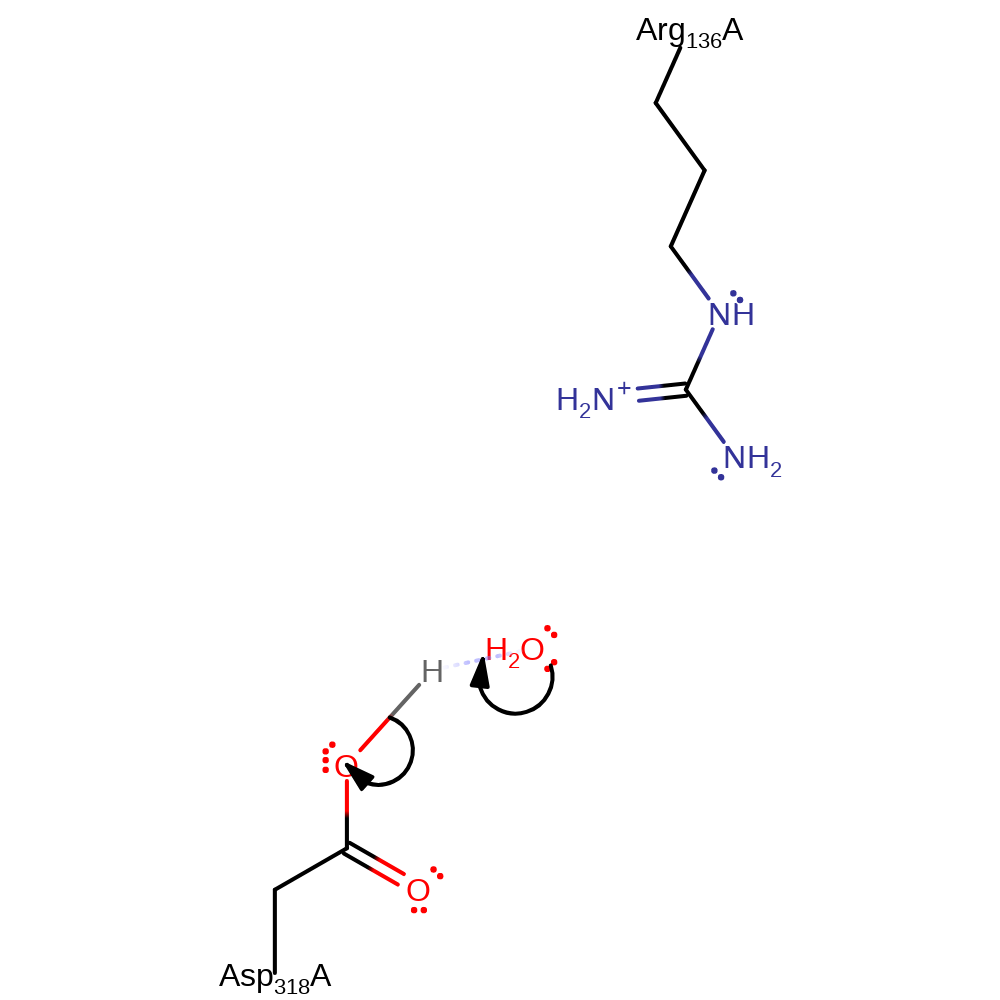
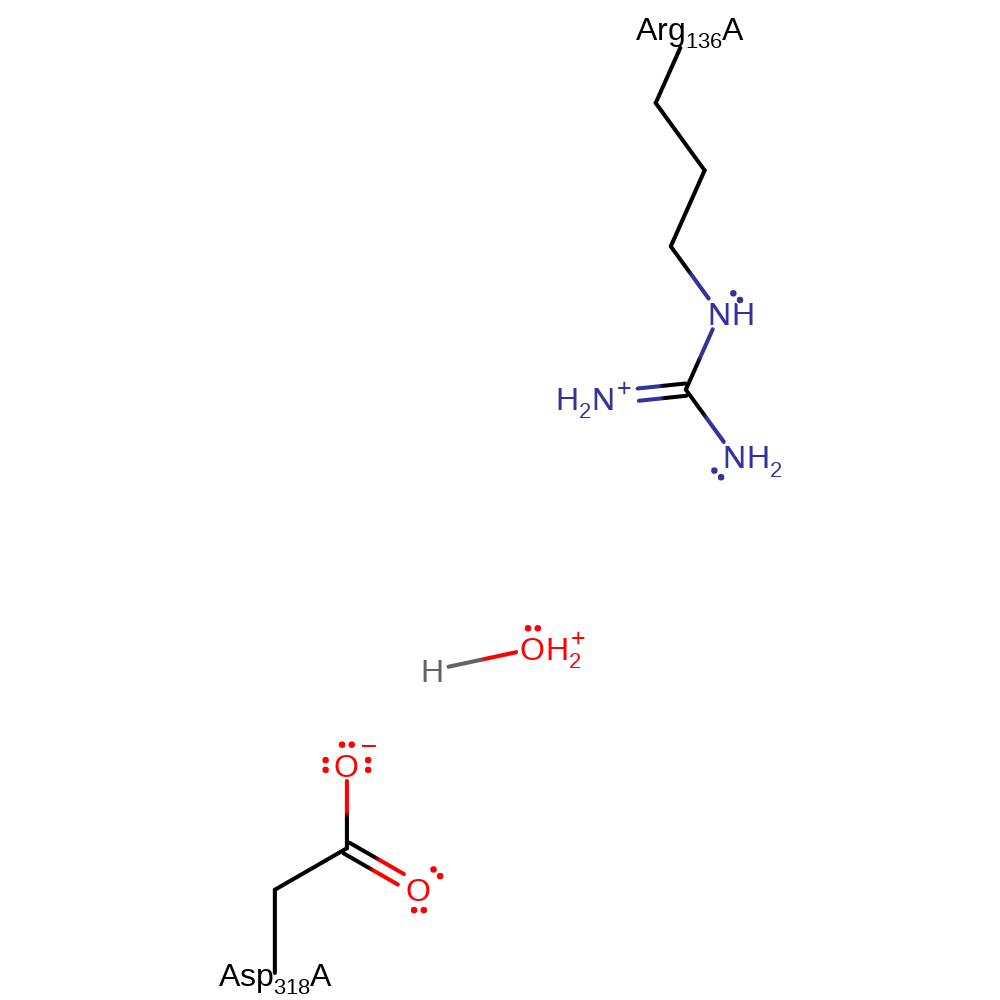
The reaction proceeds through a single step SN2-like mechanism with nucleophilic attack on the gamma phosphate of ATP by the 3C OH of the ribose sugar, facilitated by deprotonation of the OH by Asp 318. The beta and gamma phosphate groups are in an eclipsed conformation, which results in a sterically and energetically strained state, thus aiding in pentavalent transition state formation [PMID:10801355] which is stabilised by Arg 136 and a Mg(II) ion.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1lij) | ||
| Asp318 | Asp318A | Acts as a base to deprotonate the O5' hydroxyl group of adenosine to promote its nucleophilic attack on the terminal phosphate group of ATP. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Arg136 | Arg136A | Stabilises the pentavalent phosphate transition state through its positive charge interacting favourably with the negative charge developed. This allows nucleophilic attack from the adenosine on the gamma phosphate. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall product formed, overall reactant used, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Schumacher MA et al. (2000), J Mol Biol, 298, 875-893. Crystal structures of Toxoplasma gondii adenosine kinase reveal a novel catalytic mechanism and prodrug binding. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2000.3753. PMID:10801355.
- Park J et al. (2008), Cell Mol Life Sci, 65, 2875-2896. Adenosine kinase and ribokinase--the RK family of proteins. DOI:10.1007/s00018-008-8123-1. PMID:18560757.
- Park J et al. (2004), Protein J, 23, 167-177. Phosphorylated Derivatives That Activate or Inhibit Mammalian Adenosine Kinase Provide Insights into the Role of Pentavalent Ions in AK Catalysis. DOI:10.1023/B:JOPC.0000020083.81718.55.
- Maj MC et al. (2002), Biochemistry, 41, 4059-4069. Pentavalent Ions Dependency Is a Conserved Property of Adenosine Kinase from Diverse Sources: Identification of a Novel Motif Implicated in Phosphate and Magnesium Ion Binding and Substrate Inhibition†. DOI:10.1021/bi0119161.
- Maj MC et al. (2000), Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 275, 386-393. Structure-Activity Studies on Mammalian Adenosine Kinase. DOI:10.1006/bbrc.2000.3307. PMID:10964675.

Step 1. Asp318 deprotonates the -CH2-OH group of the adenosine substrate, which initiates a nucleophilic substitution against the gamma-phosphate of ATP. The adenosine 5'-hydroxyl group is positioned optimally for an in-line nucleophilic attack on the ATP gamma-phosphate atom. Asp318 is the likely candidate for proton abstraction of the 5'-hydroxyl group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp318A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg136A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp318A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall product formed, overall reactant usedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp318A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg136A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp318A | proton donor |





 Download:
Download: