Ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase
Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase is a redox driven proton pump that utilises the free energy of ubiquinol reduction for the creation of a proton gradient across membranes (periplasma in prokaryotes and intermembrane space in mitochondria) membrane. The proton-motive Q cycle mechanism best explains experimental results on the ET pathway through the four redox centres of the bc1 complex. The mechanism postulates two separate quinone binding sites, one for quinol oxidation (Qo site) and the other for quinone reduction (Qi site), and a bifurcated electron flow at the Qo site where the first electron from the the substrate quinol is transferred sequentially to the ISP domain (containing an iron-sulfur complex) to the cyt. c1 domain (containing a 1c type heme), and eventually to the soluble electron acceptor cyt. c, whereas the second electron is transferred to the b-type hemes bL and bH in sequence, ending at a quinone or a semiquinone anion at the Qi site. The complete Q cycle consumes two molecules of quinol, generates one molecule of quinone and translocates four protons to the positive side of the membrane. The exact order of the steps in this mechanism remains unclear. There is evidence of a long range interaction between both catalytic sites. Although it is not entirely clear is the oxidation/reduction of the quinol/quinone species are concerted or stepwise, evidence supports the stepwise manner shown here. It has been documented [PMID:12885240] that the ubisemiquinone radical produced during this step required an alkaline pH to be stable in the Qi site, consistent with the assumption that both Asp228 and His201 are deprotonated. Furthermore, electron nuclear double resonance experiments showed exchangeable H-bonds bonds to the ubisemiquinone radical, suggesting that the water-mediated H-bonding acts to stabilise the free radical formed.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequences
-
P08067
 (7.1.1.8)
(7.1.1.8)
P07143 (7.1.1.8)
(7.1.1.8)
P00163 (7.1.1.8)
(7.1.1.8)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c (Baker's yeast)

- PDB
-
1ezv
- STRUCTURE OF THE YEAST CYTOCHROME BC1 COMPLEX CO-CRYSTALLIZED WITH AN ANTIBODY FV-FRAGMENT
(2.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.102.10.10
 1.20.810.10
1.20.810.10  (see all for 1ezv)
(see all for 1ezv)
- Cofactors
- Heme b (3), Di-mu-sulfido-diiron(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:7.1.1.8)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Glu272 deprotonates the quinol substrate. His161 (bound to a Rieske iron-sulfur cluster) deprotonates the second alcohol group. This initiates a single electron transfer to the Rieske iron-sulfur cluster forming the semi-quinone intermediate. The alkoxide of the semi-quinone intermediate initiates a second single electron transfer (forming the first quinone product) through two heme groups to the quinone substrate, which initiates double bond rearrangement generating a semi-quinone intermediate. Water deprotonates His161, which initiates a single electron transfer from the Rieske iron-sulfur complex to the heme group of cytochrome-c1. Concurrently, water deprotonates Glu272. Glu272 deprotonates the second quinol substrate. His161 (bound to a Rieske iron-sulfur cluster) deprotonates the second alcohol group. This initiates a single electron transfer to the Rieske iron-sulfur cluster forming the semi-quinone intermediate. The alkoxide of the second semi-quinone intermediate initiates a second single electron transfer (forming the second quinone product) through two heme groups to the semi-quinone substrate, which initiates double bond rearrangement generating the quinol product, that deprotonates Lys228 through a water molecule. Water deprotonates His161, which initiates a single electron transfer from the Rieske iron-sulfur complex to the heme group of cytochrome-c1. Concurrently, water deprotonates Glu272.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ezv) | ||
| Glu272 | Glu272C | Acts as a general acid/base in the Qo site. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, radical stabiliser |
| Lys228 | Lys228C | Acts as a general acid/base in the Qi site. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser, radical stabiliser |
| His181 | His181(151)E(EA) | Binds the Riske iron-sulfur cluster. Acts as a general acid/base in the Qo site. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, radical stabiliser |
| His202 | His202C | Activates and stabilises the crystallographic water in the Qi site. | hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp229 | Asp229C | Activates the water molecule in the Qi site. | hydrogen bond acceptor, radical stabiliser, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser206 | Ser206C | Stabilises the reactive intermediates in the Qi site. | hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, electron transfer, radical formation, cofactor used, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, radical propagation, native state of cofactor regenerated, electron relay, overall product formed, proton relay, radical termination, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Mulkidjanian AY (2005), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1709, 5-34. Ubiquinol oxidation in the cytochrome bc1 complex: Reaction mechanism and prevention of short-circuiting. DOI:10.1016/j.bbabio.2005.03.009. PMID:16005845.
- Shimizu M et al. (2008), J Phys Chem B, 112, 15116-15126. Mechanism on two-electron oxidation of ubiquinol at the Qp site in cytochrome bc1 complex: B3LYP study with broken symmetry. DOI:10.1021/jp804387g. PMID:18973379.
- Wenz T et al. (2007), J Biol Chem, 282, 3977-3988. Mutational Analysis of Cytochrome b at the Ubiquinol Oxidation Site of Yeast Complex III. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m606482200. PMID:17145759.
- Gao X et al. (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 9067-9080. Structural Basis for the Quinone Reduction in thebc1Complex: A Comparative Analysis of Crystal Structures of Mitochondrial Cytochromebc1with Bound Substrate and Inhibitors at the QiSite†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi0341814. PMID:12885240.
- Lange C et al. (2001), EMBO J, 20, 6591-6600. Specific roles of protein-phospholipid interactions in the yeast cytochrome bc1 complex structure. DOI:10.1093/emboj/20.23.6591. PMID:11726495.

Step 1. The initial single electron oxidation of the quinol occurs at the Qo site. Glu272 deprotonates the quinol substrate. His161 (bound to a Rieske iron-sulfur cluster) deprotonates the second alcohol group. This initiates a single electron transfer to the Rieske iron-sulfur cluster forming the semi-quinone intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His181(151)E(EA) | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser206C | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp229C | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His202C | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu272C | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys228C | hydrogen bond donor |
| His181(151)E(EA) | proton acceptor |
| Glu272C | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, electron transfer, radical formation, cofactor used, intermediate formation, overall reactant used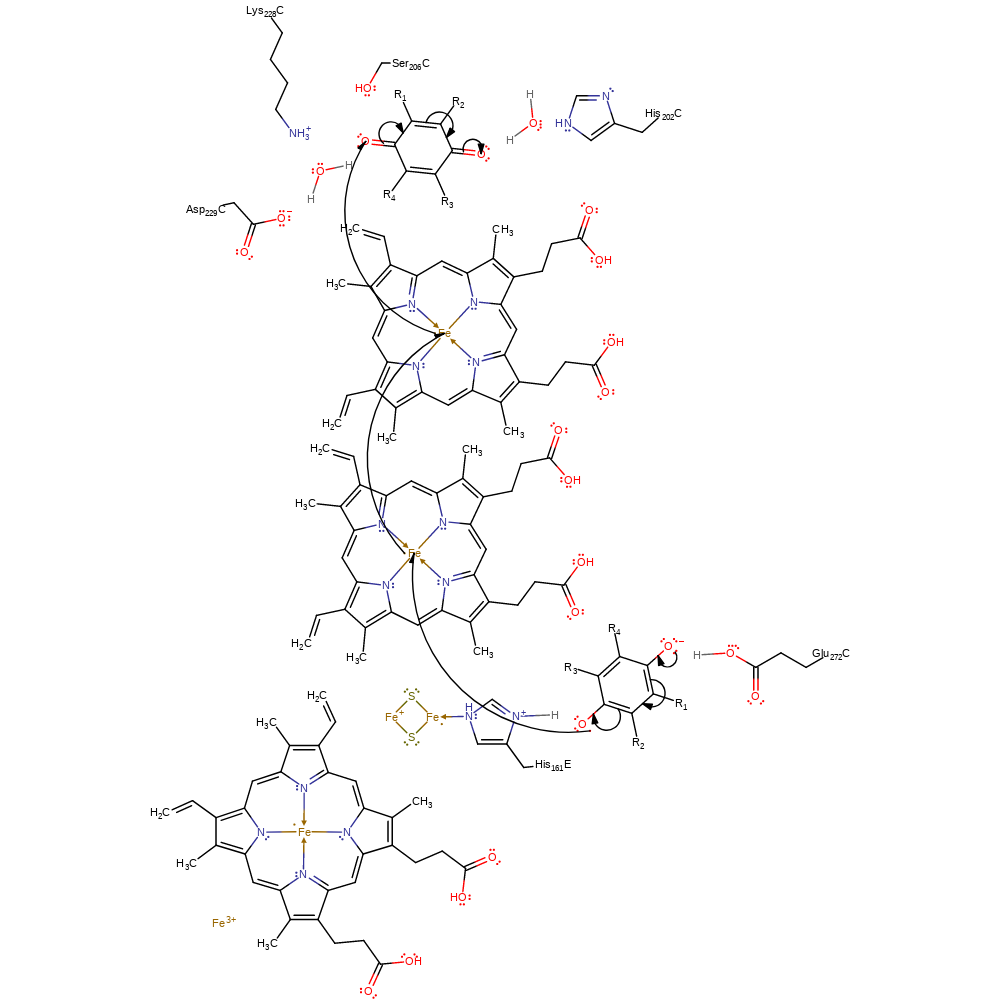
Step 2. The alkoxide of the semi-quinone intermediate initiates a second single electron transfer (forming the first quinone product) through two heme groups to the quinone substrate, which initiates double bond rearrangement generating a semi-quinone intermediate. The second electron oxidation of the semiquinone occurs at the Qo site. This second electron is transferred to hemes bL (HEM401) and bH (HEM402) in sequence, ending at the quinone in the Qi site. The rotational displacement of Glu295 in the Qo site is favourable for its proton transfer in the next reaction step. The first electron reduction of quinone occurs in the Qi site and is shown here as being concurrent with the second electron oxidation. However, it is unclear of the exact timings of these events. It has been documented [PMID:12885240] that the ubisemiquinone radical produced during this step required an alkaline pH to be stable in the Qi site, consistent with the assumption that both Asp228 and His201 are deprotonated. Furthermore, electron nuclear double resonance experiments showed exchangeable H-bonds bonds to the ubisemiquinone radical, suggesting that the water-mediated H-bonding acts to stabilise the free radical formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His181(151)E(EA) | hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser |
| Ser206C | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp229C | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His202C | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu272C | hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser |
| Lys228C | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, radical propagation, native state of cofactor regenerated, cofactor used, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, electron relay, overall product formed
Step 3. Water deprotonates His161, which initiates a single electron transfer from the Rieske iron-sulfur complex to the heme group of cytochrome-c1. Concurrently, water deprotonates Glu272. This step represents the regeneration of the Qo active site in order that the second quinol molecule may be oxidised. The transfer of the electron from the iron-sulfur cluster is shown here as being a concerted transfer from the iron-sulfur cluster to the cytochrome-c1 and then to the soluble electron acceptor. However, the exact timings of these transfers with respect to the mechanism is unclear. The rotational displacement of Glu272 occurs prior to this step and is favourable for the transfer of its proton to the bulk solvent. The Rieske iron-sulfur cluster (now Fe(II)Fe(III)S2) also undergoes a conformational change to allow it to reach the cytochrome-c1 (HEM3) for the electron transfer. These local movements are clearly complexed with the oxidation of heme bH and ubiquinone reduction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His181(151)E(EA) | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser206C | hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser |
| Asp229C | hydrogen bond acceptor, radical stabiliser |
| His202C | hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser |
| Glu272C | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys228C | hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser |
| Glu272C | proton donor |
| His181(151)E(EA) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, electron transfer, radical formation, cofactor used, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, proton relay
Step 4. Glu272 deprotonates the second quinol substrate. His161 (bound to a Rieske iron-sulfur cluster) deprotonates the second alcohol group. This initiates a single electron transfer to the Rieske iron-sulfur cluster forming the semi-quinone intermediate. The initial single electron oxidation of the second quinol occurs at the Qo site. This first electron is initially transferred to the Rieske iron-sulfur cluster.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His181(151)E(EA) | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser206C | hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser |
| Asp229C | hydrogen bond acceptor, radical stabiliser |
| His202C | hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser |
| Glu272C | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys228C | hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser |
| Glu272C | proton acceptor |
| His181(151)E(EA) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, electron transfer, radical formation, cofactor used, intermediate formation, overall reactant used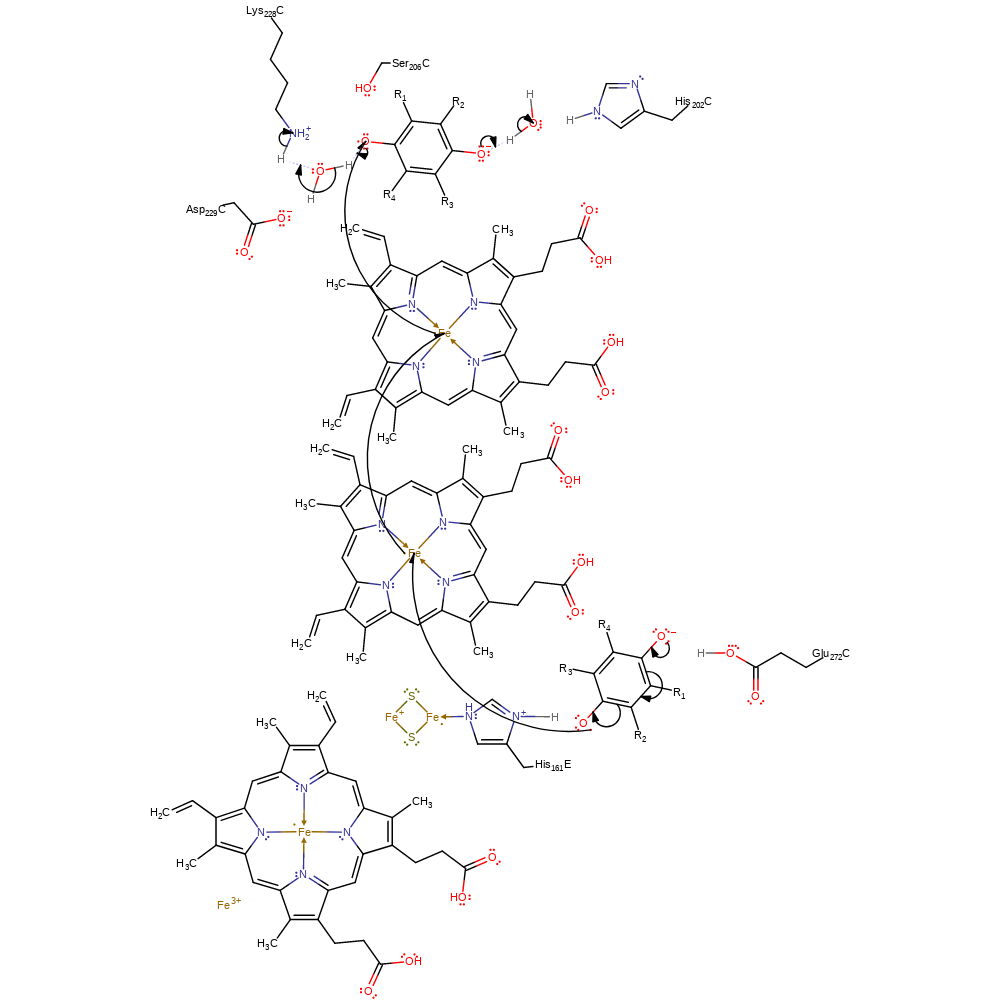
Step 5. The alkoxide of the second semi-quinone intermediate initiates a second single electron transfer (forming the second quinone product) through two heme groups to the semi-quinone substrate, which initiates double bond rearrangement generating the quinol product, that deprotonates Lys228 through a water molecule. The second electron oxidation of the semiquinone occurs at the Qo site. This second electron is transferred to hemes bL (HEM401) and bH (HEM402) in sequence, ending at the semiquinone anion in the Qi site. The rotational displacement of Glu295 in the Qo site is favourable for its proton transfer in the next reaction step. The first electron reduction of quinone occurs in the Qi site and is shown here as being concurrent with the second electron oxidation.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His181(151)E(EA) | hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser |
| Ser206C | hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser |
| Asp229C | hydrogen bond acceptor, radical stabiliser |
| His202C | hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser |
| Glu272C | hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser |
| Lys228C | hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser |
| Lys228C | proton donor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, radical termination, native state of cofactor regenerated, cofactor used, intermediate formation, electron relay, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, proton relay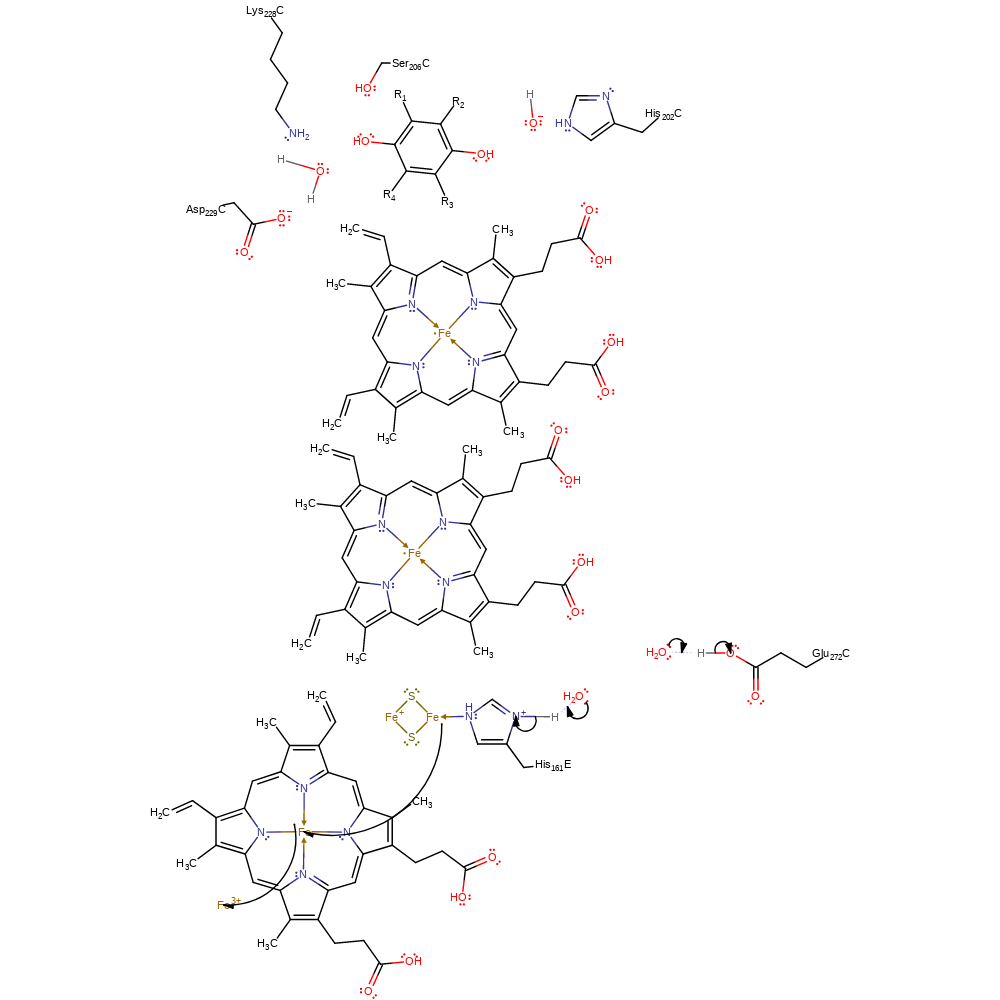
Step 6. Water deprotonates His161, which initiates a single electron transfer from the Rieske iron-sulfur complex to the heme group of cytochrome-c1. Concurrently, water deprotonates Glu272. This step represents the final regeneration of the Qo active site. The transfer of the electron from the iron-sulfur cluster is shown here as being a concerted transfer from the iron-sulfur cluster to the cytochrome-c1 and then to the soluble electron acceptor. However, the exact timings of these transfers with respect to the mechanism is unclear. The rotational displacement of Glu272 occurs prior to this step and is favourable for the transfer of its proton to the bulk solvent. The Rieske iron-sulfur cluster (now Fe(II)Fe(III)S2) also undergoes a conformational change to allow it to reach the cytochrome-c1 (HEM3) for the electron transfer. These local movements are clearly complexed with the oxidation of heme bH and ubiquinone reduction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His181(151)E(EA) | covalently attached, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser206C | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp229C | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His202C | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu272C | hydrogen bond donor |
| His181(151)E(EA) | proton donor |
| Glu272C | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, electron transfer, cofactor used, native state of cofactor regenerated, overall reactant used, overall product formed, electron relay
Step 7. The catalytic Qi site is regenerated through the uptake of two protons from the negative side of the membrane. These uptake pathways (not explicitly shown) were proposed based on analysis of bound water molecules (Lange et al. [PMID:11726495]).
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp229C | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His202C | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys228C | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His181(151)E(EA) | covalently attached |
| Lys228C | proton acceptor |





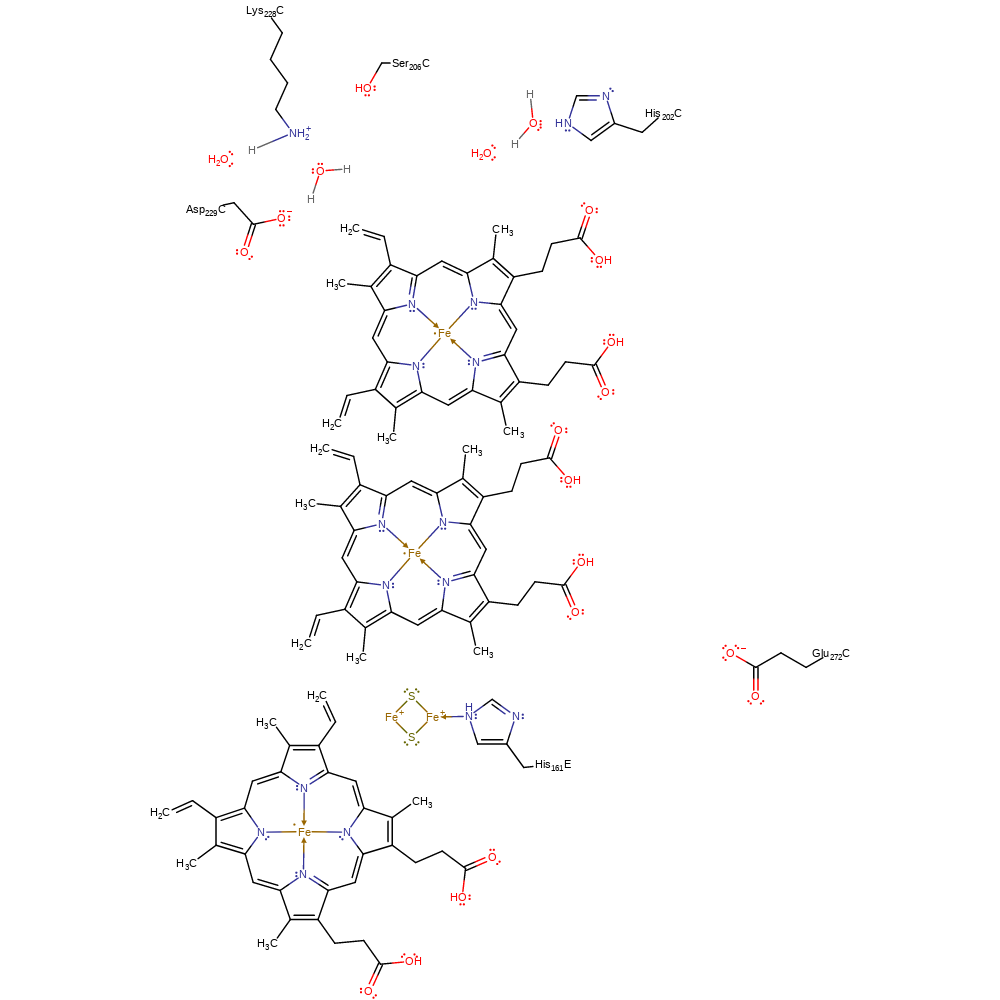 Download:
Download: