Crossover junction endodeoxyribonuclease
Endonuclease VII from Bacteriophage t4 is a junction-resolving enzyme. It has a broad substrate specificity, and recognises a variety of branched DNA structures and other structural perturbations in DNA such as Y-junctions, heteroduplex loops and abasic sites.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P13340
 (3.1.-.-)
(3.1.-.-)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Enterobacteria phage T4 (Virus)

- PDB
-
1en7
- ENDONUCLEASE VII (ENDOVII) FROM PHAGE T4
(2.4 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.1800.10
 1.10.720.10
1.10.720.10  (see all for 1en7)
(see all for 1en7)
- Cofactors
- Calcium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.22.4)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This enzyme catalyses a one step reaction which proceeds through a pentavalent transition state. His 41 acts as a general base to deprotonate water, activating it for nucleophilic attack on the phosphorus atom. This causes the P-O3' bond to break, and at the same time, His 105' protonates the O3' atom of the leaving group. Ca2+ (and possibly His 43) stabilise the pentavalent transition state.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1en7) | ||
| His43, Glu65 | His43A, Glu65A | Stabilises charge on phosphate group in transition state. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His41 | His41A | His 41 acts as a general base, deprotonating a water molecule and activating it for nucleophilic attack on the phosphorus atom. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His105 | His105B | His 105 acts as a general acid by protonating the O3' atom on the leaving group as it leaves. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, hydrolysis, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Raaijmakers H et al. (2001), J Mol Biol, 308, 311-323. Conformational flexibility in T4 endonuclease VII revealed by crystallography: implications for substrate binding and cleavage1 1Edited by K. Morikawa. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4592. PMID:11327769.
- Raaijmakers H et al. (1999), EMBO J, 18, 1447-1458. X-ray structure of T4 endonuclease VII: a DNA junction resolvase with a novel fold and unusual domain-swapped dimer architecture. DOI:10.1093/emboj/18.6.1447. PMID:10075917.

Step 1. His41 deprotonates water, which attacks the phosphate of DNA in a nucleophilic substitution that results in the cleavage of the phosphate bond, the 5' end of the DNA molecule reprotonates from His105B.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His105B | hydrogen bond donor |
| His41A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His43A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu65A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp40A | metal ligand |
| Asn62A | metal ligand |
| His41A | proton acceptor |
| His105B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, hydrolysisCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His105B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His41A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His105B | proton acceptor |
| His41A | proton donor |

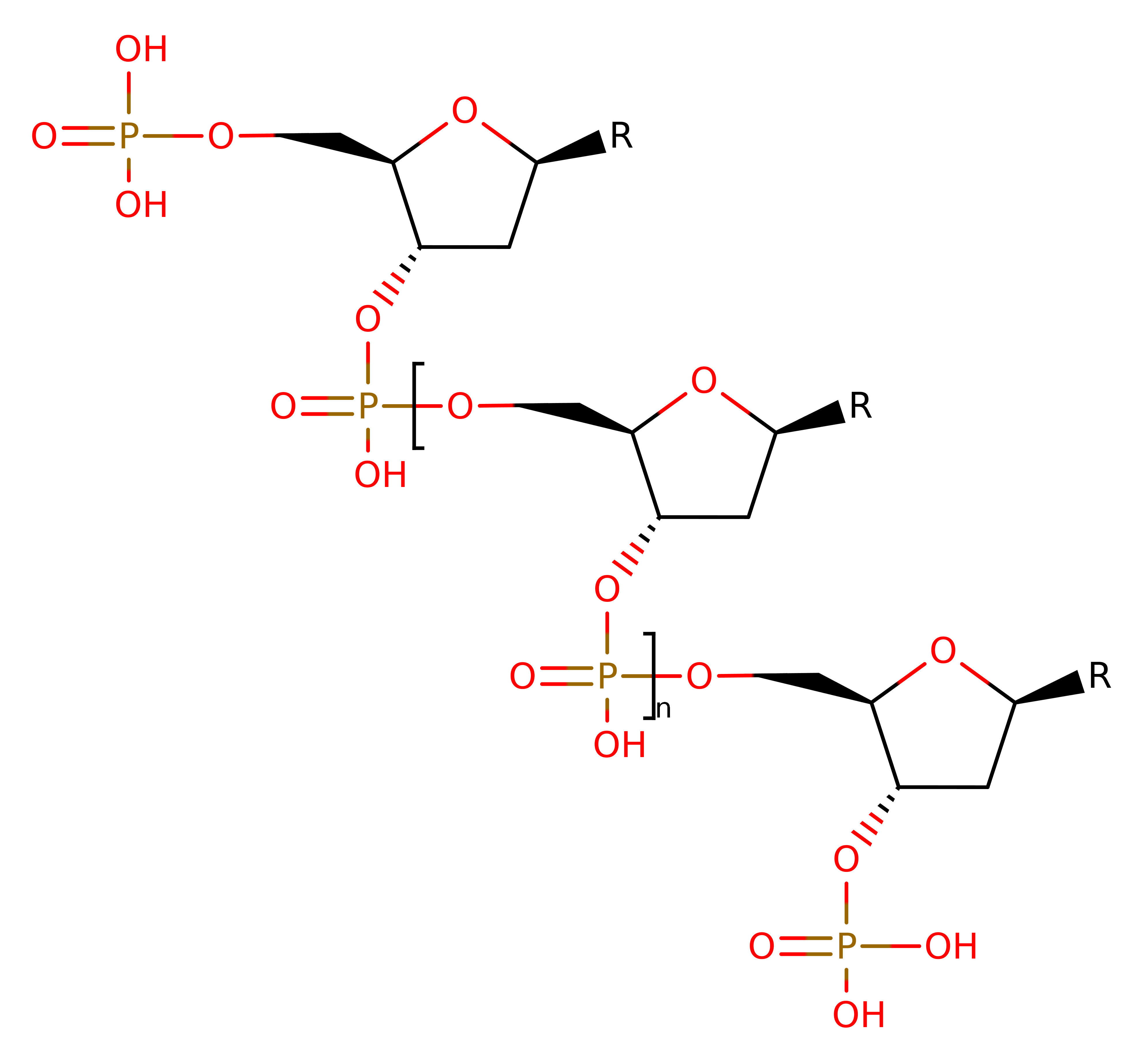
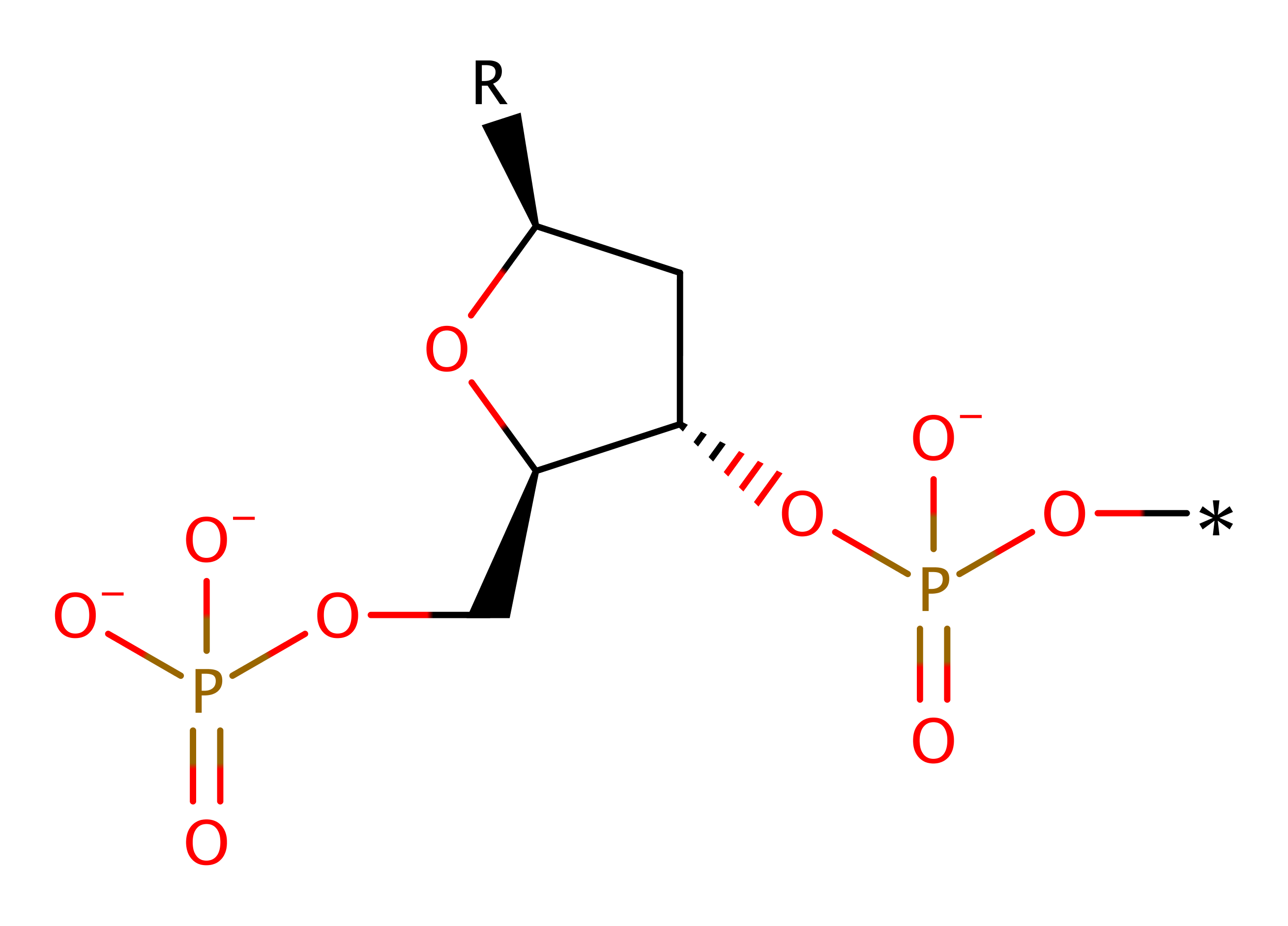
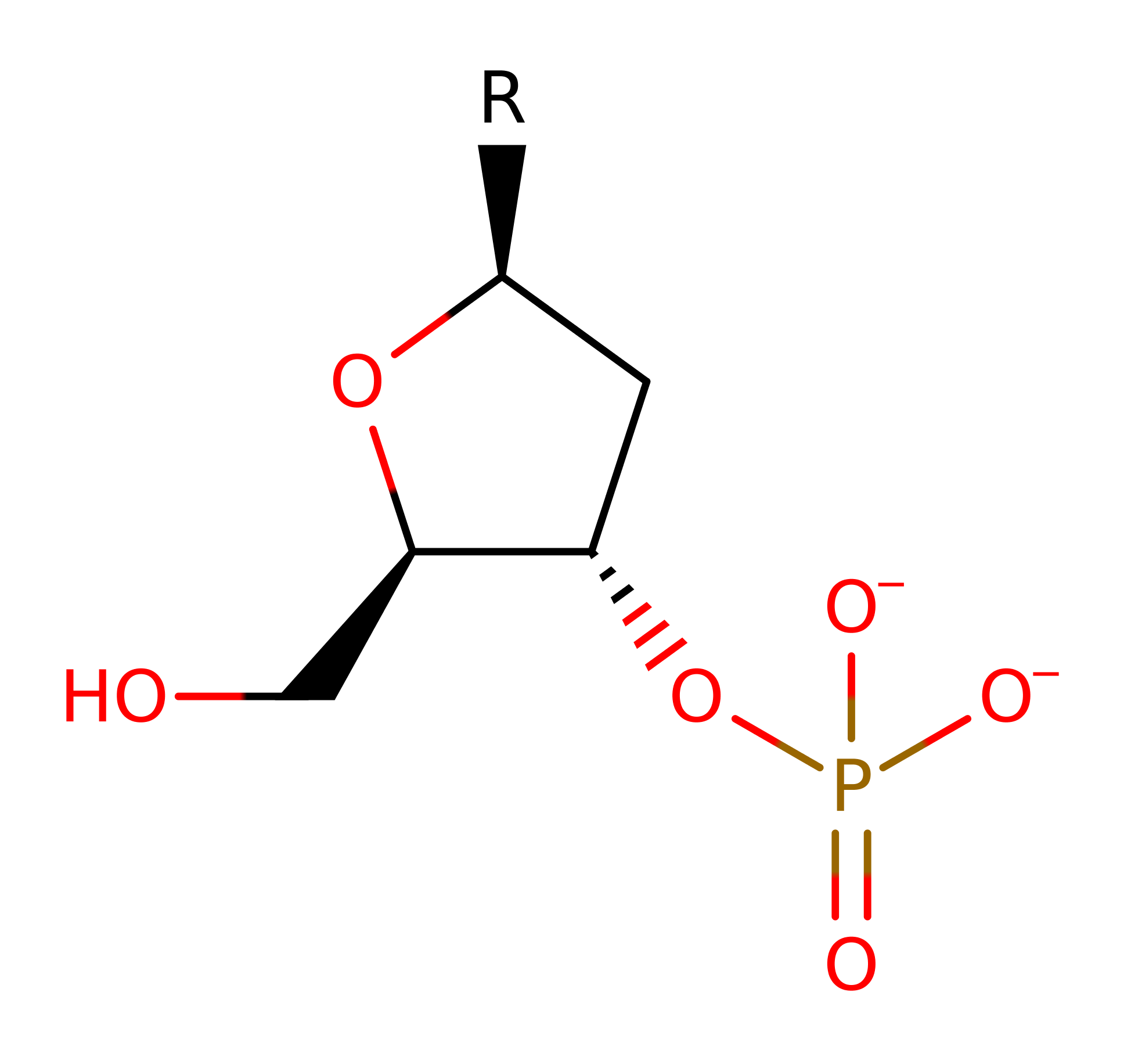


 Download:
Download: