Exodeoxyribonuclease III
Exonuclease III from Escherichia coli is a multifunctional enzyme which is able to cleave DNA in order to facilitate the removal of a particular base to create an AP site. This process occurs during replication, allowing incorrectly placed base pairs to be removed and replaced by the correct one. The efficiency of this process is essential to protect Escherichia coli from the damaging effects of mutations, and enables the fidelity of DNA polymerase activity to be increased by over 1000 times.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P09030
 (3.1.11.2)
(3.1.11.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1ako
- EXONUCLEASE III FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI
(1.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.60.10.10
 (see all for 1ako)
(see all for 1ako)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (2) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.11.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The phosphodiester bond is cleaved at the 3' end to leave a free 3' OH group and a phosphorylated 5' end. This occurs through the nucleophilic attack of a water molecule, activated by deprotonation from His 259 which is itself primed through hydrogen bonding contacts with Asp 229. The bond formed between the water molecule and the phosphorous atom allows a pentavalent phosphate transition state to develop, stabilised by electrostatic contacts from a Mg(II) ion at the active site. This collapses to release the products and cleave the DNA backbone, following protonation of the 3' by Asp 151's side chain, which is primed by contacts with Asn 7 and Asn 153 to ensure that it is protonated at physiological pH.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ako) | ||
| Asn153 | Asn153A | Forms contacts to ensure that Asp 151 is protonated at physiological pH and can act as an acid. Forms part of the magnesium 2 binding site. | activator, hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp229 | Asp229A | Acts to prime His 259 to allow it to act as an acid/base at physiological pH. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn7 | Asn7A | Forms contacts to Asp 151 to ensure that it is protonated and can act as an acid. | activator, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp258, Glu34 | Asp258A, Glu34A | Forms part of the magnesium 1 binding site. | metal ligand |
| His259 | His259A | Deprotonates the water molecule that attacks the electrophilic phosphorous atom to result in the cleavage of the phosphodiester bond. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp151 | Asp151A | Acts as acid to protonate the leaving group. Forms part of the magnesium 2 binding site. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, hydrolysis, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Mol CD et al. (1995), Nature, 374, 381-386. Structure and function of the multifunctional DNA-repair enzyme exonuclease III. DOI:10.1038/374381a0. PMID:7885481.
- Black CB et al. (1997), Eur J Biochem, 243, 684-689. Inert Chromium and Cobalt Complexes as Probes of Magnesium-Dependent Enzymes. Evaluation of the Mechanistic Role of the Essential Metal Cofactor in Escherichia Coli Exonuclease III. DOI:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.00684.x. PMID:9057832.
- Kuo CF et al. (1994), Ann N Y Acad Sci, 726, 223-235. Structure and Function of the DNA Repair Enzyme Exonuclease III from E. Coli. DOI:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb52820.x. PMID:8092679.
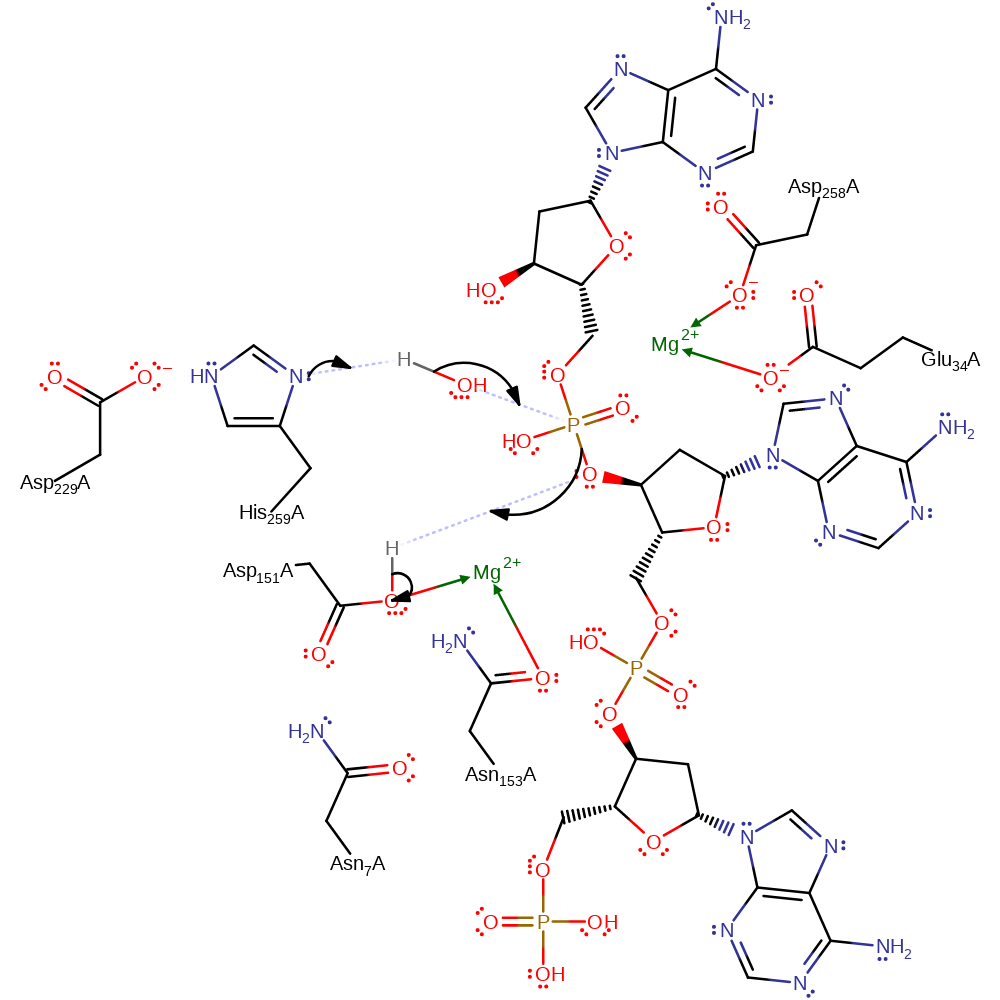
Step 1. His259 deprotonates water, which attacks the phosphate of DNA in a nucleophilic substitution that results in the cleavage of the phosphate bond, the 5' end of the DNA molecule reprotonates from Asp151.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn7A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp151A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn153A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp229A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| His259A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu34A | metal ligand |
| Asp258A | metal ligand |
| Asp151A | metal ligand |
| Asn153A | metal ligand |
| His259A | proton acceptor |
| Asp151A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, hydrolysisCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn7A | hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| Asp151A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asn153A | hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| Asp229A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His259A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu34A | metal ligand |
| Asp258A | metal ligand |
| Asp151A | metal ligand |
| Asn153A | metal ligand |
| His259A | proton donor |
| Asp151A | proton acceptor |



 Download:
Download: