Holo-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase
Holo-(acyl carrier protein) synthase (AcpS) from Bacillus subtilis is a member of the phosphopantetheinyl transferase superfamily. AcpS post-translationally modifies ACP to its holo form in order to activate it. AcpS catalyses the transfer of the 4'-phosphopantetheinyl (P-pant) moiety of coenzyme A to a serine residue on the ACP. This gives the activated ACP enzyme and Adenosine 3'5'-bisphosphate as products. This process is important as ACP enzymes play important roles in a number of biosynthetic pathways, such as the synthesis of fatty acids, vitamins, AcpS is essential in the initiation of the biosynthesis of fatty acids, polyketide antibiotics and non-ribosomal peptides.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequences
-
P96618
 (2.7.8.7)
(2.7.8.7)
P80643
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis str. 168 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1f80
- HOLO-(ACYL CARRIER PROTEIN) SYNTHASE IN COMPLEX WITH HOLO-(ACYL CARRIER PROTEIN)
(2.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.470.20
 1.10.1200.10
1.10.1200.10  (see all for 1f80)
(see all for 1f80)
- Cofactors
- Calcium(2+) (1), Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.7.8.7)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This enzyme requires either Mg(II) or Mn(II) for activity. The mechanism proceeds as follows: Asp 35 (in the substrate protein) deprotonates a water molecule. This activated water molecule then acts as a general base by deprotonating the substrate serine residue, activating it for nucleophilic attack on the beta-phosphate of CoA. The nucleophilic attack results in the transfer of the phosphopantetheinyl group to the substrate serine residue. The resulting negatively charged 3',5'-ADP is stabilised by interactions with Lys 62, the mainchain amide of His 105 and the magnesium ion. A proton is then transferred to 3',5'-ADP from either a water molecule or Lys 62.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1f80) | ||
| His105 (main-N) | His105(104)B (main-N) | The main-chain amide of His 105 stabilises the negatively charged 3',5'-ADP. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys62 | Lys62(61)A | Stabilises the negatively charged intermediate. May also act as a proton donor to 3',5'-ADP. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp36 | Asp35(40)E | This residue is part of the substrate protein (represented by UniProtKB P80643). It deprotonates a water molecule, which in turn deprotonates the substrate serine residue. | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton relay, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, intermediate collapse, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate baseReferences
- Parris KD et al. (2000), Structure, 8, 883-895. Crystal structures of substrate binding to Bacillus subtilis holo-(acyl carrier protein) synthase reveal a novel trimeric arrangement of molecules resulting in three active sites. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00178-7. PMID:10997907.
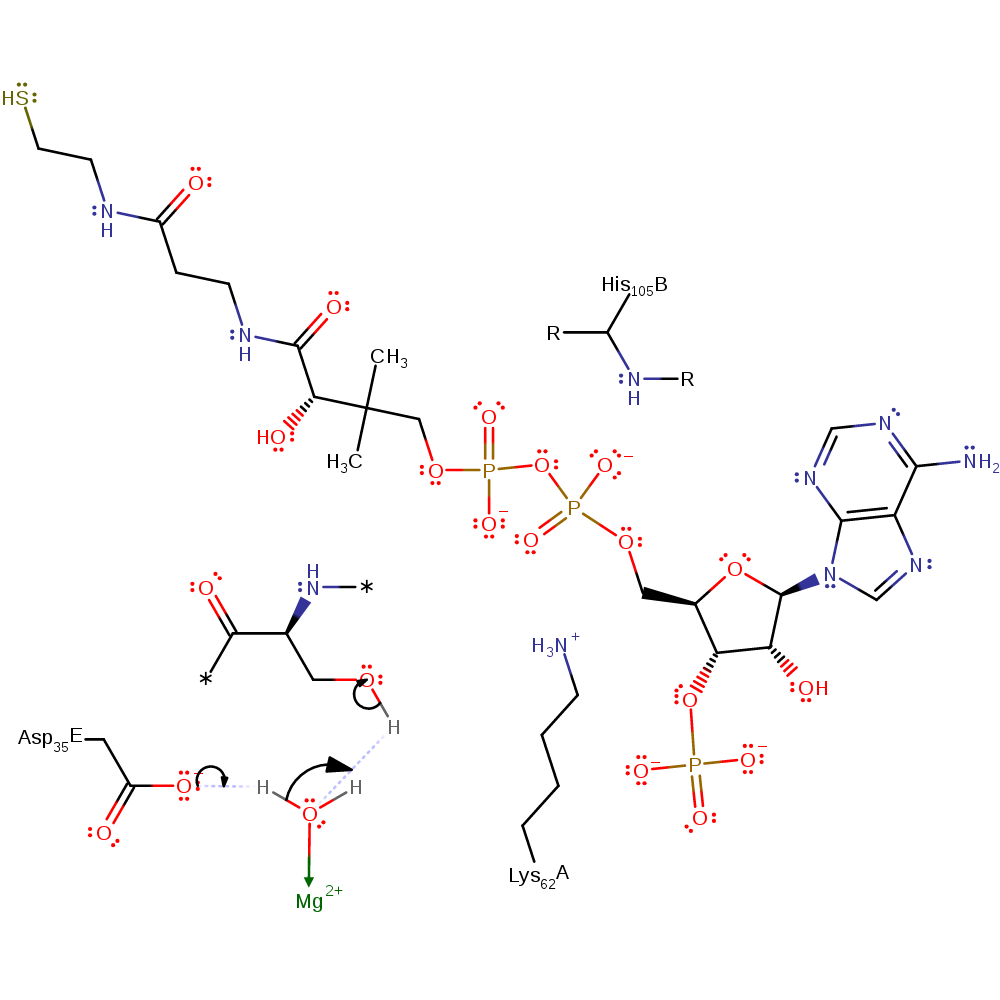
Step 1. Magnesium activated water deprotonates the Apo-ACP, activating it.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys62(61)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His105(104)B (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp35(40)E | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton relay, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, proton transfer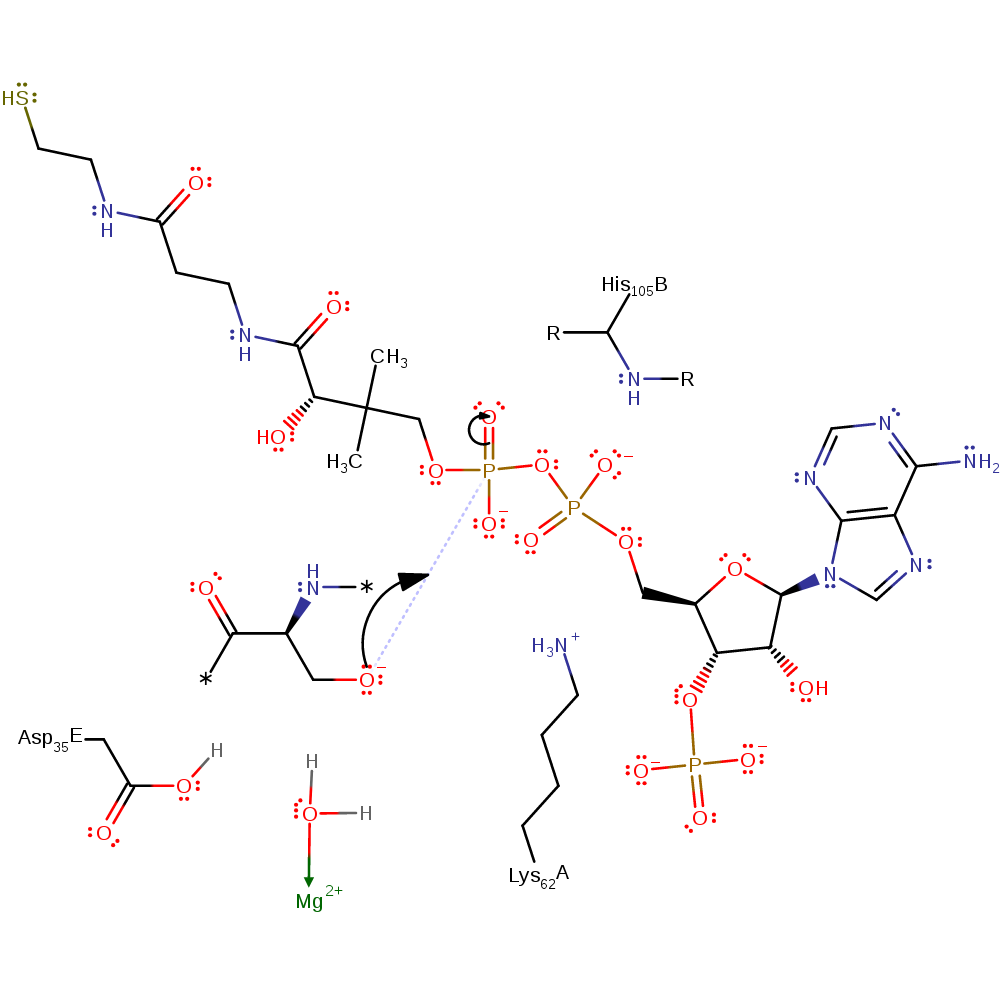
Step 2. The activated Apo-ACP attacks the CoA in a nucleophilic addition, creating a pentavalent phosphate intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys62(61)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His105(104)B (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, overall reactant used, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition
Step 3. The pentavalent phosphate intermediate collapses, initiating an elimination of the adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate product, which is reprotonated from a water molecule.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys62(61)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His105(104)B (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |





 Download:
Download: