Dihydrofolate reductase (bacterial)
Dihydrofolate reductase catalyses the reduction of 7,8-dihydrofolate (DHF) to 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate (THF) by stereospecific hydride transfer from a NADPH cofactor to the C6 atom of the pterin ring with concomitant protonation at N(5). DHFR plays a central role cell maintenance of THF reserves, which are essential for purine and thimidylate synthesis and hence for cell growth and proliferation. As DHFR is the sole source of THF, the enzyme is the Achilles heel of rapidly proliferating cells and, therefore, has been a major focus in the development of anticancer and antibacterial reagents.
Much interest has been generated in this enzyme due to its potential as a target for antibacterial and anticancer drugs. It is ubiquitous throughout evolution, but always most important in cells which are dividing rapidly, hence its value as a drug target against infections and cancer.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00381
 (1.5.1.3)
(1.5.1.3)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Lactobacillus casei (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
3dfr
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURES OF ESCHERICHIA COLI AND LACTOBACILLUS CASEI DIHYDROFOLATE REDUCTASE REFINED AT 1.7 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION. I. GENERAL FEATURES AND BINDING OF METHOTREXATE
(1.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.430.10
 (see all for 3dfr)
(see all for 3dfr)
- Cofactors
- Water (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.5.1.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This mechanism proceeds in a single step in which the hydride ion is added to C6 with concomitant protonation of the N5 from a conserved water molecule. The active site residues are responsible for maintaining the steric placement of the substrates and Asp26, shown to be critical to the mechanism, is part of a hydrogen bonding network that modifies the pKa of the N5 atom from 2.4 to 6.5 when bound in a ternary complex. Further, and somewhat unusually, catalysis in this enzyme is dependent on a number of non-polar residues.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (3dfr) | ||
| Trp22 | Trp21A | Helps bind and activate the water molecule that (along with Asp26) helps modify the pKa of the N5. | activator, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp27 | Asp26A | the ionised Asp26 contributes to a negative electrostatic environment that shifts the solution pKa of the substrate N5 atom from 2.4 to 6.5 when bound in a ternary complex. In addition, Asp26 interacts with structurally relevant waters at the active site that are important for substrate binding. Site-directed mutagenesis of Asp26 to asparagine has demonstrated its importance for catalysis, although in eukaryotic enzymes it is replaced by a Glu residue. | modifies pKa, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Thr117 | Thr116A | Stabilises the negative charge on Asp26. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Leu95 (main-C), Leu5 (main-C) | Leu94A (main-C), Leu4A (main-C) | Two mainchain carbonyls, of Leu4 and Leu94, constrain the pteridine ring in the right plane to receive protons; the sidechains of these residues are not conserved, although they are always hydrophobic. | steric role |
| Leu20 | Leu19A | Leu19 (replaced by Met in E. coli) may create a hydrophobic environment around N5 of folate in order to push the positive charge on the ring on to C6, where it can receive hydride. | enhance reactivity |
| Phe31 | Phe30A | Phe30 sterically forces the pteridine ring close to the nicotinamide. | steric locator |
| Leu28, Leu55 | Leu27A, Leu54A | Leu27 and Leu54 are both suggested to constrain the folate ring system. | steric locator |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, hydride transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic additionReferences
- Liu CT et al. (2014), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 111, 18231-18236. Escherichia colidihydrofolate reductase catalyzed proton and hydride transfers: Temporal order and the roles of Asp27 and Tyr100. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1415940111. PMID:25453098.
- Wan Q et al. (2014), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 111, 18225-18230. Toward resolving the catalytic mechanism of dihydrofolate reductase using neutron and ultrahigh-resolution X-ray crystallography. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1415856111. PMID:25453083.
- Czekster CM et al. (2011), Biochemistry, 50, 367-375. Kinetic and Chemical Mechanism of the Dihydrofolate Reductase fromMycobacterium tuberculosis. DOI:10.1021/bi1016843. PMID:21138249.
- Shrimpton P et al. (2002), Protein Sci, 11, 1442-1451. Role of water in the catalytic cycle ofE. colidihydrofolate reductase. DOI:10.1110/ps.5060102. PMID:12021443.
- Cummins PL et al. (2001), J Am Chem Soc, 123, 3418-3428. Energetically Most Likely Substrate and Active-Site Protonation Sites and Pathways in the Catalytic Mechanism of Dihydrofolate Reductase. DOI:10.1021/ja0038474. PMID:11472112.
- Casarotto MG et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 8038-8044. Direct Measurement of the pKaof Aspartic Acid 26 inLactobacillus caseiDihydrofolate Reductase: Implications for the Catalytic Mechanism. DOI:10.1021/bi990301p. PMID:10387048.
- Brown KA et al. (1992), Faraday Discuss, 93, 217-224. Exploring the molecular mechanism of dihydrofolate reductase. DOI:10.1039/fd9929300217. PMID:1290933.
- Bystroff C et al. (1990), Biochemistry, 29, 3263-3277. Crystal structures of Escherichia coli dihydrofolate reductase: the NADP+ holoenzyme and the folate.NADP+ ternary complex. Substrate binding and a model for the transition state. DOI:10.2210/pdb6dfr/pdb. PMID:2185835.
- Bolin JT et al. (1982), J Biol Chem, 257, 13650-13662. Crystal structures of Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus casei dihydrofolate reductase refined at 1.7 A resolution. I. General features and binding of methotrexate. PMID:6815178.
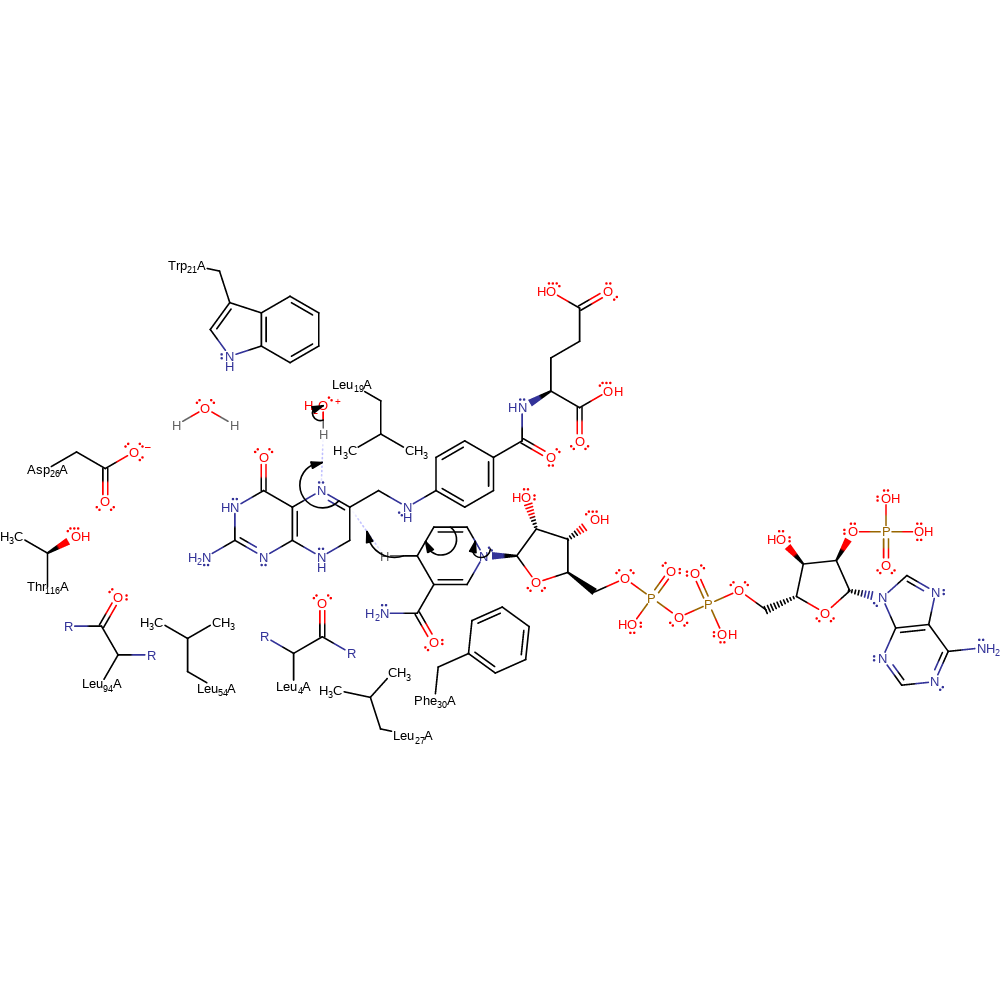
Step 1. The dihydrofolate substrate undergoes a tautomerisation reaction, resulting in the deprotonation of water.
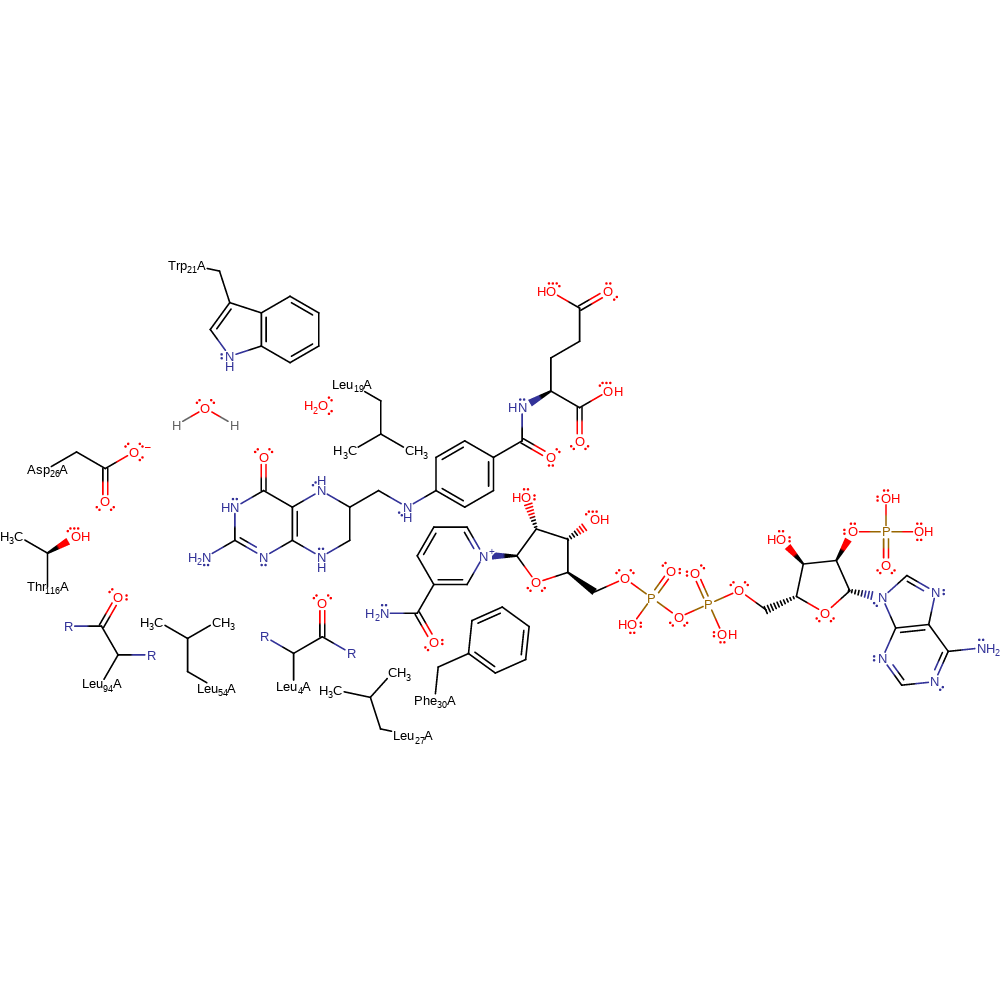
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr116A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp26A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Trp21A | hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| Leu19A | enhance reactivity |
| Phe30A | steric locator |
| Leu27A | steric locator |
| Leu54A | steric locator |
| Leu4A (main-C) | steric role |
| Leu94A (main-C) | steric role |
| Asp26A | modifies pKa |





 Download:
Download: