
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase (carbamoyl-p,aspartate)
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Complex of n-phosphonacetyl-l-aspartate with aspartate carbamoyltransferase. X-ray refinement, analysis of conformational changes and catalytic and allosteric mechanisms
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Aspartate carbamoyltransferase (r state), catalytic chain. Chain: a, c. Engineered: yes. Aspartate carbamoyltransferase regulatory chain. Chain: b, d. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Organism_taxid: 562
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dodecamer (from
)
Dodecamer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
H.Ke,W.N.Lipscomb,Y.Cho,R.B.Honzatko
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
H.M.Ke
et al.
(1988).
Complex of N-phosphonacetyl-L-aspartate with aspartate carbamoyltransferase. X-ray refinement, analysis of conformational changes and catalytic and allosteric mechanisms.
J Mol Biol,
204,
725-747.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
25-Aug-89
|
Release date:
|
15-Oct-90
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, C:
E.C.2.1.3.2
- aspartate carbamoyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
carbamoyl phosphate + L-aspartate = N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
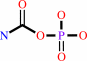 carbamoyl phosphate
carbamoyl phosphate
|
+
|
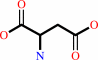 L-aspartate
L-aspartate
|
=
|
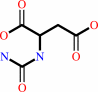 N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
|
+
|
phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 64.71% similarity
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains B, D:
E.C.?
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Mol Biol
204:725-747
(1988)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Complex of N-phosphonacetyl-L-aspartate with aspartate carbamoyltransferase. X-ray refinement, analysis of conformational changes and catalytic and allosteric mechanisms.
|
|
H.M.Ke,
W.N.Lipscomb,
Y.J.Cho,
R.B.Honzatko.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The allosteric enzyme aspartate carbamoyltransferase of Escherichia coli
consists of six regulatory chains (R) and six catalytic chains (C) in D3
symmetry. The less active T conformation, complexed to the allosteric inhibitor
CTP has been refined to 2.6 A (R-factor of 0.155). We now report refinement of
the more active R conformation, complexed to the bisubstrate analog
N-phosphonacetyl-L-aspartate (PALA) to 2.4 A (R-factor of 0.165,
root-mean-square deviations from ideal bond distances and angles of 0.013 A and
2.2 degrees, respectively). The antiparallel beta-sheet in the revised segment
8-65 of the regulatory chain of the T conformation is confirmed in the R
conformation, as is also the interchange of alanine 1 with the side-chain of
asparagine 2 in the catalytic chain. The crystallographic asymmetric unit
containing one-third of the molecule (C2R2) includes 925 sites for water
molecules, and seven side-chains in alternative conformations. The gross
conformational changes of the T to R transition are confirmed, including the
elongation of the molecule along its threefold axis by 12 A, the relative
reorientation of the catalytic trimers C3 by 10 degrees, and the rotation of the
regulatory dimers R2 about the molecular twofold axis by 15 degrees. No changes
occur in secondary structure. Essentially rigid-body transformations account for
the movement of the four domains of each catalytic-regulatory unit; these
include the allosteric effector domain, the equatorial (aspartate) domain, and
the combination of the polar (carbamyl phosphate) and zinc domain, which moves
as a rigid unit. However, interfaces change, for example the interface between
the zinc domain of the R chain and the equatorial domain of the C chain, is
nearly absent in the T state, but becomes extensive in the R state of the
enzyme; also one catalytic-regulatory interface (C1-R4) of the T state
disappears in the more active R state of the enzyme. Segments 50-55, 77-86 and
231-246 of the catalytic chain and segments 51-55, 67-72 and 150-153 of the
regulatory chain show conformational changes that go beyond the rigid-body
movement of their corresponding domains. The localized conformational changes in
the catalytic chain all derive from the interactions of the enzyme with the
inhibitor PALA; these changes may be important for the catalytic mechanism. The
conformation changes in segments 67-72 and 150-153 of the regulatory chain may
be important for the allosteric control of substrate binding. On the basis of
the conformational differences of the T and R states of the enzyme, we present a
plausible scheme for catalysis that assumes the ordered binding of substrates
and the ordered release o

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.A.Stieglitz,
J.Xia,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2009).
The first high pH structure of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Proteins,
74,
318-327.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.D.Rabinowitz,
J.J.Hsiao,
K.R.Gryncel,
E.R.Kantrowitz,
X.J.Feng,
G.Li,
and
H.Rabitz
(2008).
Dissecting enzyme regulation by multiple allosteric effectors: nucleotide regulation of aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
5881-5888.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.West,
J.Xia,
H.Tsuruta,
W.Guo,
E.M.O'Day,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2008).
Time evolution of the quaternary structure of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase upon reaction with the natural substrates and a slow, tight-binding inhibitor.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
384,
206-218.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.P.Cardia,
J.Eldo,
J.Xia,
E.M.O'Day,
H.Tsuruta,
K.R.Gryncel,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2008).
Use of L-asparagine and N-phosphonacetyl-L-asparagine to investigate the linkage of catalysis and homotropic cooperativity in E. coli aspartate transcarbomoylase.
|
| |
Proteins,
71,
1088-1096.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Vitali,
M.J.Colaneri,
and
E.Kantrowitz
(2008).
Crystal structure of the catalytic trimer of Methanococcus jannaschii aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Proteins,
71,
1324-1334.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Vitali,
and
M.J.Colaneri
(2008).
Structure of the catalytic trimer of Methanococcus jannaschii aspartate transcarbamoylase in an orthorhombic crystal form.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
64,
776-780.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.D.Daily,
T.J.Upadhyaya,
and
J.J.Gray
(2008).
Contact rearrangements form coupled networks from local motions in allosteric proteins.
|
| |
Proteins,
71,
455-466.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Stec,
M.K.Williams,
K.A.Stieglitz,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2007).
Comparison of two T-state structures of regulatory-chain mutants of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase suggests that His20 and Asp19 modulate the response to heterotropic effectors.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
63,
1243-1253.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Shi,
X.Yu,
J.Cabrera-Luque,
T.Y.Chen,
L.Roth,
H.Morizono,
N.M.Allewell,
and
M.Tuchman
(2007).
A single mutation in the active site swaps the substrate specificity of N-acetyl-L-ornithine transcarbamylase and N-succinyl-L-ornithine transcarbamylase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
16,
1689-1699.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Wang,
J.Eldo,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2007).
Structural model of the R state of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase with substrates bound.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
371,
1261-1273.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Fetler,
E.R.Kantrowitz,
and
P.Vachette
(2007).
Direct observation in solution of a preexisting structural equilibrium for a mutant of the allosteric aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
104,
495-500.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Eldo,
J.P.Cardia,
E.M.O'Day,
J.Xia,
H.Tsuruta,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2006).
N-phosphonacetyl-L-isoasparagine a potent and specific inhibitor of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
49,
5932-5938.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.De Vos,
P.Hulpiau,
B.Vergauwen,
S.N.Savvides,
and
J.Van Beeumen
(2005).
Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of a cold-adapted aspartate carbamoyltransferase from Moritella profunda.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
61,
279-281.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Wang,
K.A.Stieglitz,
J.P.Cardia,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2005).
Structural basis for ordered substrate binding and cooperativity in aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
102,
8881-8886.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.A.Stieglitz,
S.C.Pastra-Landis,
J.Xia,
H.Tsuruta,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2005).
A single amino acid substitution in the active site of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase prevents the allosteric transition.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
349,
413-423.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.West,
H.Tsuruta,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2004).
A fluorescent probe-labeled Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase that monitors the allosteric conformational state.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
945-951.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Alam,
K.A.Stieglitz,
M.D.Caban,
S.Gourinath,
H.Tsuruta,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2004).
240s loop interactions stabilize the T state of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
23302-23310.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Serre,
B.Penverne,
J.L.Souciet,
S.Potier,
H.Guy,
D.Evans,
P.Vicart,
and
G.Hervé
(2004).
Integrated allosteric regulation in the S. cerevisiae carbamylphosphate synthetase - aspartate transcarbamylase multifunctional protein.
|
| |
BMC Biochem,
5,
6.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.P.Macol,
H.Tsuruta,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2002).
Importance of domain closure for the catalysis and regulation of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
26852-26857.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Fetler,
P.Tauc,
D.P.Baker,
C.P.Macol,
E.R.Kantrowitz,
and
P.Vachette
(2002).
Replacement of Asp-162 by Ala prevents the cooperative transition by the substrates while enhancing the effect of the allosteric activator ATP on E. coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
11,
1074-1081.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.S.Chan,
J.B.Sakash,
C.P.Macol,
J.M.West,
H.Tsuruta,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2002).
The role of intersubunit interactions for the stabilization of the T state of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
49755-49760.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.T.Beernink,
Y.R.Yang,
R.Graf,
D.S.King,
S.S.Shah,
and
H.K.Schachman
(2001).
Random circular permutation leading to chain disruption within and near alpha helices in the catalytic chains of aspartate transcarbamoylase: effects on assembly, stability, and function.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
10,
528-537.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Ni,
and
H.K.Schachman
(2001).
In vivo assembly of aspartate transcarbamoylase from fragmented and circularly permuted catalytic polypeptide chains.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
10,
519-527.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Shi,
H.Morizono,
M.Aoyagi,
M.Tuchman,
and
N.M.Allewell
(2000).
Crystal structure of human ornithine transcarbamylase complexed with carbamoyl phosphate and L-norvaline at 1.9 A resolution.
|
| |
Proteins,
39,
271-277.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Endrizzi,
P.T.Beernink,
T.Alber,
and
H.K.Schachman
(2000).
Binding of bisubstrate analog promotes large structural changes in the unregulated catalytic trimer of aspartate transcarbamoylase: implications for allosteric regulation.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
97,
5077-5082.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Sakash,
R.S.Chan,
H.Tsuruta,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2000).
Three of the six possible intersubunit stabilizing interactions involving Glu-239 are sufficient for restoration of the homotropic and heterotropic properties of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
275,
752-758.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Qiu,
and
J.N.Davidson
(2000).
Substitutions in the aspartate transcarbamoylase domain of hamster CAD disrupt oligomeric structure.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
97,
97.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Thomas,
K.Hinsen,
M.J.Field,
and
D.Perahia
(1999).
Tertiary and quaternary conformational changes in aspartate transcarbamylase: a normal mode study.
|
| |
Proteins,
34,
96.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Jin,
B.Stec,
W.N.Lipscomb,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1999).
Insights into the mechanisms of catalysis and heterotropic regulation of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase based upon a structure of the enzyme complexed with the bisubstrate analogue N-phosphonacetyl-L-aspartate at 2.1 A.
|
| |
Proteins,
37,
729-742.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.T.Beernink,
J.A.Endrizzi,
T.Alber,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1999).
Assessment of the allosteric mechanism of aspartate transcarbamoylase based on the crystalline structure of the unregulated catalytic subunit.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
96,
5388-5393.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Durbecq,
T.L.Thia-Toong,
D.Charlier,
V.Villeret,
M.Roovers,
R.Wattiez,
C.Legrain,
and
N.Glansdorff
(1999).
Aspartate carbamoyltransferase from the thermoacidophilic archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Cloning, sequence analysis, enzyme purification and characterization.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
264,
233-241.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.K.Williams,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1998).
Threonine 82 in the regulatory chain is important for nucleotide affinity and for the allosteric stabilization of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1429,
249-258.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.J.LiCata,
D.S.Burz,
N.J.Moerke,
and
N.M.Allewell
(1998).
The magnitude of the allosteric conformational transition of aspartate transcarbamylase is altered by mutations.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
17381-17385.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Purcarea,
G.Hervé,
M.M.Ladjimi,
and
R.Cunin
(1997).
Aspartate transcarbamylase from the deep-sea hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus abyssi: genetic organization, structure, and expression in Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
179,
4143-4157.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Trewhella
(1997).
Insights into biomolecular function from small-angle scattering.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
7,
702-708.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Liu,
M.E.Wales,
and
J.R.Wild
(1997).
Conversion of the allosteric regulatory patterns of aspartate transcarbamoylase by exchange of a single beta-strand between diverged regulatory chains.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
3126-3132.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Sanchez,
M.Baetens,
M.Van de Casteele,
M.Roovers,
C.Legrain,
and
N.Glansdorff
(1997).
Ornithine carbamoyltransferase from the extreme thermophile Thermus thermophilus--analysis of the gene and characterisation of the protein.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
248,
466-474.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.J.LiCata,
and
N.M.Allewell
(1997).
Functionally linked hydration changes in Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamylase and its catalytic subunit.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
10161-10167.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Ha,
M.T.McCann,
M.Tuchman,
and
N.M.Allewell
(1997).
Substrate-induced conformational change in a trimeric ornithine transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
94,
9550-9555.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.F.Kolodziej,
T.Tan,
and
D.E.Koshland
(1996).
Producing positive, negative, and no cooperativity by mutations at a single residue located at the subunit interface in the aspartate receptor of Salmonella typhimurium.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
14782-14792.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.P.Baker,
L.Fetler,
P.Vachette,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1996).
The allosteric activator ATP induces a substrate-dependent alteration of the quaternary structure of a mutant aspartate transcarbamoylase impaired in active site closure.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
5,
2276-2286.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.B.Murata,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1996).
Structural similarity between ornithine and aspartate transcarbamoylases of Escherichia coli: characterization of the active site and evidence for an interdomain carboxy-terminal helix in ornithine transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
5,
709-718.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.B.Murata,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1996).
Structural similarity between ornithine and aspartate transcarbamoylases of Escherichia coli: implications for domain switching.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
5,
719-728.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Rynkiewicz,
and
B.A.Seaton
(1996).
Chemical rescue by guanidine derivatives of an arginine-substituted site-directed mutant of Escherichia coli ornithine transcarbamylase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
16174-16179.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Zhang,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1996).
In vivo formation of allosteric aspartate transcarbamoylase containing circularly permuted catalytic polypeptide chains: implications for protein folding and assembly.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
5,
1290-1300.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.H.Lee,
B.W.Ley,
E.R.Kantrowitz,
M.H.O'Leary,
and
F.C.Wedler
(1995).
Domain closure in the catalytic chains of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase influences the kinetic mechanism.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
15620-15627.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.P.Baker,
L.Fetler,
R.T.Keiser,
P.Vachette,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1995).
Weakening of the interface between adjacent catalytic chains promotes domain closure in Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
4,
258-267.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.C.Wedler,
B.W.Ley,
B.H.Lee,
M.H.O'Leary,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1995).
L-aspartate association contributes to rate limitation and induction of the T-->R transition in Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase. Equilibrium exchanges and kinetic isotope effects with a Vmax-enhanced mutant, Asp-236-->Ala.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
9725-9733.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Villeret,
C.Tricot,
V.Stalon,
and
O.Dideberg
(1995).
Crystal structure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa catabolic ornithine transcarbamoylase at 3.0-A resolution: a different oligomeric organization in the transcarbamoylase family.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
92,
10762-10766.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.O.Villoutreix,
V.Z.Spassov,
B.P.Atanasov,
G.Hervé,
and
M.M.Ladjimi
(1994).
Structural modeling and electrostatic properties of aspartate transcarbamylase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
|
| |
Proteins,
19,
230-243.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.B.Peterson,
B.B.Zhou,
D.Hsieh,
A.N.Creager,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1994).
Association of the catalytic subunit of aspartate transcarbamoylase with a zinc-containing polypeptide fragment of the regulatory chain leads to increases in thermal stability.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
3,
960-966.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.V.Grishin,
and
M.A.Phillips
(1994).
The subunit interfaces of oligomeric enzymes are conserved to a similar extent to the overall protein sequences.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
3,
2455-2458.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.England,
C.Leconte,
P.Tauc,
and
G.Hervé
(1994).
Apparent cooperativity for carbamoylphosphate in Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase only reflects cooperativity for aspartate.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
222,
775-780.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Tauc,
R.T.Keiser,
E.R.Kantrowitz,
and
P.Vachette
(1994).
Glu-50 in the catalytic chain of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase plays a crucial role in the stability of the R quaternary structure.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
3,
1998-2004.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.N.Perham
(1994).
Structural aspects of biomolecular recognition and self-assembly.
|
| |
Biosens Bioelectron,
9,
753-760.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.B.Zhou,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1993).
Peptide-protein interaction markedly alters the functional properties of the catalytic subunit of aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
2,
103-112.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Orengo,
and
J.M.Thornton
(1993).
Alpha plus beta folds revisited: some favoured motifs.
|
| |
Structure,
1,
105-120.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.J.Tanner,
P.E.Smith,
and
K.L.Krause
(1993).
Molecular dynamics simulations and rigid body (TLS) analysis of aspartate carbamoyltransferase: evidence for an uncoupled R state.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
2,
927-935.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.P.Kosman,
J.E.Gouaux,
and
W.N.Lipscomb
(1993).
Crystal structure of CTP-ligated T state aspartate transcarbamoylase at 2.5 A resolution: implications for ATCase mutants and the mechanism of negative cooperativity.
|
| |
Proteins,
15,
147-176.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.M.Powers,
Y.R.Yang,
M.J.Fogli,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1993).
Reconstitution of active catalytic trimer of aspartate transcarbamoylase from proteolytically cleaved polypeptide chains.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
2,
1001-1012.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.R.Yang,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1993).
Aspartate transcarbamoylase containing circularly permuted catalytic polypeptide chains.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
90,
11980-11984.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.R.Yang,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1993).
In vivo formation of active aspartate transcarbamoylase from complementing fragments of the catalytic polypeptide chains.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
2,
1013-1023.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.A.Lynch,
and
D.E.Koshland
(1992).
The fifth Datta Lecture. Structural similarities between the aspartate receptor of bacterial chemotaxis and the trp repressor of E. coli. Implications for transmembrane signaling.
|
| |
FEBS Lett,
307,
3-9.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Stebbins,
D.E.Robertson,
M.F.Roberts,
R.C.Stevens,
W.N.Lipscomb,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1992).
Arginine 54 in the active site of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase is critical for catalysis: a site-specific mutagenesis, NMR, and X-ray crystallographic study.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
1,
1435-1446.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.E.Cohen,
M.Takama,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1992).
1H NMR studies on the catalytic subunit of aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
89,
11881-11885.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.B.Peterson,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1991).
Role of a carboxyl-terminal helix in the assembly, interchain interactions, and stability of aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
88,
458-462.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.W.Markby,
B.B.Zhou,
and
H.K.Schachman
(1991).
A 70-amino acid zinc-binding polypeptide from the regulatory chain of aspartate transcarbamoylase forms a stable complex with the catalytic subunit leading to markedly altered enzyme activity.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
88,
10568-10572.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Van Vliet,
X.G.Xi,
C.De Staercke,
B.de Wannemaeker,
A.Jacobs,
J.Cherfils,
M.M.Ladjimi,
G.Hervé,
and
R.Cunin
(1991).
Heterotropic interactions in aspartate transcarbamoylase: turning allosteric ATP activation into inhibition as a consequence of a single tyrosine to phenylalanine mutation.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
88,
9180-9183.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Newton,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1990).
The regulatory subunit of Escherichia coli aspartate carbamoyltransferase may influence homotropic cooperativity and heterotropic interactions by a direct interaction with the loop containing residues 230-245 of the catalytic chain.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
87,
2309-2313.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.R.Kantrowitz,
and
W.N.Lipscomb
(1990).
Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase: the molecular basis for a concerted allosteric transition.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
15,
53-59.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.N.Davidson,
G.N.Rao,
L.Niswander,
C.Andreano,
C.Tamer,
and
K.C.Chen
(1990).
Organization and nucleotide sequence of the 3' end of the human CAD gene.
|
| |
DNA Cell Biol,
9,
667-676.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.I.Christopherson,
and
S.D.Lyons
(1990).
Potent inhibitors of de novo pyrimidine and purine biosynthesis as chemotherapeutic agents.
|
| |
Med Res Rev,
10,
505-548.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Gouaux,
R.C.Stevens,
H.M.Ke,
and
W.N.Lipscomb
(1989).
Crystal structure of the Glu-239----Gln mutant of aspartate carbamoyltransferase at 3.1-A resolution: an intermediate quaternary structure.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
86,
8212-8216.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.P.Simmer,
R.E.Kelly,
J.L.Scully,
D.R.Grayson,
A.G.Rinker,
S.T.Bergh,
and
D.R.Evans
(1989).
Mammalian aspartate transcarbamylase (ATCase): sequence of the ATCase domain and interdomain linker in the CAD multifunctional polypeptide and properties of the isolated domain.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
86,
4382-4386.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.F.Perutz
(1989).
Mechanisms of cooperativity and allosteric regulation in proteins.
|
| |
Q Rev Biophys,
22,
139-237.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

