 |
PDBsum entry 1frp

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Hydrolase(phosphoric monoester)
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1frp
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase(phosphoric monoester)
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase complexed with fructose-2,6-bisphosphate, amp and zn2+ at 2.0 angstroms resolution. Aspects of synergism between inhibitors
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase. Chain: a, b. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Sus scrofa. Pig. Organism_taxid: 9823
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Tetramer (from
)
Tetramer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
Y.Xue,S.Huang,J.-Y.Liang,Y.Zhang,W.N.Lipscomb
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
Y.Xue
et al.
(1994).
Crystal structure of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase complexed with fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, AMP, and Zn2+ at 2.0-A resolution: aspects of synergism between inhibitors.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
91,
12482-12486.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
26-Aug-94
|
Release date:
|
30-Nov-94
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00636
(F16P1_PIG) -
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 from Sus scrofa
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
338 a.a.
321 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 4 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.3.11
- fructose-bisphosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pentose Phosphate Pathway (later stages)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + H2O = beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
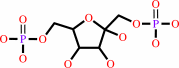 beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 80.00% similarity
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
91:12482-12486
(1994)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase complexed with fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, AMP, and Zn2+ at 2.0-A resolution: aspects of synergism between inhibitors.
|
|
Y.Xue,
S.Huang,
J.Y.Liang,
Y.Zhang,
W.N.Lipscomb.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The crystal structure of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (Fru-1,6-Pase; EC 3.1.3.11)
complexed with Zn2+ and two allosteric regulators, AMP and fructose
2,6-bisphosphate (Fru-2,6-P2) has been determined at 2.0-A resolution. In the
refined model, the crystallographic R factor is 0.189 with rms deviations of
0.014 A and 2.8 degrees from ideal geometries for bond lengths and bond angles,
respectively. A 15 degrees rotation is observed between the upper dimer C1C2 and
the lower dimer C3C4 relative to the R-form structure (fructose 6-phosphate
complex), consistent with that expected from a T-form structure. The major
difference between the structure of the previously determined Fru-2,6-P2 complex
(R form) and that of the current quaternary T-form complex lies in the active
site domain. A zinc binding site distinct from the three binding sites
established earlier was identified within each monomer. Helix H4 (residues
123-127) was found to be better defined than in previously studied ligated
Fru-1,6-Pase structures. Interactions between monomers in the active site domain
were found involving H4 residues from one monomer and residues Tyr-258 and
Arg-243 from the adjacent monomer. Cooperativity between AMP and Fru-2,6-P2 in
signal transmission probably involves the following features: an AMP site, the
adjacent B3 strand (residues 113-118), the metal site, the immediate active
site, the short helix H4 (residues 123-127), and Tyr-258 and Arg-243 from the
adjacent monomer within the upper (or lower) dimer. The closest distance between
the immediate active site and that on the adjacent monomer is only 5 A. Thus,
the involvement of H4 in signal transmission adds another important pathway to
the scheme of the allosteric mechanism of Fru-1,6-Pase.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.Bera,
and
A.Patra
(2011).
Study of potential binding of biologically important sugars with a dinuclear cobalt(II) complex.
|
| |
Carbohydr Res,
346,
733-738.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Brown,
A.Singer,
V.V.Lunin,
M.Proudfoot,
T.Skarina,
R.Flick,
S.Kochinyan,
R.Sanishvili,
A.Joachimiak,
A.M.Edwards,
A.Savchenko,
and
A.F.Yakunin
(2009).
Structural and biochemical characterization of the type II fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase GlpX from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
3784-3792.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.C.Ludwig,
F.N.Pardo,
J.L.Asenjo,
M.A.Maureira,
A.J.Yañez,
and
J.C.Slebe
(2007).
Unraveling multistate unfolding of pig kidney fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase using single tryptophan mutants.
|
| |
FEBS J,
274,
5337-5349.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Stierand,
P.C.Maass,
and
M.Rarey
(2006).
Molecular complexes at a glance: automated generation of two-dimensional complex diagrams.
|
| |
Bioinformatics,
22,
1710-1716.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Das,
and
M.Gerstein
(2004).
A method using active-site sequence conservation to find functional shifts in protein families: application to the enzymes of central metabolism, leading to the identification of an anomalous isocitrate dehydrogenase in pathogens.
|
| |
Proteins,
55,
455-463.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Wen,
S.W.Nelson,
R.B.Honzatko,
H.J.Fromm,
and
J.W.Petrich
(2001).
Environment of tryptophan 57 in porcine fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase studied by time-resolved fluorescence and site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
Photochem Photobiol,
74,
679-685.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Tanase,
T.Takei,
M.Hidai,
and
S.Yano
(2001).
Substrate-dependent chemoselective aldose-aldose and aldose-ketose isomerizations of carbohydrates promoted by a combination of calcium ion and monoamines.
|
| |
Carbohydr Res,
333,
303-312.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Zhao,
S.Xu,
L.Du,
and
G.Xu
(2000).
AMP makes native snake muscle fructose-1, 6-bisphosphatase to an alkaline enzyme.
|
| |
Sci China C Life Sci,
43,
1-7.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Y.Choe,
H.J.Fromm,
and
R.B.Honzatko
(2000).
Crystal structures of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase: mechanism of catalysis and allosteric inhibition revealed in product complexes.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
8565-8574.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.M.Weeks,
A.W.Roszak,
M.Erman,
R.Kaiser,
H.Jörnvall,
and
D.Ghosh
(1999).
Structure of rabbit liver fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase at 2.3 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
55,
93.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Y.Choe,
B.W.Poland,
H.J.Fromm,
and
R.B.Honzatko
(1998).
Role of a dynamic loop in cation activation and allosteric regulation of recombinant porcine fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
11441-11450.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Hodgson,
Z.Jia,
and
W.C.Plaxton
(1998).
A fluorescence study of ligand-induced conformational changes in cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase from germinating castor oil seeds.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1388,
285-294.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Stec,
R.Abraham,
E.Giroux,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1996).
Crystal structures of the active site mutant (Arg-243-->Ala) in the T and R allosteric states of pig kidney fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase expressed in Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
5,
1541-1553.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.E.Sáez,
C.D.Figueroa,
I.I.Concha,
and
J.C.Slebe
(1996).
Localization of the fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase at the nuclear periphery.
|
| |
J Cell Biochem,
63,
453-462.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Lu,
B.Stec,
E.L.Giroux,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1996).
Evidence for an active T-state pig kidney fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase: interface residue Lys-42 is important for allosteric inhibition and AMP cooperativity.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
5,
2333-2342.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Villeret,
S.Huang,
H.J.Fromm,
and
W.N.Lipscomb
(1995).
Crystallographic evidence for the action of potassium, thallium, and lithium ions on fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
92,
8916-8920.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

