 |
PDBsum entry 1fpi

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Hydrolase (phosphoric monoester)
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1fpi
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase (phosphoric monoester)
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (d-fructose-1,6-bisphosphate 1- phosphohydrolase) complexed with amp, 2,5-anhydro-d-glucitol-1,6- bisphosphate and potassium ions (100 mm)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: d-fructose-1,6-bisphosphate 1-phosphohydrolase. Ec: 3.1.3.11
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Sus scrofa. Pig. Organism_taxid: 9823. Organ: kidney
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Tetramer (from
)
Tetramer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
V.Villeret,W.N.Lipscomb
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
V.Villeret
et al.
(1995).
Crystallographic evidence for the action of potassium, thallium, and lithium ions on fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
92,
8916-8920.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
02-Jun-95
|
Release date:
|
20-Jun-96
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00636
(F16P1_PIG) -
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 from Sus scrofa
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
338 a.a.
317 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 3 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.3.11
- fructose-bisphosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pentose Phosphate Pathway (later stages)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + H2O = beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 95.00% similarity
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
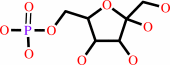 beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
92:8916-8920
(1995)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystallographic evidence for the action of potassium, thallium, and lithium ions on fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase.
|
|
V.Villeret,
S.Huang,
H.J.Fromm,
W.N.Lipscomb.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (Fru-1,6-Pase; D-fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
1-phosphohydrolase, EC 3.1.3.11) requires two divalent metal ions to hydrolyze
alpha-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. Although not required for catalysis,
monovalent cations modify the enzyme activity; K+ and Tl+ ions are activators,
whereas Li+ ions are inhibitors. Their mechanisms of action are still unknown.
We report here crystallographic structures of pig kidney Fru-1,6-Pase complexed
with K+, Tl+, or both Tl+ and Li+. In the T form Fru-1,6-Pase complexed with the
substrate analogue 2,5-anhydro-D-glucitol 1,6-bisphosphate (AhG-1,6-P2) and Tl+
or K+ ions, three Tl+ or K+ binding sites are found. Site 1 is defined by
Glu-97, Asp-118, Asp-121, Glu-280, and a 1-phosphate oxygen of AhG-1,6-P2; site
2 is defined by Glu-97, Glu-98, Asp-118, and Leu-120. Finally, site 3 is defined
by Arg-276, Glu-280, and the 1-phosphate group of AhG-1,6-P2. The Tl+ or K+ ions
at sites 1 and 2 are very close to the positions previously identified for the
divalent metal ions. Site 3 is specific to K+ or Tl+. In the divalent metal ion
complexes, site 3 is occupied by the guanidinium group of Arg-276. These
observations suggest that Tl+ or K+ ions can substitute for Arg-276 in the
active site and polarize the 1-phosphate group, thus facilitating nucleophilic
attack on the phosphorus center. In the T form complexed with both Tl+ and Li+
ions, Li+ replaces Tl+ at metal site 1. Inhibition by lithium very likely occurs
as it binds to this site, thus retarding turnover or phosphate release. The
present study provides a structural basis for a similar mechanism of inhibition
for inositol monophosphatase, one of the potential targets of lithium ions in
the treatment of manic depression.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
P.D.Kiser,
G.H.Lorimer,
and
K.Palczewski
(2009).
Use of thallium to identify monovalent cation binding sites in GroEL.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
65,
967-971.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Ganguly,
F.Wang,
M.Kaushik,
M.P.Stone,
L.A.Marky,
and
B.Gold
(2007).
A study of 7-deaza-2'-deoxyguanosine 2'-deoxycytidine base pairing in DNA.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
35,
6181-6195.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.An,
Q.J.Chen,
M.F.Chai,
P.L.Lu,
Z.Su,
Z.X.Qin,
J.Chen,
and
X.C.Wang
(2007).
AtNHX8, a member of the monovalent cation: proton antiporter-1 family in Arabidopsis thaliana, encodes a putative Li/H antiporter.
|
| |
Plant J,
49,
718-728.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Gold,
L.M.Marky,
M.P.Stone,
and
L.D.Williams
(2006).
A review of the role of the sequence-dependent electrostatic landscape in DNA alkylation patterns.
|
| |
Chem Res Toxicol,
19,
1402-1414.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Gill,
F.Mohammed,
R.Badyal,
L.Coates,
P.Erskine,
D.Thompson,
J.Cooper,
M.Gore,
and
S.Wood
(2005).
High-resolution structure of myo-inositol monophosphatase, the putative target of lithium therapy.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
545-555.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Ramírez-Silva,
and
J.Oria-Hernández
(2003).
Selectivity of pyruvate kinase for Na+ and K+ in water/dimethylsulfoxide mixtures.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
270,
2377-2385.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.B.Howerton,
A.Nagpal,
and
L.D.Williams
(2003).
Surprising roles of electrostatic interactions in DNA-ligand complexes.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
69,
87-99.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Prasad,
K.J.Wright,
D.Banerjee Roy,
L.A.Bush,
A.M.Cantwell,
and
E.Di Cera
(2003).
Redesigning the monovalent cation specificity of an enzyme.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
100,
13785-13790.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Phiel,
and
P.S.Klein
(2001).
Molecular targets of lithium action.
|
| |
Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol,
41,
789-813.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Y.Choe,
H.J.Fromm,
and
R.B.Honzatko
(2000).
Crystal structures of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase: mechanism of catalysis and allosteric inhibition revealed in product complexes.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
8565-8574.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.L.De Wall,
E.S.Meadows,
L.J.Barbour,
and
G.W.Gokel
(2000).
Synthetic receptors as models for alkali metal cation-pi binding sites in proteins.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
97,
6271-6276.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.M.Weeks,
A.W.Roszak,
M.Erman,
R.Kaiser,
H.Jörnvall,
and
D.Ghosh
(1999).
Structure of rabbit liver fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase at 2.3 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
55,
93.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Y.Choe,
B.W.Poland,
H.J.Fromm,
and
R.B.Honzatko
(1998).
Role of a dynamic loop in cation activation and allosteric regulation of recombinant porcine fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
11441-11450.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Basu,
R.P.Rambo,
J.Strauss-Soukup,
J.H.Cate,
A.R.Ferré-D'Amaré,
S.A.Strobel,
and
J.A.Doudna
(1998).
A specific monovalent metal ion integral to the AA platform of the RNA tetraloop receptor.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
5,
986-992.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.M.Wilbanks,
and
D.B.McKay
(1998).
Structural replacement of active site monovalent cations by the epsilon-amino group of lysine in the ATPase fragment of bovine Hsc70.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
7456-7462.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.R.Bishop,
and
V.L.Davidson
(1997).
Catalytic role of monovalent cations in the mechanism of proton transfer which gates an interprotein electron transfer reaction.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
13586-13592.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Ramírez-Silva,
J.Oria,
A.Gómez-Puyou,
and
M.Tuena de Gómez-Puyou
(1997).
The contribution of water to the selectivity of pyruvate kinase for Na+ and K+.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
250,
583-589.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.R.Guinto,
and
E.Di Cera
(1996).
Large heat capacity change in a protein-monovalent cation interaction.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
8800-8804.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Zhang,
V.Villeret,
W.N.Lipscomb,
and
H.J.Fromm
(1996).
Kinetics and mechanisms of activation and inhibition of porcine liver fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase by monovalent cations.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
3038-3043.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

