
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.3.1.87
- aralkylamine N-acetyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 2-arylethylamine + acetyl-CoA = an N-acetyl-2-arylethylamine + CoA + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
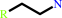 2-arylethylamine
2-arylethylamine
|
+
|
 acetyl-CoA
acetyl-CoA
|
=
|
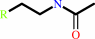 N-acetyl-2-arylethylamine
N-acetyl-2-arylethylamine
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Mol Cell
3:23-32
(1999)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Melatonin biosynthesis: the structure of serotonin N-acetyltransferase at 2.5 A resolution suggests a catalytic mechanism.
|
|
A.B.Hickman,
D.C.Klein,
F.Dyda.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Conversion of serotonin to N-acetylserotonin, the precursor of the circadian
neurohormone melatonin, is catalyzed by serotonin N-acetyltransferase (AANAT) in
a reaction requiring acetyl coenzyme A (AcCoA). AANAT is a globular protein
consisting of an eight-stranded beta sheet flanked by five alpha helices; a
conserved motif in the center of the beta sheet forms the cofactor binding site.
Three polypeptide loops converge above the AcCoA binding site, creating a
hydrophobic funnel leading toward the cofactor and serotonin binding sites in
the protein interior. Two conserved histidines not found in other NATs are
located at the bottom of the funnel in the active site, suggesting a catalytic
mechanism for acetylation involving imidazole groups acting as general acid/base
catalysts.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 5.
Figure 5. The Serotonin Binding Site Is Buried in the Protein
Interior(A) Hydrophobic residues lining the funnel. For clarity,
only the acetyl and β-mercaptoethyl groups of AcCoA are shown
modeled in the active site.(B) View into the hydrophobic funnel
looking down toward ND1 of His-122 (in blue); the surrounding
hydrophobic residues are shown in white. Figure was created by
PovChem (P. Thiessen, Chem. Dept., School of Chemical Sciences,
U. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign), a front end for POV-Ray
3.0.
|
 |
Figure 6.
Figure 6. Proposed Catalytic MechanismThe proposed mechanism
involving His-122 as a general base catalyst in substrate
deprotonation, and the subsequent formation of a tetravalent
intermediate. The conserved residue Tyr-168 is positioned 3.5
Å away from the modeled position of the sulfur atom of
AcCoA and could serve as a general acid catalyst to protonate
the incipient thiolate anion of CoA. AAA stands for an
arylalkylamine substrate.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Mol Cell
(1999,
3,
23-32)
copyright 1999.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
 Google scholar
Google scholar
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.E.Almonacid,
E.R.Yera,
J.B.Mitchell,
and
P.C.Babbitt
(2010).
Quantitative comparison of catalytic mechanisms and overall reactions in convergently evolved enzymes: implications for classification of enzyme function.
|
| |
PLoS Comput Biol,
6,
e1000700.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Pavlicek,
S.L.Coon,
S.Ganguly,
J.L.Weller,
S.A.Hassan,
D.L.Sackett,
and
D.C.Klein
(2008).
Evidence that proline focuses movement of the floppy loop of arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.87).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
14552-14558.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.C.Klein
(2007).
Arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase: "the Timezyme".
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
4233-4237.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Gu,
T.W.Geders,
B.Wang,
W.H.Gerwick,
K.Håkansson,
J.L.Smith,
and
D.H.Sherman
(2007).
GNAT-like strategy for polyketide chain initiation.
|
| |
Science,
318,
970-974.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Szewczuk,
S.A.Saldanha,
S.Ganguly,
E.M.Bowers,
M.Javoroncov,
B.Karanam,
J.C.Culhane,
M.A.Holbert,
D.C.Klein,
R.Abagyan,
and
P.A.Cole
(2007).
De novo discovery of serotonin N-acetyltransferase inhibitors.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
50,
5330-5338.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.S.Hegde,
J.Chandler,
M.W.Vetting,
M.Yu,
and
J.S.Blanchard
(2007).
Mechanistic and structural analysis of human spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
7187-7195.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.K.Gardino,
S.J.Smerdon,
and
M.B.Yaffe
(2006).
Structural determinants of 14-3-3 binding specificities and regulation of subcellular localization of 14-3-3-ligand complexes: a comparison of the X-ray crystal structures of all human 14-3-3 isoforms.
|
| |
Semin Cancer Biol,
16,
173-182.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.R.Hussein,
E.E.Abu-Dief,
A.T.Abou El-Ghait,
M.A.Adly,
and
M.H.Abdelraheem
(2006).
Morphological evaluation of the radioprotective effects of melatonin against X-ray-induced early and acute testis damage in Albino rats: an animal model.
|
| |
Int J Exp Pathol,
87,
237-250.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.L.Burk,
B.Xiong,
C.Breitbach,
and
A.M.Berghuis
(2005).
Structures of aminoglycoside acetyltransferase AAC(6')-Ii in a novel crystal form: structural and normal-mode analyses.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
1273-1279.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.L.Card,
N.A.Peterson,
C.A.Smith,
B.Rupp,
B.M.Schick,
and
E.N.Baker
(2005).
The crystal structure of Rv1347c, a putative antibiotic resistance protein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, reveals a GCN5-related fold and suggests an alternative function in siderophore biosynthesis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
13978-13986.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Boutin,
V.Audinot,
G.Ferry,
and
P.Delagrange
(2005).
Molecular tools to study melatonin pathways and actions.
|
| |
Trends Pharmacol Sci,
26,
412-419.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.R.Hussein,
E.E.Abu-Dief,
M.H.Abd El-Reheem,
and
A.Abd-Elrahman
(2005).
Ultrastructural evaluation of the radioprotective effects of melatonin against X-ray-induced skin damage in Albino rats.
|
| |
Int J Exp Pathol,
86,
45-55.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.D.Boehr,
S.I.Jenkins,
and
G.D.Wright
(2003).
The molecular basis of the expansive substrate specificity of the antibiotic resistance enzyme aminoglycoside acetyltransferase-6'-aminoglycoside phosphotransferase-2". The role of ASP-99 as an active site base important for acetyl transfer.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
12873-12880.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.L.Burk,
N.Ghuman,
L.E.Wybenga-Groot,
and
A.M.Berghuis
(2003).
X-ray structure of the AAC(6')-Ii antibiotic resistance enzyme at 1.8 A resolution; examination of oligomeric arrangements in GNAT superfamily members.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
12,
426-437.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Zheng,
Z.Zhang,
S.Ganguly,
J.L.Weller,
D.C.Klein,
and
P.A.Cole
(2003).
Cellular stabilization of the melatonin rhythm enzyme induced by nonhydrolyzable phosphonate incorporation.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
10,
1054-1057.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.W.Vetting,
S.S.Hegde,
F.Javid-Majd,
J.S.Blanchard,
and
S.L.Roderick
(2002).
Aminoglycoside 2'-N-acetyltransferase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis in complex with coenzyme A and aminoglycoside substrates.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
9,
653-658.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Tsuboi,
Y.Kotani,
K.Ogawa,
T.Hatanaka,
S.Yatsushiro,
M.Otsuka,
and
Y.Moriyama
(2002).
An intramolecular disulfide bridge as a catalytic switch for serotonin N-acetyltransferase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
44229-44235.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.T.Watson,
T.D.Minogue,
D.L.Val,
S.B.von Bodman,
and
M.E.Churchill
(2002).
Structural basis and specificity of acyl-homoserine lactone signal production in bacterial quorum sensing.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
9,
685-694.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Spessert,
M.Rapp,
and
L.Vollrath
(2001).
Serine/threonine phosphatase inhibitors decrease adrenergic arylalkylamine n-acetyltransferase induction in the rat pineal gland.
|
| |
J Neuroendocrinol,
13,
581-587.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Ganguly,
P.Mummaneni,
P.J.Steinbach,
D.C.Klein,
and
S.L.Coon
(2001).
Characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae homolog of the melatonin rhythm enzyme arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.87).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
276,
47239-47247.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Y.Roth,
J.M.Denu,
and
C.D.Allis
(2001).
Histone acetyltransferases.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
70,
81.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.A.Farazi,
G.Waksman,
and
J.I.Gordon
(2001).
Structures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae N-myristoyltransferase with bound myristoylCoA and peptide provide insights about substrate recognition and catalysis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
6335-6343.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Obsil,
R.Ghirlando,
D.C.Klein,
S.Ganguly,
and
F.Dyda
(2001).
Crystal structure of the 14-3-3zeta:serotonin N-acetyltransferase complex. a role for scaffolding in enzyme regulation.
|
| |
Cell,
105,
257-267.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Dyda,
D.C.Klein,
and
A.B.Hickman
(2000).
GCN5-related N-acetyltransferases: a structural overview.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct,
29,
81.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Ferry,
A.Loynel,
N.Kucharczyk,
S.Bertin,
M.Rodriguez,
P.Delagrange,
J.P.Galizzi,
E.Jacoby,
J.P.Volland,
D.Lesieur,
P.Renard,
E.Canet,
J.L.Fauchère,
and
J.A.Boutin
(2000).
Substrate specificity and inhibition studies of human serotonin N-acetyltransferase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
275,
8794-8805.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.A.Farazi,
J.K.Manchester,
and
J.I.Gordon
(2000).
Transient-state kinetic analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae myristoylCoA:protein N-myristoyltransferase reveals that a step after chemical transformation is rate limiting.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
15807-15816.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Yan,
N.A.Barlev,
R.H.Haley,
S.L.Berger,
and
R.Marmorstein
(2000).
Crystal structure of yeast Esa1 suggests a unified mechanism for catalysis and substrate binding by histone acetyltransferases.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
6,
1195-1205.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.B.Hickman,
M.A.Namboodiri,
D.C.Klein,
and
F.Dyda
(1999).
The structural basis of ordered substrate binding by serotonin N-acetyltransferase: enzyme complex at 1.8 A resolution with a bisubstrate analog.
|
| |
Cell,
97,
361-369.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.M.Khalil,
J.De Angelis,
M.Ishii,
and
P.A.Cole
(1999).
Mechanism-based inhibition of the melatonin rhythm enzyme: pharmacologic exploitation of active site functional plasticity.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
96,
12418-12423.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.G.Tanner,
R.C.Trievel,
M.H.Kuo,
R.M.Howard,
S.L.Berger,
C.D.Allis,
R.Marmorstein,
and
J.M.Denu
(1999).
Catalytic mechanism and function of invariant glutamic acid 173 from the histone acetyltransferase GCN5 transcriptional coactivator.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
18157-18160.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.C.Trievel,
J.R.Rojas,
D.E.Sterner,
R.N.Venkataramani,
L.Wang,
J.Zhou,
C.D.Allis,
S.L.Berger,
and
R.Marmorstein
(1999).
Crystal structure and mechanism of histone acetylation of the yeast GCN5 transcriptional coactivator.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
96,
8931-8936.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Sternglanz,
and
H.Schindelin
(1999).
Structure and mechanism of action of the histone acetyltransferase Gcn5 and similarity to other N-acetyltransferases.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
96,
8807-8808.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.L.Coon,
V.Bégay,
D.Deurloo,
J.Falcón,
and
D.C.Klein
(1999).
Two arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase genes mediate melatonin synthesis in fish.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
9076-9082.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

