 |
PDBsum entry 1u7t

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1u7t
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of abad/hsd10 with a bound inhibitor
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
3-hydroxyacyl-coa dehydrogenase type ii. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: type ii hadh, endoplasmic reticulum-associated amyloid beta- peptide binding protein, short-chain type dehydrogenase/reductase xh98g2, amyloid beta-peptide-binding alcohol dehydrogenase, abad. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: hadh2, erab, xh98g2, schad. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Tetramer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.215
|
R-free:
|
0.263
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
C.R.Kissinger,P.A.Rejto,L.A.Pelletier,R.E.Showalter,J.E.Villafranca
|
Key ref:

|
 |
C.R.Kissinger
et al.
(2004).
Crystal structure of human ABAD/HSD10 with a bound inhibitor: implications for design of Alzheimer's disease therapeutics.
J Mol Biol,
342,
943-952.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
04-Aug-04
|
Release date:
|
05-Oct-04
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q99714
(HCD2_HUMAN) -
3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase type-2 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
261 a.a.
255 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.159
- 7alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
cholate + NAD+ = 3alpha,12alpha-dihydroxy-7-oxo-5beta-cholanate + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 cholate
cholate
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 62.86% similarity
|
=
|
 3alpha,12alpha-dihydroxy-7-oxo-5beta-cholanate
3alpha,12alpha-dihydroxy-7-oxo-5beta-cholanate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.178
- 3-hydroxy-2-methylbutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(2S,3S)-3-hydroxy-2-methylbutanoyl-CoA + NAD+ = 2-methyl-3-oxobutanoyl- CoA + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(2S,3S)-3-hydroxy-2-methylbutanoyl-CoA
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 50.00% similarity
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 62.86% similarity
|
=
|
2-methyl-3-oxobutanoyl- CoA
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.239
- 3alpha-(17beta)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (NAD(+)).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
testosterone + NAD+ = androst-4-ene-3,17-dione + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
testosterone
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 62.86% similarity
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
 androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 5:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.35
- 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a (3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA + NAD+ = a 3-oxoacyl-CoA + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 50.77% similarity
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 62.86% similarity
|
=
|
 3-oxoacyl-CoA
3-oxoacyl-CoA
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 6:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.53
- 3alpha(or 20beta)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
androstan-3alpha,17beta-diol + NAD+ = 17beta-hydroxyandrostanone + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
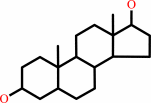 androstan-3alpha,17beta-diol
androstan-3alpha,17beta-diol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 62.86% similarity
|
=
|
17beta-hydroxyandrostanone
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 7:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.62
- 17beta-estradiol 17-dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
17beta-estradiol + NAD+ = estrone + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
17beta-estradiol + NADP+ = estrone + NADPH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
17beta-estradiol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 62.86% similarity
|
=
|
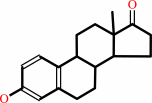 estrone
estrone
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
17beta-estradiol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 59.46% similarity
|
=
|
 estrone
estrone
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
342:943-952
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of human ABAD/HSD10 with a bound inhibitor: implications for design of Alzheimer's disease therapeutics.
|
|
C.R.Kissinger,
P.A.Rejto,
L.A.Pelletier,
J.A.Thomson,
R.E.Showalter,
M.A.Abreo,
C.S.Agree,
S.Margosiak,
J.J.Meng,
R.M.Aust,
D.Vanderpool,
B.Li,
A.Tempczyk-Russell,
J.E.Villafranca.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The enzyme 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 10 (HSD10), also known as
amyloid beta-peptide-binding alcohol dehydrogenase (ABAD), has been implicated
in the development of Alzheimer's disease. This protein, a member of the
short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase family of enzymes, has been shown to bind
beta-amyloid and to participate in beta-amyloid neurotoxicity. We have
determined the crystal structure of human ABAD/HSD10 complexed with NAD(+) and
an inhibitory small molecule. The inhibitor occupies the substrate-binding site
and forms a covalent adduct with the NAD(+) cofactor. The crystal structure
provides a basis for the design of potent, highly specific ABAD/HSD10 inhibitors
with potential application in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Structure of the ABAD/HSD10 monomer. (a) Stereo
C^a trace of ABAD/HSD10 monomer. Every tenth residue is
numbered. The bound NAD-inhibitor adduct is shown. (b) Ribbon
diagram of ABAD/HSD10 monomer, with the NAD-inhibitor adduct
shown in ball-and-stick representation. The ribbon is white at
the amino terminus and becomes darker blue moving toward the
carboxy terminus. C^a positions of residues in the insertion
regions of ABAD/HSD10 relative to other SDR enzymes (residues
102-107 and 141-146, see Figure 2) are shown as yellow spheres.
|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3. Ribbon representation of the ABAD/HSD10 tetramer.
The tetramer is viewed down one of three mutually perpendicular
2-fold axes. Individual monomers are shown in red, green, blue
and yellow. The bound NAD^+ and NAD-inhibitor adduct molecules
are shown in ball-and-stick representation.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2004,
342,
943-952)
copyright 2004.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.E.Muirhead,
E.Borger,
L.Aitken,
S.J.Conway,
and
F.J.Gunn-Moore
(2010).
The consequences of mitochondrial amyloid beta-peptide in Alzheimer's disease.
|
| |
Biochem J,
426,
255-270.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Rauk
(2009).
The chemistry of Alzheimer's disease.
|
| |
Chem Soc Rev,
38,
2698-2715.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Gargouri,
C.Manigand,
C.Maugé,
T.Granier,
B.Langlois d'Estaintot,
O.Cala,
I.Pianet,
K.Bathany,
J.Chaudière,
and
B.Gallois
(2009).
Structure and epimerase activity of anthocyanidin reductase from Vitis vinifera.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
65,
989.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Y.Yang,
X.Y.He,
S.E.Olpin,
V.R.Sutton,
J.McMenamin,
M.Philipp,
R.B.Denman,
and
M.Malik
(2009).
Mental retardation linked to mutations in the HSD17B10 gene interfering with neurosteroid and isoleucine metabolism.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
14820-14824.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Kristofiková,
M.Bocková,
K.Hegnerová,
A.Bartos,
J.Klaschka,
J.Rícný,
D.Rípová,
and
J.Homola
(2009).
Enhanced levels of mitochondrial enzyme 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 10 in patients with Alzheimer disease and multiple sclerosis.
|
| |
Mol Biosyst,
5,
1174-1179.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Ren,
H.W.Xu,
F.Davey,
M.Taylor,
J.Aiton,
P.Coote,
F.Fang,
J.Yao,
D.Chen,
J.X.Chen,
S.D.Yan,
and
F.J.Gunn-Moore
(2008).
Endophilin I expression is increased in the brains of Alzheimer disease patients.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
5685-5691.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.T.Guo,
J.W.Jaromczyk,
and
Y.Xu
(2007).
Analysis of chameleon sequences and their implications in biological processes.
|
| |
Proteins,
67,
548-558.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.X.Chen,
and
S.D.Yan
(2007).
Pathogenic role of mitochondrial [correction of mitochondral] amyloid-beta peptide.
|
| |
Expert Rev Neurother,
7,
1517-1525.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Yang,
Y.Yang,
J.Wu,
and
J.Zhu
(2007).
Stable expression of a novel fusion peptide of thioredoxin-1 and ABAD-inhibiting peptide protects PC12 cells from intracellular amyloid-beta.
|
| |
J Mol Neurosci,
33,
180-188.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.T.Marques,
A.Antunes,
P.A.Fernandes,
and
M.J.Ramos
(2006).
Comparative evolutionary genomics of the HADH2 gene encoding Abeta-binding alcohol dehydrogenase/17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 10 (ABAD/HSD10).
|
| |
BMC Genomics,
7,
202.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Inbar,
C.Q.Li,
S.A.Takayama,
M.R.Bautista,
and
J.Yang
(2006).
Oligo(ethylene glycol) derivatives of thioflavin T as inhibitors of protein-amyloid interactions.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
7,
1563-1566.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Y.Yang,
X.Y.He,
and
H.Schulz
(2005).
3-Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase and short chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase in human health and disease.
|
| |
FEBS J,
272,
4874-4883.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

