 |
PDBsum entry 1rfu

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of pyridoxal kinase complexed with adp and plp
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Pyridoxal kinase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h. Synonym: pyridoxine kinase. Ec: 2.7.1.35
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Ovis aries. Sheep. Organism_taxid: 9940
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from
)
Dimer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.229
|
R-free:
|
0.281
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
D.-C.Liang,T.Jiang,M.-H.Li
|
Key ref:

|
 |
M.H.Li
et al.
(2004).
Conformational changes in the reaction of pyridoxal kinase.
J Biol Chem,
279,
17459-17465.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
10-Nov-03
|
Release date:
|
27-Apr-04
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P82197
(PDXK_SHEEP) -
Pyridoxal kinase from Ovis aries
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
312 a.a.
312 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.1.35
- pyridoxal kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
pyridoxal + ATP = pyridoxal 5'-phosphate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
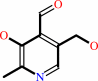 pyridoxal
pyridoxal
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
279:17459-17465
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Conformational changes in the reaction of pyridoxal kinase.
|
|
M.H.Li,
F.Kwok,
W.R.Chang,
S.Q.Liu,
S.C.Lo,
J.P.Zhang,
T.Jiang,
D.C.Liang.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
To understand the processes involved in the catalytic mechanism of pyridoxal
kinase (PLK),1 we determined the crystal structures of PLK.AMP-PCP-pyridoxamine,
PLK.ADP.PLP, and PLK.ADP complexes. Comparisons of these structures have
revealed that PLK exhibits different conformations during its catalytic process.
After the binding of AMP-PCP (an analogue that replaced ATP) and pyridoxamine to
PLK, this enzyme retains a conformation similar to that of the PLK.ATP complex.
The distance between the reacting groups of the two substrates is 5.8 A apart,
indicating that the position of ATP is not favorable to spontaneous transfer of
its phosphate group. However, the structure of PLK.ADP.PLP complex exhibited
significant changes in both the conformation of the enzyme and the location of
the ligands at the active site. Therefore, it appears that after binding of both
substrates, the enzyme-substrate complex requires changes in the protein
structure to enable the transfer of the phosphate group from ATP to vitamin
B(6). Furthermore, a conformation of the enzyme-substrate complex before the
transition state of the enzymatic reaction was also hypothesized.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
FIG. 2. Pyridoxal binding site. The molecule in the center
is the pyridoxamine bound in the PLK·AMP-PCP-pyridoxamine
complex. The surrounding residues are shown in green, and the
hydrogen bonds between the pyridoxamine and the residues are
shown as purple dashes. The corresponding residues in the
PLK·ATP complex are in blue. A comparison of these
structures reveals local conformational adjustments of the
pyridoxal binding site when the substrates binds.
|
 |
Figure 5.
FIG. 5. The ADP molecule bound in the PLK·ADP
complex and the residues interacting with it. The hydrogen bonds
between them are shown as blue dashes. The molecule shown as a
thin black line is the ADP in the PLK·ADP·PLP
complex. A significant conformational change happens between the
two ADP molecules.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2004,
279,
17459-17465)
copyright 2004.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
F.N.Musayev,
M.L.di Salvo,
T.P.Ko,
A.K.Gandhi,
A.Goswami,
V.Schirch,
and
M.K.Safo
(2007).
Crystal Structure of human pyridoxal kinase: structural basis of M(+) and M(2+) activation.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
16,
2184-2194.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Newman,
S.K.Das,
S.E.Sedelnikova,
and
D.W.Rice
(2006).
Cloning, purification and preliminary crystallographic analysis of a putative pyridoxal kinase from Bacillus subtilis.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
62,
1006-1009.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.K.Safo,
F.N.Musayev,
M.L.di Salvo,
S.Hunt,
J.B.Claude,
and
V.Schirch
(2006).
Crystal structure of pyridoxal kinase from the Escherichia coli pdxK gene: implications for the classification of pyridoxal kinases.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
188,
4542-4552.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.K.Safo,
F.N.Musayev,
S.Hunt,
M.L.di Salvo,
N.Scarsdale,
and
V.Schirch
(2004).
Crystal structure of the PdxY Protein from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
186,
8074-8082.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

