
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 624 a.a.
624 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 340 a.a.
340 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 64 a.a.
64 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 317 a.a.
317 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase/hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of g protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in complex with galpha-q and gbetagamma subunits
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2. Chain: a. Fragment: residues 28-689. Synonym: beta-ark-1, beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes. Guanine nucleotide-binding protein g(i)/g(s)/g(t) subunit beta-1. Chain: b.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Bos taurus. Bovine. Organism_taxid: 9913. Gene: grk2, adrbk1. Expressed in: trichoplusia ni. Expression_system_taxid: 7111. Expression_system_cell_line: high-5 cells. Gene: gnb1. Gene: gng2.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Tetramer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
3.06Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.236
|
R-free:
|
0.292
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.J.G.Tesmer
|
Key ref:

|
 |
V.M.Tesmer
et al.
(2005).
Snapshot of activated G proteins at the membrane: the Galphaq-GRK2-Gbetagamma complex.
Science,
310,
1686-1690.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
19-Oct-05
|
Release date:
|
20-Dec-05
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P21146
(ARBK1_BOVIN) -
Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 from Bos taurus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
689 a.a.
624 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P62871
(GBB1_BOVIN) -
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1 from Bos taurus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
340 a.a.
339 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P63212
(GBG2_BOVIN) -
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2 from Bos taurus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
71 a.a.
64 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.2.7.11.15
- [beta-adrenergic-receptor] kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[beta-adrenergic receptor] + ATP = [beta-adrenergic receptor]-phosphate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
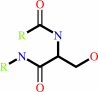 [beta-adrenergic receptor]
[beta-adrenergic receptor]
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
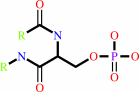 [beta-adrenergic receptor]-phosphate
[beta-adrenergic receptor]-phosphate
|
+
|
ADP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 96.43% similarity
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chain Q:
E.C.3.6.5.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Science
310:1686-1690
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Snapshot of activated G proteins at the membrane: the Galphaq-GRK2-Gbetagamma complex.
|
|
V.M.Tesmer,
T.Kawano,
A.Shankaranarayanan,
T.Kozasa,
J.J.Tesmer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) plays a key role in the
desensitization of G protein-coupled receptor signaling by phosphorylating
activated heptahelical receptors and by sequestering heterotrimeric G proteins.
We report the atomic structure of GRK2 in complex with Galphaq and Gbetagamma,
in which the activated Galpha subunit of Gq is fully dissociated from Gbetagamma
and dramatically reoriented from its position in the inactive Galphabetagamma
heterotrimer. Galphaq forms an effector-like interaction with the GRK2 regulator
of G protein signaling (RGS) homology domain that is distinct from and does not
overlap with that used to bind RGS proteins such as RGS4.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. Comparison of the inactive G  ß ß  heterotrimer and
the G heterotrimer and
the G  [i/q]-GRK2-Gß [i/q]-GRK2-Gß
 complex. (A) Side
view of G complex. (A) Side
view of G  [q]ß [q]ß  .
G .
G  [q]ß [q]ß  was homology
modeled by using the structure of G was homology
modeled by using the structure of G  [i]ß[1] [i]ß[1]
 [2] (5). The
expected membrane surface is modeled as a gray rectangle that
extends out from the plane of the figure (31), and the
heterotrimer is oriented as proposed in (6). G [2] (5). The
expected membrane surface is modeled as a gray rectangle that
extends out from the plane of the figure (31), and the
heterotrimer is oriented as proposed in (6). G  [q] is cyan with
orange ß-strands, Gß is blue, and G [q] is cyan with
orange ß-strands, Gß is blue, and G  is
green. The three switch regions (labeled I, II, and III) and the
N-terminal helix of G is
green. The three switch regions (labeled I, II, and III) and the
N-terminal helix of G  [q] are red and
yellow, respectively. GDP and G [q] are red and
yellow, respectively. GDP and G  [q]-Cys9 and
Cys10, which can be palmitoylated, are shown as ball-and-stick
models. (B) Top view of G [q]-Cys9 and
Cys10, which can be palmitoylated, are shown as ball-and-stick
models. (B) Top view of G  [q]ß [q]ß  from the
perspective of the modeled membrane surface. (C) Side view of
the G from the
perspective of the modeled membrane surface. (C) Side view of
the G  [i/q]-GRK2-Gß [i/q]-GRK2-Gß
 complex. For
purposes of comparison, GRK2-bound Gß complex. For
purposes of comparison, GRK2-bound Gß  was centered in
the same position as Gß was centered in
the same position as Gß  in panel (A). The
chimeric N-terminal helix of GRK2-bound G in panel (A). The
chimeric N-terminal helix of GRK2-bound G  [i/q] is
disordered in the crystal structure. The kinase domain of GRK2
is yellow with olive ß strands, the RH domain is purple,
and the PH domain is tan. Mg2+ (black sphere) and AIF[4]^-
(green and magenta) are bound in the active site of G [i/q] is
disordered in the crystal structure. The kinase domain of GRK2
is yellow with olive ß strands, the RH domain is purple,
and the PH domain is tan. Mg2+ (black sphere) and AIF[4]^-
(green and magenta) are bound in the active site of G  [i/q]. (D) Top
view of the G [i/q]. (D) Top
view of the G  [i/q]-GRK2-Gß [i/q]-GRK2-Gß
 complex from the
same orientation as (B). Residues 114 to 121 in complex from the
same orientation as (B). Residues 114 to 121 in  5
of GRK2 (shaded pink) alter their conformation upon docking with
the effector-binding pocket of G 5
of GRK2 (shaded pink) alter their conformation upon docking with
the effector-binding pocket of G  [i/q] (see SOM
text). [i/q] (see SOM
text).
|
 |
Figure 3.
Fig. 3. The GRK2-binding surface of G  [q]. (A)
Stereoview of the interface. The switch II and [q]. (A)
Stereoview of the interface. The switch II and  3
helices from G 3
helices from G  [i/q] are shown
as C [i/q] are shown
as C  traces; the traces; the  5
and 5
and  6 helices from
GRK2 are shown as cartoon ribbons. Side chains of interfacial
residues are shown as ball-and-stick models, with carbon atoms
from G 6 helices from
GRK2 are shown as cartoon ribbons. Side chains of interfacial
residues are shown as ball-and-stick models, with carbon atoms
from G  [i/q] and GRK2
colored cyan and yellow, respectively. Hydrogen bonds are shown
as dashed black lines. Residues targeted by site-directed
mutagenesis in this study are underlined. (B) Sequence alignment
of the switch regions and the [i/q] and GRK2
colored cyan and yellow, respectively. Hydrogen bonds are shown
as dashed black lines. Residues targeted by site-directed
mutagenesis in this study are underlined. (B) Sequence alignment
of the switch regions and the  3/ß5
sequence for representative members of all four G 3/ß5
sequence for representative members of all four G  subfamilies.
Switch regions (I to III) are outlined in black and are assigned
on the basis of comparison of the active and deactivated
structures of G subfamilies.
Switch regions (I to III) are outlined in black and are assigned
on the basis of comparison of the active and deactivated
structures of G  [i1]. Secondary
structure is represented by cylinders and arrows for [i1]. Secondary
structure is represented by cylinders and arrows for  helices and
ß strands, respectively. G helices and
ß strands, respectively. G  residues that
contact effectors are green, those that bind GAPs are red, and
those that contact both are purple. Contacting residues that
were chimeric (i.e., nonnative) in the crystal structures of the
G residues that
contact effectors are green, those that bind GAPs are red, and
those that contact both are purple. Contacting residues that
were chimeric (i.e., nonnative) in the crystal structures of the
G  [t] and G [t] and G  [13] effector
complexes are shown in a lighter shade of the appropriate color.
Green boxes outline G [13] effector
complexes are shown in a lighter shade of the appropriate color.
Green boxes outline G  [i] residues
proposed to interact with adenylyl cyclase (50), and asterisks
indicate conserved residues that contribute to the hydrophobic
effector-binding pocket. The crystal structures used for these
assignments are those of G [i] residues
proposed to interact with adenylyl cyclase (50), and asterisks
indicate conserved residues that contribute to the hydrophobic
effector-binding pocket. The crystal structures used for these
assignments are those of G  [i/q]-GRK2-Gß [i/q]-GRK2-Gß
 (this study), G (this study), G
 [i]-RGS4 [Protein
Data Bank (PDB) code 1AGR [PDB]
] (12), G [i]-RGS4 [Protein
Data Bank (PDB) code 1AGR [PDB]
] (12), G  [t]-PDE [t]-PDE  -RGS9 (1FQJ) (8),
G -RGS9 (1FQJ) (8),
G  [13]-p115RhoGEF
(1SHZ) (10), and G [13]-p115RhoGEF
(1SHZ) (10), and G  [s]-adenylyl
cyclase (1AZS) (7). The sequences are those of mouse G [s]-adenylyl
cyclase (1AZS) (7). The sequences are those of mouse G  [q] (M55412 [GenBank]
), mouse G [q] (M55412 [GenBank]
), mouse G  [11] (NP_034431
[GenBank]
), mouse G [11] (NP_034431
[GenBank]
), mouse G  [14] (NP_032163
[GenBank]
), human G [14] (NP_032163
[GenBank]
), human G  [16] (M63904 [GenBank]
), rat G [16] (M63904 [GenBank]
), rat G  [i1] (M17527 [GenBank]
), bovine G [i1] (M17527 [GenBank]
), bovine G  [t] (P04695 [GenBank]
), mouse G [t] (P04695 [GenBank]
), mouse G  [13] (NP_034433
[GenBank]
), and bovine G [13] (NP_034433
[GenBank]
), and bovine G  [s] (M13006 [GenBank]
). (C) Mutational analysis of G [s] (M13006 [GenBank]
). (C) Mutational analysis of G  [q] residues that
directly interact with GRK2. Lysates of HEK293 cells expressing
G [q] residues that
directly interact with GRK2. Lysates of HEK293 cells expressing
G  [q] mutants were
subjected to limited trypsin digestion in the presence and
absence (shown only for wild type) of [q] mutants were
subjected to limited trypsin digestion in the presence and
absence (shown only for wild type) of  and
immunoblotted with G and
immunoblotted with G  [q]-specific
antibody (upper left) (31). [q]-specific
antibody (upper left) (31).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the AAAs:
Science
(2005,
310,
1686-1690)
copyright 2005.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.M.Lyon,
V.M.Tesmer,
V.D.Dhamsania,
D.M.Thal,
J.Gutierrez,
S.Chowdhury,
K.C.Suddala,
J.K.Northup,
and
J.J.Tesmer
(2011).
An autoinhibitory helix in the C-terminal region of phospholipase C-β mediates Gαq activation.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
18,
999.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Nishimura,
K.Kitano,
J.Takasaki,
M.Taniguchi,
N.Mizuno,
K.Tago,
T.Hakoshima,
and
H.Itoh
(2010).
Structural basis for the specific inhibition of heterotrimeric Gq protein by a small molecule.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
13666-13671.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Raveh,
A.Cooper,
L.Guy-David,
and
E.Reuveny
(2010).
Nonenzymatic rapid control of GIRK channel function by a G protein-coupled receptor kinase.
|
| |
Cell,
143,
750-760.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.U.Gehret,
B.W.Jones,
P.N.Tran,
L.B.Cook,
E.K.Greuber,
and
P.M.Hinkle
(2010).
Role of helix 8 of the thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor in phosphorylation by G protein-coupled receptor kinase.
|
| |
Mol Pharmacol,
77,
288-297.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.U.Gehret,
and
P.M.Hinkle
(2010).
Importance of regions outside the cytoplasmic tail of G-protein-coupled receptors for phosphorylation and dephosphorylation.
|
| |
Biochem J,
428,
235-245.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Huang,
H.Wu,
N.Hao,
F.Blombach,
J.van der Oost,
X.Li,
X.C.Zhang,
and
Z.Rao
(2010).
Functional study on GTP hydrolysis by the GTP-binding protein from Sulfolobus solfataricus, a member of the HflX family.
|
| |
J Biochem,
148,
103-113.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.R.Temple,
C.D.Jones,
and
A.M.Jones
(2010).
Evolution of a signaling nexus constrained by protein interfaces and conformational States.
|
| |
PLoS Comput Biol,
6,
e1000962.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Baameur,
D.H.Morgan,
H.Yao,
T.M.Tran,
R.A.Hammitt,
S.Sabui,
J.S.McMurray,
O.Lichtarge,
and
R.B.Clark
(2010).
Role for the regulator of G-protein signaling homology domain of G protein-coupled receptor kinases 5 and 6 in beta 2-adrenergic receptor and rhodopsin phosphorylation.
|
| |
Mol Pharmacol,
77,
405-415.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Philip,
G.Kadamur,
R.G.Silos,
J.Woodson,
and
E.M.Ross
(2010).
Synergistic activation of phospholipase C-beta3 by Galpha(q) and Gbetagamma describes a simple two-state coincidence detector.
|
| |
Curr Biol,
20,
1327-1335.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.J.Tesmer,
V.M.Tesmer,
D.T.Lodowski,
H.Steinhagen,
and
J.Huber
(2010).
Structure of human G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in complex with the kinase inhibitor balanol.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
53,
1867-1870.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.R.England,
J.Huang,
M.J.Jennings,
R.D.Makde,
and
S.Tan
(2010).
RCC1 uses a conformationally diverse loop region to interact with the nucleosome: a model for the RCC1-nucleosome complex.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
398,
518-529.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.R.Pearce,
D.Komander,
and
D.R.Alessi
(2010).
The nuts and bolts of AGC protein kinases.
|
| |
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,
11,
9.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Aittaleb,
C.A.Boguth,
and
J.J.Tesmer
(2010).
Structure and function of heterotrimeric G protein-regulated Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors.
|
| |
Mol Pharmacol,
77,
111-125.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.H.Han,
W.Renthal,
R.H.Ring,
Z.Rahman,
K.Psifogeorgou,
D.Howland,
S.Birnbaum,
K.Young,
R.Neve,
E.J.Nestler,
and
V.Zachariou
(2010).
Brain region specific actions of regulator of G protein signaling 4 oppose morphine reward and dependence but promote analgesia.
|
| |
Biol Psychiatry,
67,
761-769.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Gutman,
C.Walliser,
T.Piechulek,
P.Gierschik,
and
Y.I.Henis
(2010).
Differential regulation of phospholipase C-beta2 activity and membrane interaction by Galphaq, Gbeta1gamma2, and Rac2.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
3905-3915.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Haga
(2010).
[G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK)].
|
| |
Nippon Yakurigaku Zasshi,
136,
215-218.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Jiang,
X.Xie,
Y.Zhang,
X.Luo,
X.Wang,
F.Fan,
D.Zheng,
Z.Wang,
and
Y.Chen
(2010).
Regulation of G-protein signaling by RKTG via sequestration of the G betagamma subunit to the Golgi apparatus.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
30,
78-90.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Guilfoyle,
M.J.Maher,
M.Rapp,
R.Clarke,
S.Harrop,
and
M.Jormakka
(2009).
Structural basis of GDP release and gating in G protein coupled Fe2+ transport.
|
| |
EMBO J,
28,
2677-2685.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Kimple,
M.Soundararajan,
S.Q.Hutsell,
A.K.Roos,
D.J.Urban,
V.Setola,
B.R.Temple,
B.L.Roth,
S.Knapp,
F.S.Willard,
and
D.P.Siderovski
(2009).
Structural determinants of G-protein alpha subunit selectivity by regulator of G-protein signaling 2 (RGS2).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
19402-19411.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.C.Huang,
K.Yoshino-Koh,
and
J.J.Tesmer
(2009).
A surface of the kinase domain critical for the allosteric activation of G protein-coupled receptor kinases.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
17206-17215.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.S.Pao,
B.L.Barker,
and
J.L.Benovic
(2009).
Role of the amino terminus of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in receptor phosphorylation.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
7325-7333.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Suzuki,
K.Tsumoto,
N.Hajicek,
K.Daigo,
R.Tokita,
S.Minami,
T.Kodama,
T.Hamakubo,
and
T.Kozasa
(2009).
Activation of leukemia-associated RhoGEF by Galpha13 with significant conformational rearrangements in the interface.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
5000-5009.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Suzuki,
N.Hajicek,
and
T.Kozasa
(2009).
Regulation and physiological functions of G12/13-mediated signaling pathways.
|
| |
Neurosignals,
17,
55-70.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Ye,
K.T.Nguyen,
S.V.Le Clair,
and
Z.Chen
(2009).
In situ molecular level studies on membrane related peptides and proteins in real time using sum frequency generation vibrational spectroscopy.
|
| |
J Struct Biol,
168,
61-77.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.S.Lee,
W.Ma,
X.Zhang,
H.Kantarjian,
and
M.Albitar
(2009).
Structural effects of clinically observed mutations in JAK2 exons 13-15: comparison with V617F and exon 12 mutations.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
9,
58.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Namkung,
C.Dipace,
E.Urizar,
J.A.Javitch,
and
D.R.Sibley
(2009).
G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2 constitutively regulates D2 dopamine receptor expression and signaling independently of receptor phosphorylation.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
34103-34115.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Goc,
T.E.Angel,
B.Jastrzebska,
B.Wang,
P.L.Wintrode,
and
K.Palczewski
(2008).
Different properties of the native and reconstituted heterotrimeric G protein transducin.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
12409-12419.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Shankaranarayanan,
D.M.Thal,
V.M.Tesmer,
D.L.Roman,
R.R.Neubig,
T.Kozasa,
and
J.J.Tesmer
(2008).
Assembly of high order G alpha q-effector complexes with RGS proteins.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
34923-34934.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.V.Smrcka
(2008).
G protein betagamma subunits: central mediators of G protein-coupled receptor signaling.
|
| |
Cell Mol Life Sci,
65,
2191-2214.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Johnston,
F.S.Willard,
J.K.Ramer,
R.Blaesius,
C.N.Roques,
and
D.P.Siderovski
(2008).
State-selective binding peptides for heterotrimeric G-protein subunits: novel tools for investigating G-protein signaling dynamics.
|
| |
Comb Chem High Throughput Screen,
11,
370-381.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Johnston,
K.Afshar,
J.T.Snyder,
G.G.Tall,
P.Gönczy,
D.P.Siderovski,
and
F.S.Willard
(2008).
Structural determinants underlying the temperature-sensitive nature of a Galpha mutant in asymmetric cell division of Caenorhabditis elegans.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
21550-21558.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.M.Ross
(2008).
Coordinating speed and amplitude in G-protein signaling.
|
| |
Curr Biol,
18,
R777-R783.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Mayer,
B.Wulffen,
C.Huber,
J.Brockmann,
B.Flicke,
L.Neumann,
D.Hafenbradl,
B.M.Klebl,
M.J.Lohse,
C.Krasel,
and
M.Blind
(2008).
An RNA molecule that specifically inhibits G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in vitro.
|
| |
RNA,
14,
524-534.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Wacker,
D.B.Feller,
X.B.Tang,
M.C.Defino,
Y.Namkung,
J.S.Lyssand,
A.J.Mhyre,
X.Tan,
J.B.Jensen,
and
C.Hague
(2008).
Disease-causing mutation in GPR54 reveals the importance of the second intracellular loop for class A G-protein-coupled receptor function.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
31068-31078.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.C.Slep,
M.A.Kercher,
T.Wieland,
C.K.Chen,
M.I.Simon,
and
P.B.Sigler
(2008).
Molecular architecture of Galphao and the structural basis for RGS16-mediated deactivation.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
105,
6243-6248.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.B.Keever,
J.E.Jones,
and
B.T.Andresen
(2008).
G protein-coupled receptor kinase 4gamma interacts with inactive Galpha(s) and Galpha13.
|
| |
Biochem Biophys Res Commun,
367,
649-655.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Soundararajan,
F.S.Willard,
A.J.Kimple,
A.P.Turnbull,
L.J.Ball,
G.A.Schoch,
C.Gileadi,
O.Y.Fedorov,
E.F.Dowler,
V.A.Higman,
S.Q.Hutsell,
M.Sundström,
D.A.Doyle,
and
D.P.Siderovski
(2008).
Structural diversity in the RGS domain and its interaction with heterotrimeric G protein alpha-subunits.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
105,
6457-6462.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Singh,
B.Wang,
T.Maeda,
K.Palczewski,
and
J.J.Tesmer
(2008).
Structures of rhodopsin kinase in different ligand states reveal key elements involved in G protein-coupled receptor kinase activation.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
14053-14062.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.B.Penn,
and
J.L.Benovic
(2008).
Regulation of heterotrimeric G protein signaling in airway smooth muscle.
|
| |
Proc Am Thorac Soc,
5,
47-57.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Austin,
W.W.Ja,
and
R.W.Roberts
(2008).
Evolution of class-specific peptides targeting a hot spot of the Galphas subunit.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
377,
1406-1418.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.C.Strickfaden,
and
P.M.Pryciak
(2008).
Distinct Roles for Two G{alpha} G Interfaces in Cell Polarity Control by a Yeast Heterotrimeric G Protein.
|
| |
Mol Biol Cell,
19,
181-197.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.M.Oldham,
and
H.E.Hamm
(2008).
Heterotrimeric G protein activation by G-protein-coupled receptors.
|
| |
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,
9,
60-71.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Chen,
W.D.Singer,
S.M.Danesh,
P.C.Sternweis,
and
S.R.Sprang
(2008).
Recognition of the activated states of Galpha13 by the rgRGS domain of PDZRhoGEF.
|
| |
Structure,
16,
1532-1543.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.L.Lomize,
I.D.Pogozheva,
M.A.Lomize,
and
H.I.Mosberg
(2007).
The role of hydrophobic interactions in positioning of peripheral proteins in membranes.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
7,
44.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Willets,
C.P.Nelson,
S.R.Nahorski,
and
R.A.Challiss
(2007).
The regulation of M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor desensitization by synaptic activity in cultured hippocampal neurons.
|
| |
J Neurochem,
103,
2268-2280.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Rojas,
M.E.Yohe,
S.Gershburg,
T.Kawano,
T.Kozasa,
and
J.Sondek
(2007).
Galphaq directly activates p63RhoGEF and Trio via a conserved extension of the Dbl homology-associated pleckstrin homology domain.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
29201-29210.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.L.Parker,
M.S.Parker,
F.R.Sallee,
and
A.Balasubramaniam
(2007).
Oligomerization of neuropeptide Y (NPY) Y2 receptors in CHO cells depends on functional pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins.
|
| |
Regul Pept,
144,
72-81.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.L.Williams,
S.Lutz,
N.K.Charlie,
C.Vettel,
M.Ailion,
C.Coco,
J.J.Tesmer,
E.M.Jorgensen,
T.Wieland,
and
K.G.Miller
(2007).
Trio's Rho-specific GEF domain is the missing Galpha q effector in C. elegans.
|
| |
Genes Dev,
21,
2731-2746.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Lutz,
A.Shankaranarayanan,
C.Coco,
M.Ridilla,
M.R.Nance,
C.Vettel,
D.Baltus,
C.R.Evelyn,
R.R.Neubig,
T.Wieland,
and
J.J.Tesmer
(2007).
Structure of Galphaq-p63RhoGEF-RhoA complex reveals a pathway for the activation of RhoA by GPCRs.
|
| |
Science,
318,
1923-1927.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.S.Ferguson
(2007).
Phosphorylation-independent attenuation of GPCR signalling.
|
| |
Trends Pharmacol Sci,
28,
173-179.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Morikawa,
A.Muroya,
Y.Nakajima,
T.Tanaka,
K.Hirai,
S.Sugio,
K.Wakamatsu,
and
T.Kohno
(2007).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of the receptor-uncoupled mutant of Galphai1.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
63,
139-141.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.M.Oldham,
N.Van Eps,
A.M.Preininger,
W.L.Hubbell,
and
H.E.Hamm
(2007).
Mapping allosteric connections from the receptor to the nucleotide-binding pocket of heterotrimeric G proteins.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
104,
7927-7932.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Swardfager,
and
J.Mitchell
(2007).
Purification of visual arrestin from squid photoreceptors and characterization of arrestin interaction with rhodopsin and rhodopsin kinase.
|
| |
J Neurochem,
101,
223-231.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Wu,
T.Buranda,
P.C.Simons,
G.P.Lopez,
W.E.McIntire,
J.C.Garrison,
E.R.Prossnitz,
and
L.A.Sklar
(2007).
Rapid-mix flow cytometry measurements of subsecond regulation of G protein-coupled receptor ternary complex dynamics by guanine nucleotides.
|
| |
Anal Biochem,
371,
10-20.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zheng,
D.Xu,
and
X.Gu
(2007).
Functional divergence after gene duplication and sequence-structure relationship: a case study of G-protein alpha subunits.
|
| |
J Exp Zoolog B Mol Dev Evol,
308,
85-96.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Johnston,
E.S.Lobanova,
A.S.Shavkunov,
J.Low,
J.K.Ramer,
R.Blaesius,
Z.Fredericks,
F.S.Willard,
B.Kuhlman,
V.Y.Arshavsky,
and
D.P.Siderovski
(2006).
Minimal determinants for binding activated G alpha from the structure of a G alpha(i1)-peptide dimer.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
45,
11390-11400.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.D.Sherrill,
and
W.E.Miller
(2006).
G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) kinase 2 regulates agonist-independent Gq/11 signaling from the mouse cytomegalovirus GPCR M33.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
39796-39805.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.L.Neitzel,
and
J.R.Hepler
(2006).
Cellular mechanisms that determine selective RGS protein regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling.
|
| |
Semin Cell Dev Biol,
17,
383-389.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Pellicena,
and
J.Kuriyan
(2006).
Protein-protein interactions in the allosteric regulation of protein kinases.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
16,
702-709.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|

| |

