GMP reductase
Guanosine monophosphate reductase (GMPR) is crucial for catalysis of the irreversible GMP deamination to IMP with the use of NADPH. It converts nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide derivatives of G to A nucleotides, and thus maintains the intracellular balance of A and G nucleotides. GMP is a homotetramer with mixed alpha helices and beta sheets.The monomers are stabilised by interactions across their edges and through Cys-Cys bonds. GMPR1 inhibitors are tested for applications is treating Alzheimer's disease and the increase of GMPR expression is linked to suppression of melanoma cancers.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
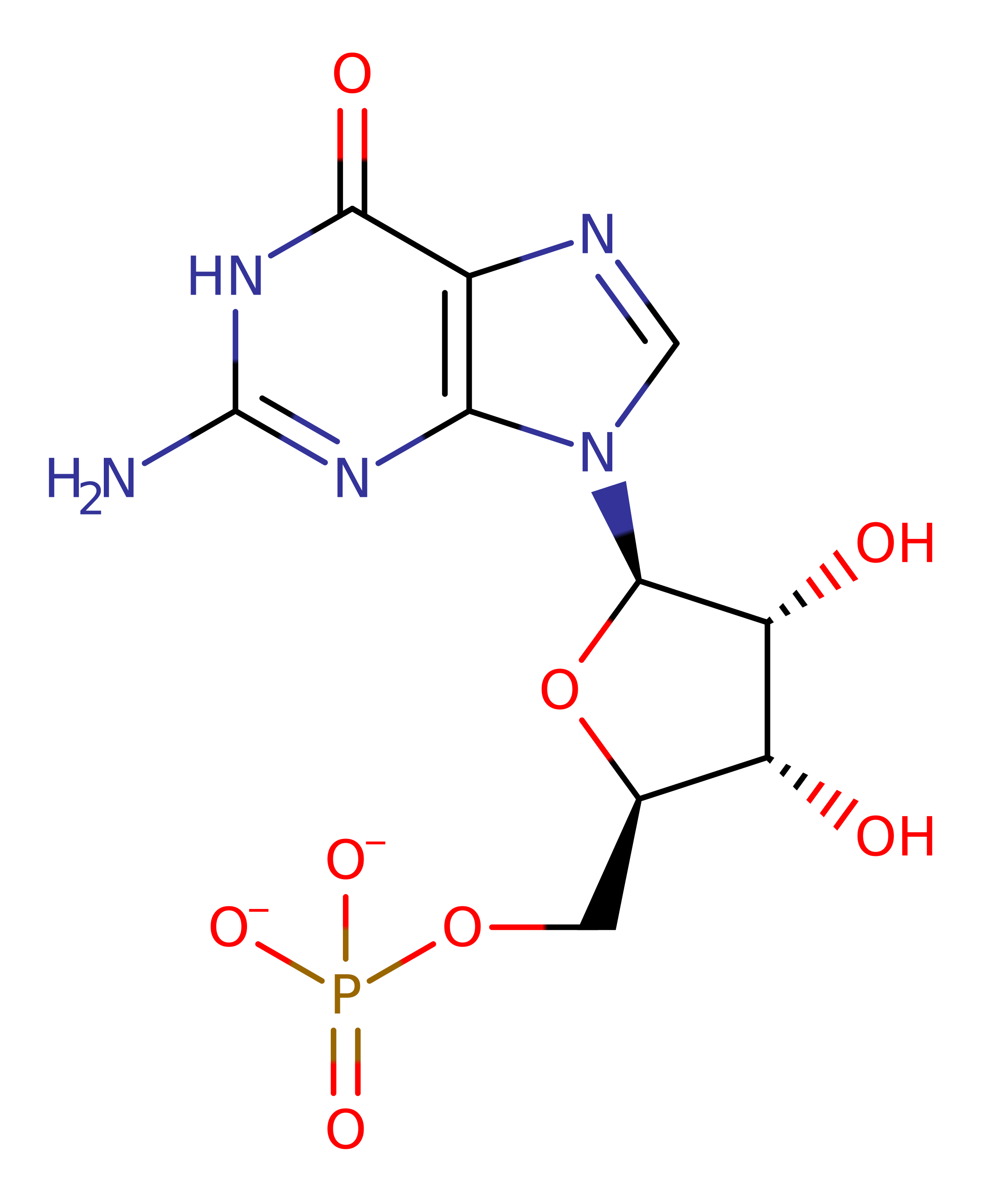
P36959
 (1.7.1.7)
(1.7.1.7)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
2ble
- Structure of human guanosine monophosphate reductase GMPR1 in complex with GMP
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.70
 (see all for 2ble)
(see all for 2ble)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.7.1.7)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The reaction is two step process. The Thr188 and Glu289 dyad activate the amino group by donating a proton to it. In concert Cys186 performs a nucleophilic attack on the C2 atom of GMP resulting in the formation of a C-S bond between the enzyme and substrate. This C-S bond is then cleaved by the addition of a hydride from NADPH to the C2 atom of the substrate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2ble) | ||
| Cys186 | Cys186(208)A | Cys186 acts as a nucleophile attacking the C2 atom of GMP. | nucleofuge, nucleophile |
| Thr188, Glu289 | Thr188(210)A, Glu289(311)A | The Thr188/Glu289 dyad act as proton donors and activators for the reaction by protonating the amino group on the substrate. This activates the amino group and initiates the reaction with Cys186. | proton relay, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, hydride transfer, intramolecular rearrangement, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, overall product formedReferences
- Patton GC et al. (2011), Nat Chem Biol, 7, 950-958. Cofactor mobility determines reaction outcome in the IMPDH and GMPR (β-α)8 barrel enzymes. DOI:10.1038/nchembio.693. PMID:22037469.
- Rosenberg MM et al. (2018), Biochemistry, 57, 3146-3154. Dynamic Characteristics of Guanosine-5'-monophosphate Reductase Complexes Revealed by High-Resolution 31P Field-Cycling NMR Relaxometry. DOI:10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00142. PMID:29547266.
- Rosenberg MM et al. (2016), J Biol Chem, 291, 22988-22998. Substrate and Cofactor Dynamics on Guanosine Monophosphate Reductase Probed by High Resolution Field Cycling 31P NMR Relaxometry. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M116.739516. PMID:27613871.
- Li J et al. (2006), J Mol Biol, 355, 980-988. Crystal structure of human guanosine monophosphate reductase 2 (GMPR2) in complex with GMP. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.11.047. PMID:16359702.

Step 1. Cys186 performs a nucleophilic attack on C2 of the GMP. In concert Thr188 acts as a proton relay between Glu289 and the leaving amino group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys186(208)A | nucleophile |
| Thr188(210)A | proton donor |
| Glu289(311)A | proton donor |
| Thr188(210)A | proton relay, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation
Step 2. NADPH then donates a hydride to the C2 atom of GMP. This breaks the C-S bond formed by Cys186.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys186(208)A | nucleofuge |





 Download:
Download: