DDT-dehydrochlorinase
This glutathione reductase is known to perform the conjugation of reduced glutathione to a wide number of exogenous and endogenous hydrophobic electrophiles [PMID:22082028, PMID:20417639]. Has DDT dehydrochlorinase activity [PMID:20417639] and may also be involved in detoxification [PMID:22082028]. Docking and NMR studies have shown that the DDT molecule binds in the H-site.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P20432
 (2.5.1.18, 4.5.1.1)
(2.5.1.18, 4.5.1.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly)

- PDB
-
3mak
- Crystal structure of Glutathione transferase dmGSTD1 from Drosophila melanogaster, in complex with glutathione
(1.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.30.10
 (see all for 3mak)
(see all for 3mak)
- Cofactors
- Glutathione (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.5.1.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
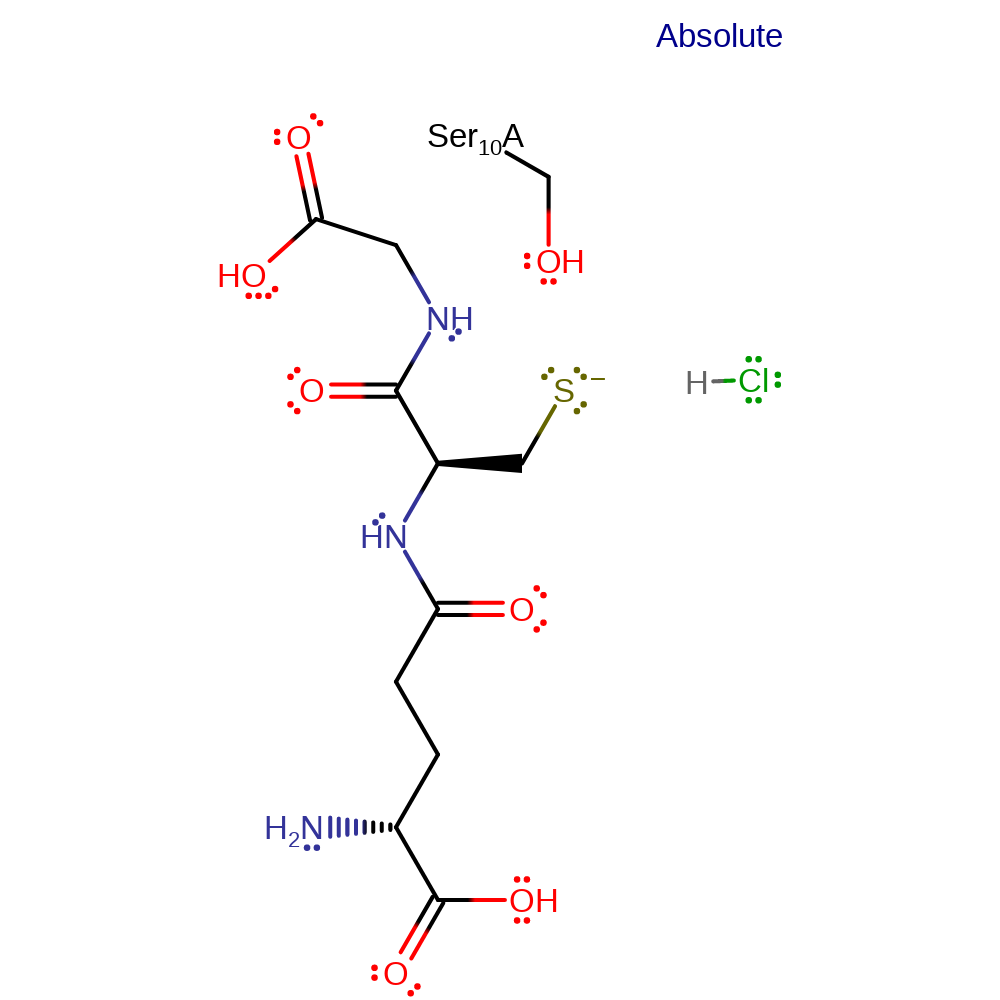
The thiolate group of activated ionic GSH abstracts the DDT beta-hydrogen, which eliminates a chloride ion from DDT to yield the final product DDE. The chloride anion then abstracts the proton from GSH to regenerate the enzyme active site.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (3mak) | ||
| Ser10 | Ser10A | Stabilises the thiolate anion of glutathione. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular elimination, overall reactant used, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated, native state of cofactor regeneratedReferences
- Wang Y et al. (2008), J Struct Biol, 164, 228-235. Structure of an insect epsilon class glutathione S-transferase from the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae provides an explanation for the high DDT-detoxifying activity. DOI:10.1016/j.jsb.2008.08.003. PMID:18778777.
- Saisawang C et al. (2012), Biochem J, 442, 181-190. A preliminary characterization of the cytosolic glutathione transferase proteome from Drosophila melanogaster. DOI:10.1042/BJ20111747. PMID:22082028.
- Wongsantichon J et al. (2012), Arch Biochem Biophys, 521, 77-83. Structural evidence for conformational changes of Delta class glutathione transferases after ligand binding. DOI:10.1016/j.abb.2012.03.023. PMID:22475449.
- Ayres CF et al. (2011), PLoS One, 6, e29237-. Comparative genomics of the anopheline glutathione S-transferase epsilon cluster. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0029237. PMID:22206003.
- Low WY et al. (2010), J Mol Biol, 399, 358-366. Recognition and detoxification of the insecticide DDT by Drosophila melanogaster glutathione S-transferase D1. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2010.04.020. PMID:20417639.
- Chen L et al. (2003), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 59, 2211-2217. Structure of an insect delta-class glutathione S-transferase from a DDT-resistant strain of the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. PMID:14646079.

Step 1. Activated glutathione abstracts the beta proton from the DDT substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser10A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular elimination, overall reactant used, overall product formed
Step 2. In an inferred return step the activated glutathione species is regenerated. The species responsible for the final proton abstraction is not known, shown here as the product chloride anion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser10A | electrostatic stabiliser |




 Download:
Download: