E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme
Ubiquitination is mediated by three enzymes, E1 (PDB:3cmm), E2 (PDB:1ayz) and E3 (PDB:1c4z). The first, E1, is essential for ubiquitin activation and transferring the substrate onto the second cascade enzyme, E2, which responsible for mediating repeated ubiquitination at the eventual substrate, which is brought into proximity of E2 by the active site of E3, the enzyme which also regulates substrate specificity.
This entry represents the second of the three reactions occurring in this cascade: ubiquitin:[E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme] ligase (AMP-forming). The E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme acquires the activated ubquitin from the E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme (EC 6.2.1.45) and binds it via a transthioesterification reaction to itself. In the human enzyme the catalytic centre is located at Cys-87 where ubiquitin is bound via its C-terminal glycine in a thioester linkage.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequences
-
P22515
 (6.2.1.45)
(6.2.1.45)
P06104 (2.3.2.23)
(2.3.2.23)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c (Baker's yeast)

- PDB
-
3cmm
- Crystal Structure of the Uba1-Ubiquitin Complex
(2.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.10.2660
 (see all for 3cmm)
(see all for 3cmm)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.3.2.23)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The ubiquitin accepting enzyme E2 attacks the high energy thioester bond at the active site of E1, forming an oxyanion intermediate. The intermediate then collapses, forming the E2 product and regenerating the active form of E1. It is unclear how the E1 Cys returns to its protonation state.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (3cmm) | ||
| Cys600 | Cys600(591)A | This is the E1 substrate and is ubiquitinated at the start of the reaction and passes the ubiquitin group to the cysteine of the E2 substrate. | nucleofuge |
| Cys88 | Not found | This is the nucleophilic substrate of the reaction. | nucleophile |
| Thr601 | Thr601(592)A | Thr601 may activate the incoming nucleophile of E2 towards attack at the high energy thio-ester intermediate [PMID:14998368]. | modifies pKa |
| Asn781 (main-N), Asp782 (main-N), Arg603 | Asn781(772)A (main-N), Asp782(773)A (main-N), Arg603(594)A | Helps stabilise the reactive intermediates and transition states formed during the course of the reaction. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Passmore LA et al. (2004), Biochem J, 379, 513-525. Getting into position: the catalytic mechanisms of protein ubiquitylation. DOI:10.1042/bj20040198. PMID:14998368.
- van Wijk SJ et al. (2010), FASEB J, 24, 981-993. The family of ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s): deciding between life and death of proteins. DOI:10.1096/fj.09-136259. PMID:19940261.
- Ye Y et al. (2009), Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 10, 755-764. Building ubiquitin chains: E2 enzymes at work. DOI:10.1038/nrm2780. PMID:19851334.
- Mohideen F et al. (2009), Nat Struct Mol Biol, 16, 945-952. A molecular basis for phosphorylation-dependent SUMO conjugation by the E2 UBC9. DOI:10.1038/nsmb.1648. PMID:19684601.
- Yunus AA et al. (2006), Nat Struct Mol Biol, 13, 491-499. Lysine activation and functional analysis of E2-mediated conjugation in the SUMO pathway. DOI:10.1038/nsmb1104. PMID:16732283.
- Scheffner M et al. (1995), Nature, 373, 81-83. Protein ubiquitination involving an E1–E2–E3 enzyme ubiquitin thioester cascade. DOI:10.1038/373081a0. PMID:7800044.
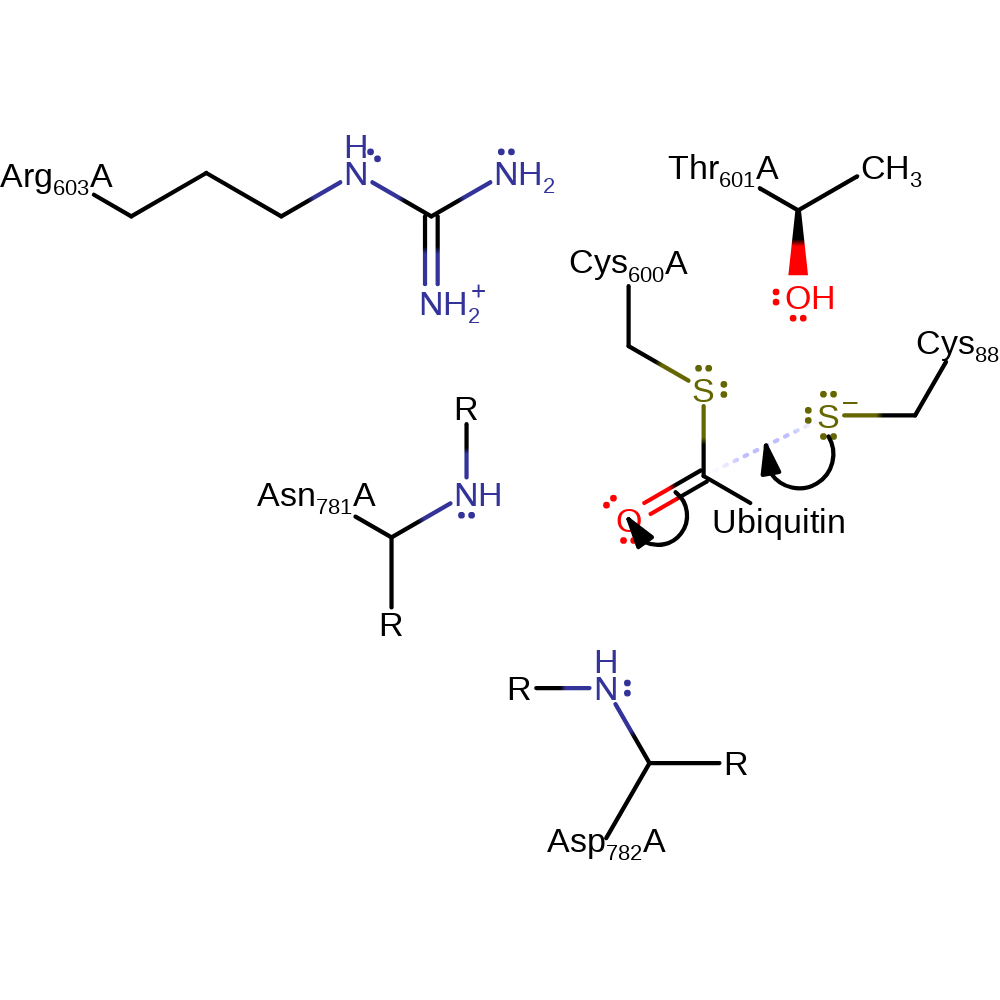
Step 1. The ubiquitin accepting enzyme E2 attacks the high energy thioester bond at the active site of E1, forming an oxyanion intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr601(592)A | modifies pKa |
| Arg603(594)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn781(772)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp782(773)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys88 | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used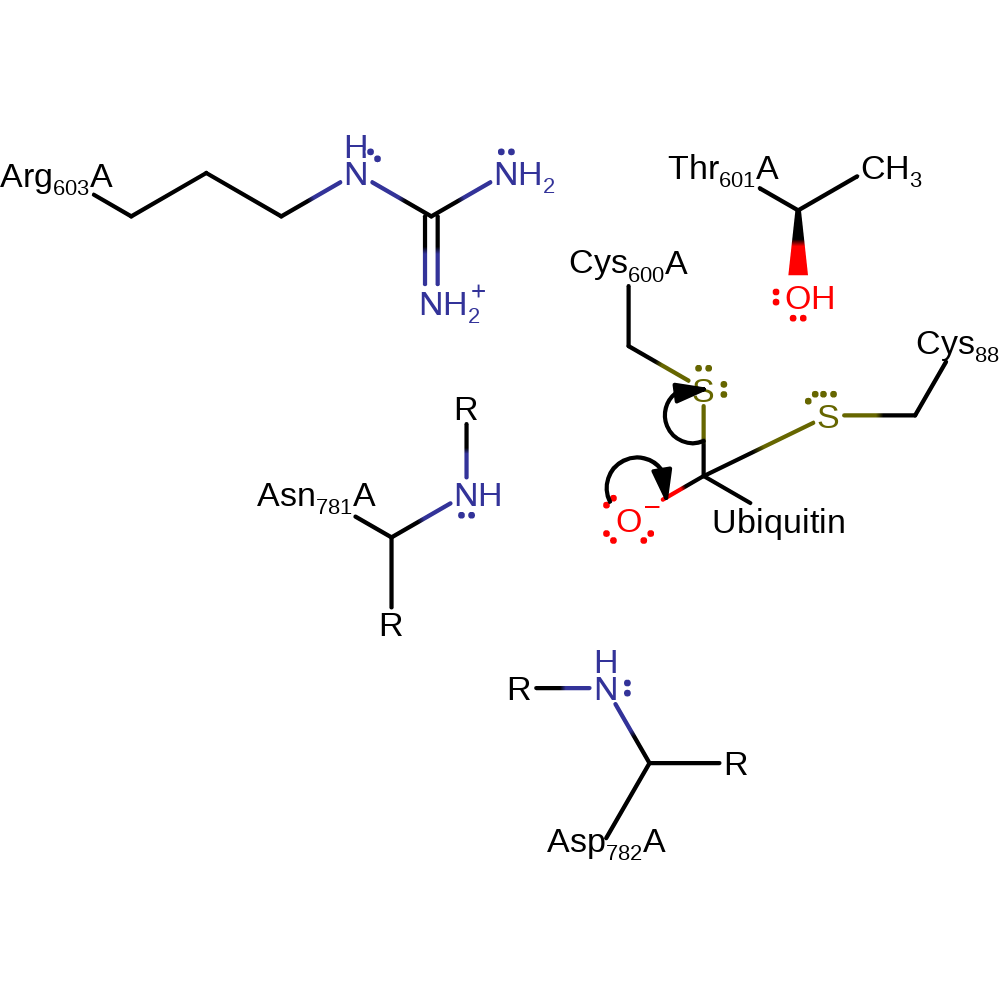
Step 2. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, completing the transfer of ubiquitin from the Cys600 residue of E1 to Cys88 of E2. The active site of E1 is regenerated.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr601(592)A | modifies pKa |
| Arg603(594)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn781(772)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp782(773)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys600(591)A | nucleofuge |


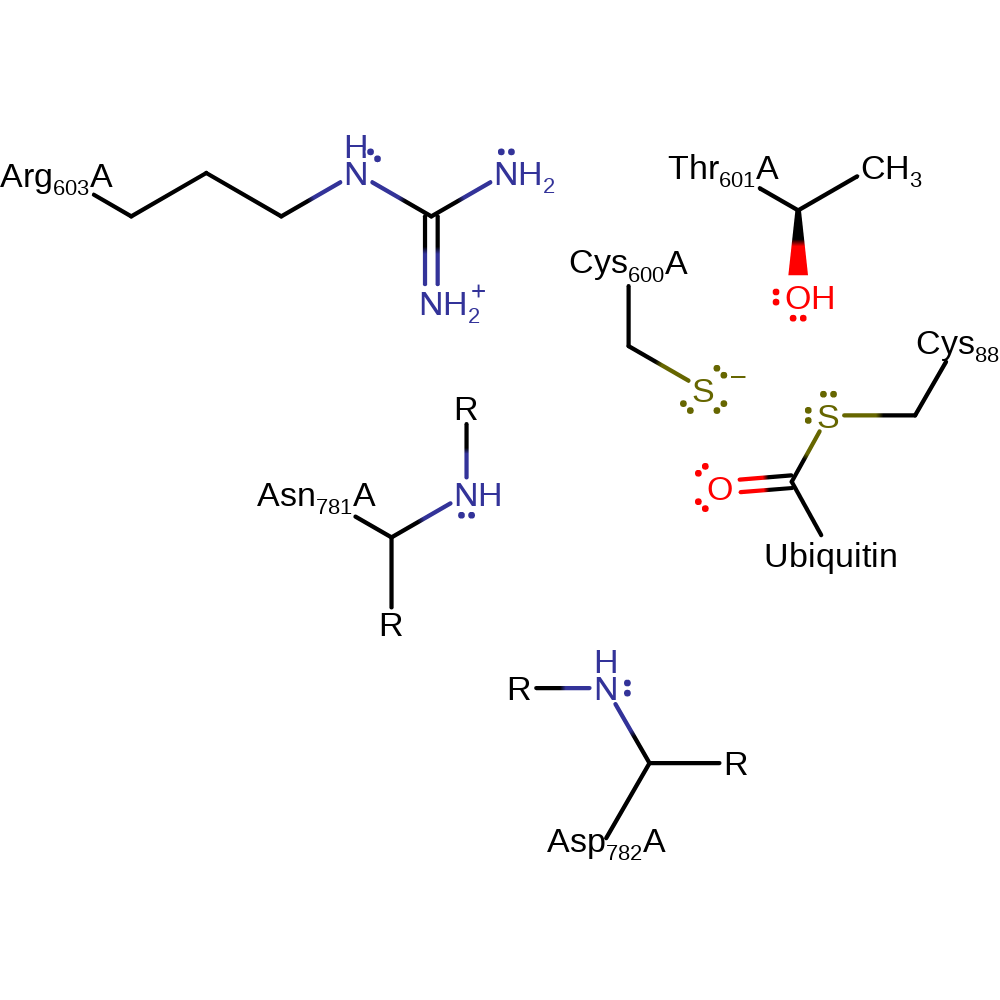 Download:
Download: