Scytalone dehydratase
Scytalone dehydratase (SD) catalySes the dehydrations of scytalone and vermelone in the fungal melanin biosynthetic pathway. It was first identified in a phytopathogenic fungus, Magnaporthe grisea (Rice blast fungus), which causes rice blast disease. Scytalone dehydratase is a molecular target of inhibitor design efforts aimed at protecting rice plants from fungal disease [PMID:9922139, PMID:14716498].
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P56221
 (4.2.1.94)
(4.2.1.94)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Magnaporthe oryzae 70-15 (Fungus)

- PDB
-
1std
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF SCYTALONE DEHYDRATASE: A DISEASE DETERMINANT OF THE RICE PATHOGEN, MAGNAPORTHE GRISEA
(2.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.10.450.50
 (see all for 1std)
(see all for 1std)
- Cofactors
- Water (1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
It is thought this mechanism proceeds through the syn elimination of water from the substrates in an E1cb-like manner. Here the substrate undergoes keto-enol tautomerisation, followed by elimination of water.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1std) | ||
| Tyr50 | Tyr50A | Acts as a general acid/base in the tautomerisation step. Although the the phenol has a pKa of between 10 and 11 in water, it would become more acidic when complexed with the active-site water molecule and the second tyrosine (Y30). | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Tyr30 | Tyr30A | Modifies the pKa of Tyr50. | modifies pKa |
| Asp31 | Asp31A | Modifies the pKa of His85. | modifies pKa |
| His110 | His110A | H110 is primarily involved in recognition of the scytalone over vermelone, but it is also thought to assist in stretching the bond of the C3 hydroxyl leaving group. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His85 | His85A | Due to its hydrophobic environment, H85 is thought to have a pKa below 6.0, allowing it to serve as the base in a syn elimination. Even though its basicity is raised by sharing a hydrogen bond with D31, H85 needs to approximate the pKa of the Cα methylene in the transition state, and the acidity of this methylene is greatly enhanced by the enzyme through multiple interactions with the C1 carbonyl. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, overall reactant used, dehydration, overall product formed, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Basarab GS et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 6012-6024. Catalytic Mechanism of Scytalone Dehydratase: Site-Directed Mutagenisis, Kinetic Isotope Effects, and Alternate Substrates. DOI:10.1021/bi982952b. PMID:10320327.
- Okimoto N et al. (2004), J Am Chem Soc, 126, 13132-13139. Cooperative motions of protein and hydration water molecules: molecular dynamics study of scytalone dehydratase. DOI:10.1021/ja048053u. PMID:15469312.
- Zheng YJ et al. (2002), Biochemistry, 41, 820-826. Roles of Substrate Distortion and Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding in Enzymatic Catalysis by Scytalone Dehydratase. DOI:10.1021/bi015848u. PMID:11790103.
- Jordan DB et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 2276-2282. Stereochemistry of the Enolization of Scytalone by Scytalone Dehydratase. DOI:10.1021/bi991839y.
- Jordan DB et al. (2000), Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 10, 23-26. Binding dynamics of two water molecules constrained within the scytalone dehydratase binding pocket. PMID:10636235.
- Zheng YJ et al. (1998), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 95, 4158-4163. Role of a critical water in scytalone dehydratase-catalyzed reaction. PMID:9539706.
- Lundqvist T et al. (1994), Structure, 2, 937-944. Crystal structure of scytalone dehydratase--a disease determinant of the rice pathogen, Magnaporthe grisea. PMID:7866745.
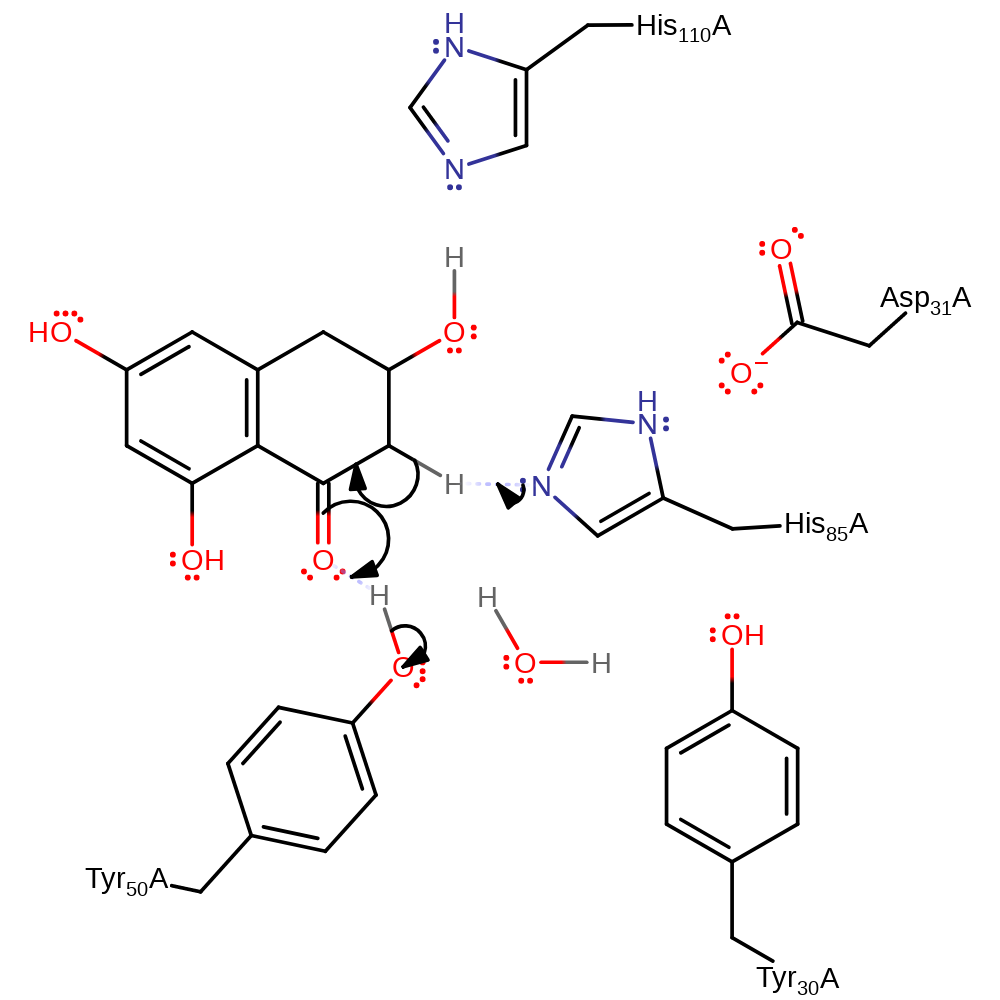
Step 1. His85 abstracts the syn proton from the substrate, initiating a keto-enol tautomerisation reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr30A | modifies pKa |
| Asp31A | modifies pKa |
| His110A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr50A | proton donor |
| His85A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, overall reactant used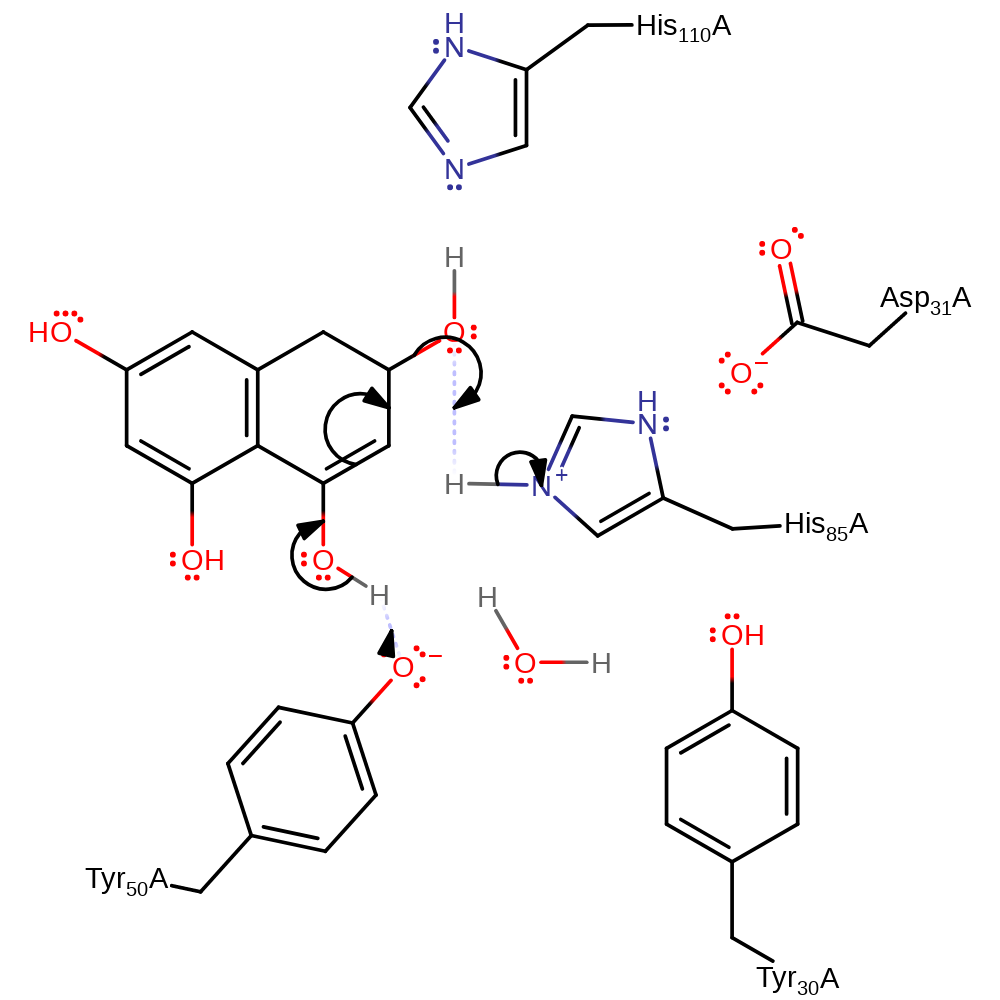
Step 2. The substrate undergoes a second tautomerisation reaction, resulting in the elimination of water and the regeneration of the active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr30A | modifies pKa |
| Asp31A | modifies pKa |
| His110A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His85A | proton donor |
| Tyr50A | proton acceptor |



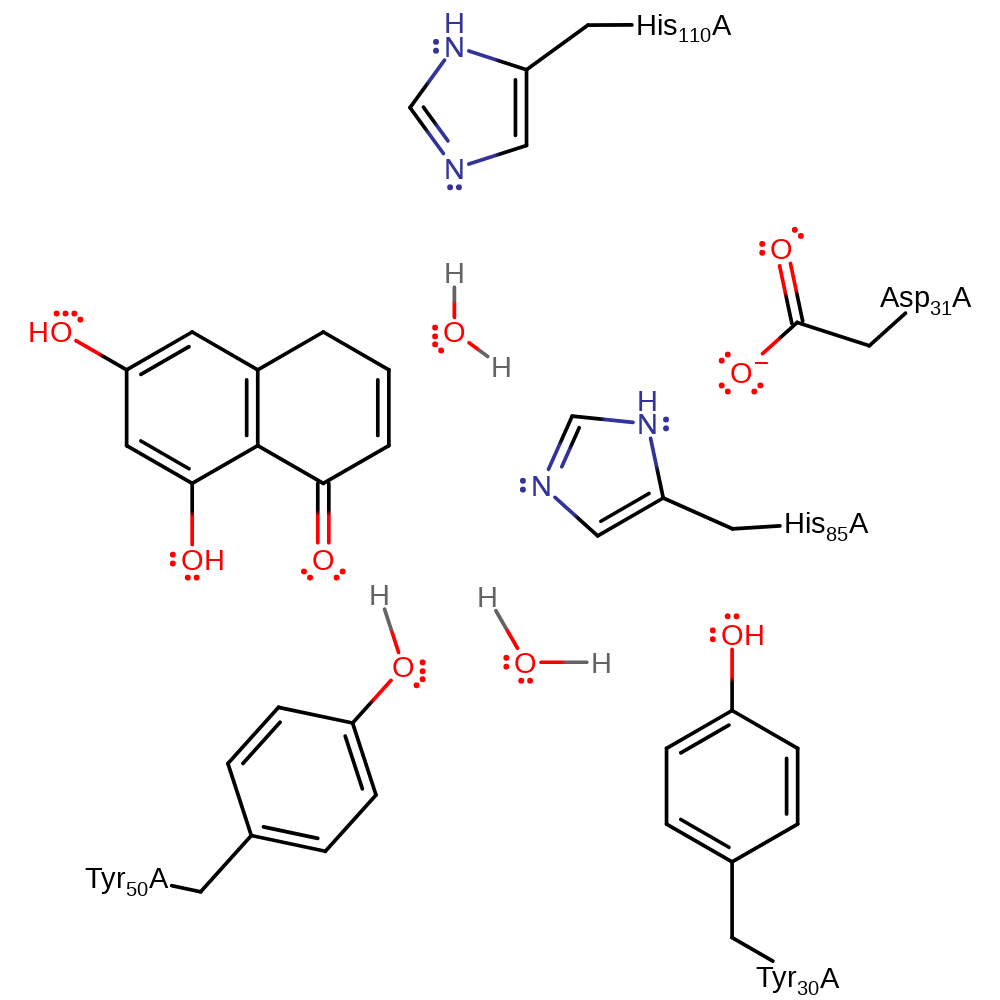 Download:
Download: