Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP)
GTP-utilising phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) catalyses the first committed (rate-limiting) step in hepatic gluconeogenesis, namely the reversible decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and carbon dioxide using GTP as a source of phosphate.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P35558
 (2.7.11.-, 4.1.1.32)
(2.7.11.-, 4.1.1.32)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1nhx
- PEPCK COMPLEX WITH A GTP-COMPETITIVE INHIBITOR
(2.1 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.170.8.10
 3.40.449.10
3.40.449.10  3.90.228.20
3.90.228.20  (see all for 1nhx)
(see all for 1nhx)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1), Manganese(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.1.1.32)
+
→
+
+
Alternative enzyme names: PEP carboxylase, Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, Phosphoenolpyruvic carboxykinase, Phosphoenolpyruvic carboxykinase (GTP), Phosphoenolpyruvic carboxylase (GTP), Phosphopyruvate (guanosine triphosphate) carboxykinase, Phosphopyruvate carboxylase, Phosphopyruvate carboxylase (GTP), PEPCK, PEP carboxykinase, GTP:oxaloacetate carboxy-lyase (transphosphorylating),
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Phosphoryl transfer occurring through a direct inline transfer of the phosphoryl group progressing through an enol-pyruvate intermediate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1nhx) | ||
| Tyr235 | Tyr235(238)A | The aromatic ring of Tyr235 helps to position PEP in the active site and the hydroxyl group allows an optimal PEP–Mn2+ distance for efficient phosphoryl transfer and overall catalysis. | electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Ser286 | Ser286(289)A | The exact role of this residue is currently unclear. It is possible that this serine could be functioning by forming a hexacoordinated activated phosphate during the phosphoryl transfer step. In the complexes with OAA, the S286 hydroxyl group is observed to interact with the C4 carbonyl oxygen (O5) that is cis to the site of phosphorylation, further stabilizing the inner-sphere coordinated OAA molecule. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys288 | Cys288(291)A | In the apo enzyme, this residue forms part of the manganese binding site. During the course of the reaction it is displaced by the substrate and water molecules to form the active complex. | metal ligand |
| His264, Lys244, Asp311 | His264(267)A, Lys244(247)A, Asp311(314)A | Forms part of the manganese binding site. | metal ligand |
| Arg87, Arg405 | Arg87(90)A, Arg405(408)A | The C1 carboxylate of OAA is sandwiched between R87 and R405 in an environment that would serve to facilitate decarboxylation. In the reverse reaction, these two arginines would form the CO2 binding site. | enhance reactivity, electrostatic stabiliser |
*PDB label guide - RESx(y)B(C) - RES: Residue Name; x: Residue ID in PDB file;
y: Residue ID in PDB sequence if different from PDB file; B: PDB Chain;
C: Biological Assembly Chain if different from PDB. If label is "Not Found" it means this residue is not found in the reference PDB.
Chemical Components
decarboxylation, intramolecular elimination, overall product formed, overall reactant usedReferences
- Carlson GM et al. (2009), J Biol Chem, 284, 27037-27041. Structural insights into the mechanism of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase catalysis. DOI:10.1074/jbc.R109.040568. PMID:19638345.
- Machová I et al. (2015), PLoS One, 10, e0120682-. Structural and functional studies of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0120682. PMID:25798914.
- Dharmarajan L et al. (2008), FEBS J, 275, 5810-5819. Tyr235 of human cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase influences catalysis through an anion-quadrupole interaction with phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylate. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06702.x. PMID:19021757.
- Holyoak T et al. (2006), Biochemistry, 45, 8254-8263. Structural insights into the mechanism of PEPCK catalysis. DOI:10.1021/bi060269g. PMID:16819824.
- Foley LH et al. (2003), Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 35, 3871-3874. X-Ray Structures of Two Xanthine Inhibitors Bound to PEPCK and N-3 Modifications of Substituted 1,8-Dibenzylxanthines. DOI:10.1002/chin.200403146. PMID:14552798.
- Dunten P et al. (2002), J Mol Biol, 316, 257-264. Crystal structure of human cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase reveals a new GTP-binding site. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5364. PMID:11851336.
- Sudom AM et al. (2001), J Mol Biol, 314, 83-92. The phosphoryl-transfer mechanism of Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase from the use of AlF3. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5120. PMID:11724534.
- Matte A et al. (1997), J Biol Chem, 272, 8105-8108. Structure and Mechanism of Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.272.13.8105. PMID:9139042.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg87(90)A | enhance reactivity |
| Arg405(408)A | enhance reactivity |
| Cys288(291)A | metal ligand |
| Ser286(289)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr235(238)A | electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Lys244(247)A | metal ligand |
| Asp311(314)A | metal ligand |
| His264(267)A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
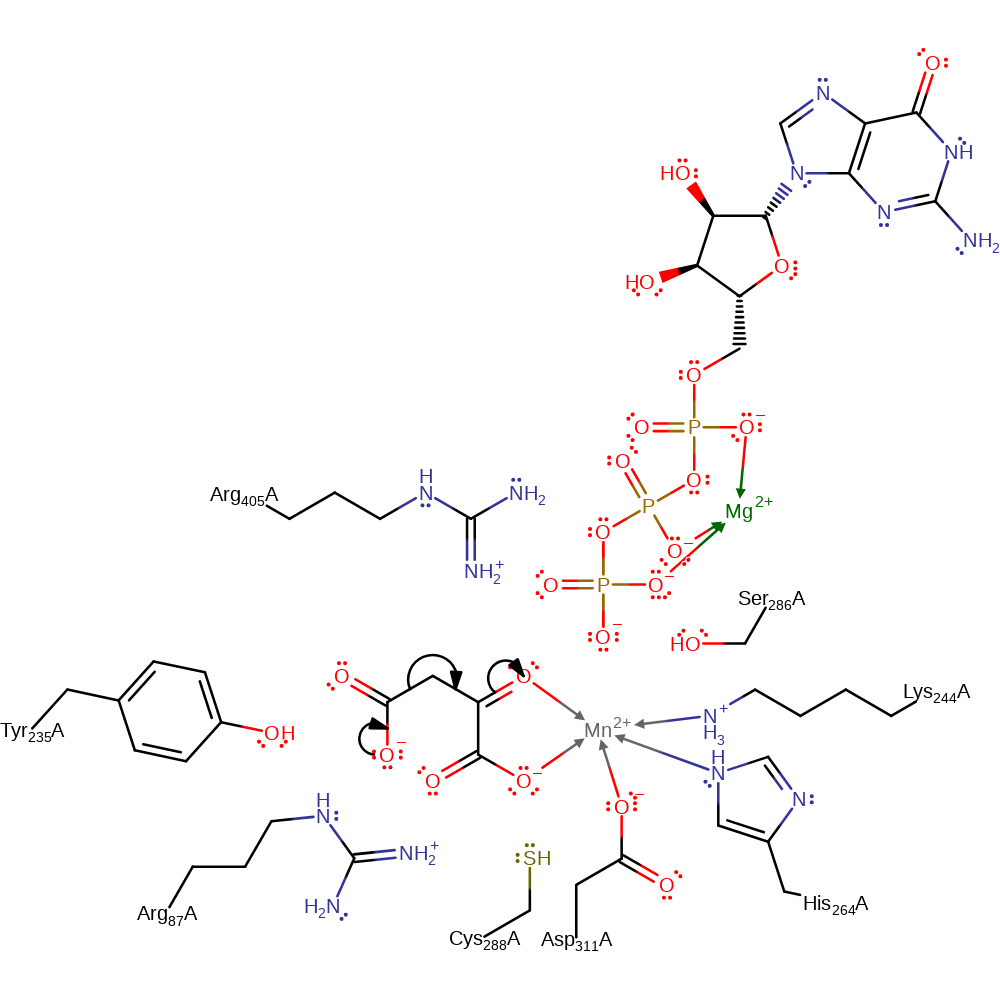
decarboxylation, ingold: intramolecular elimination, overall product formed, overall reactant used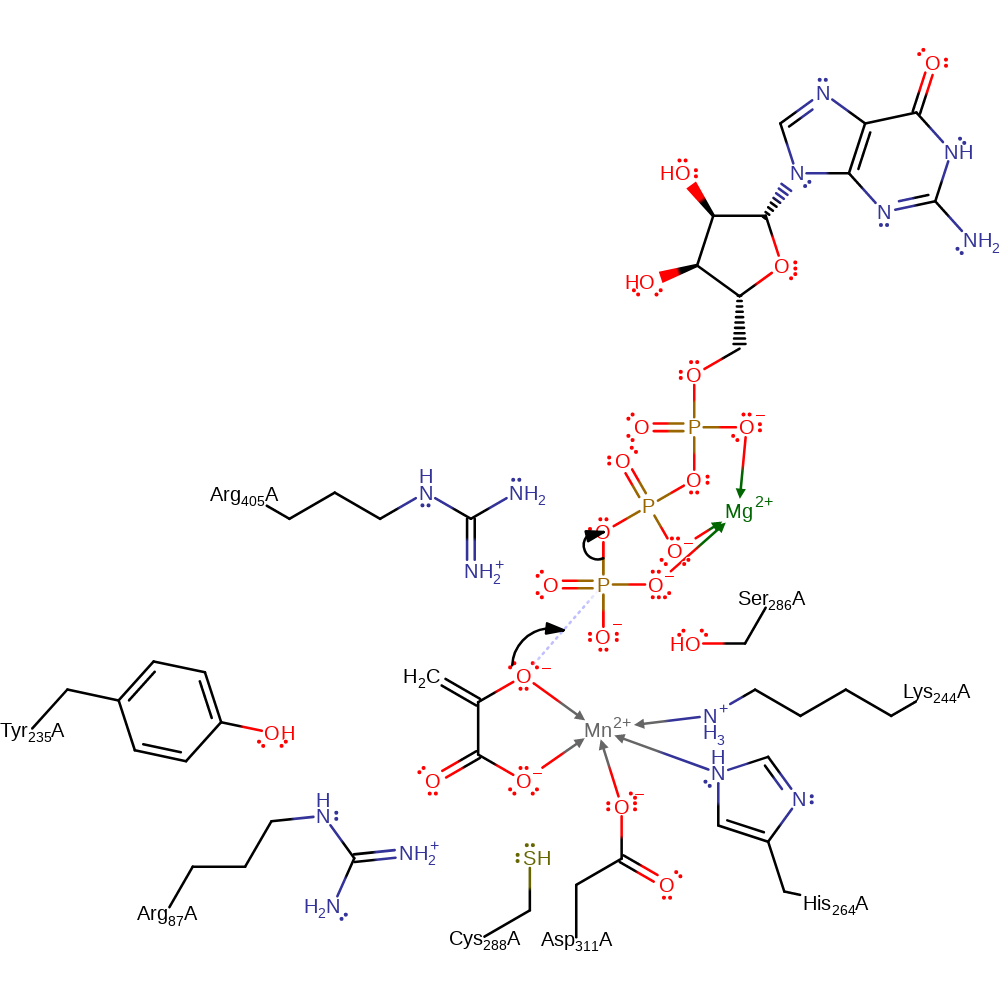
Step 2. The enolate intermediate attacks the alpha phosphate, eliminating GDP.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys244(247)A | metal ligand |
| Asp311(314)A | metal ligand |
| His264(267)A | metal ligand |
| Arg87(90)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr235(238)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser286(289)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg405(408)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr235(238)A | steric role |





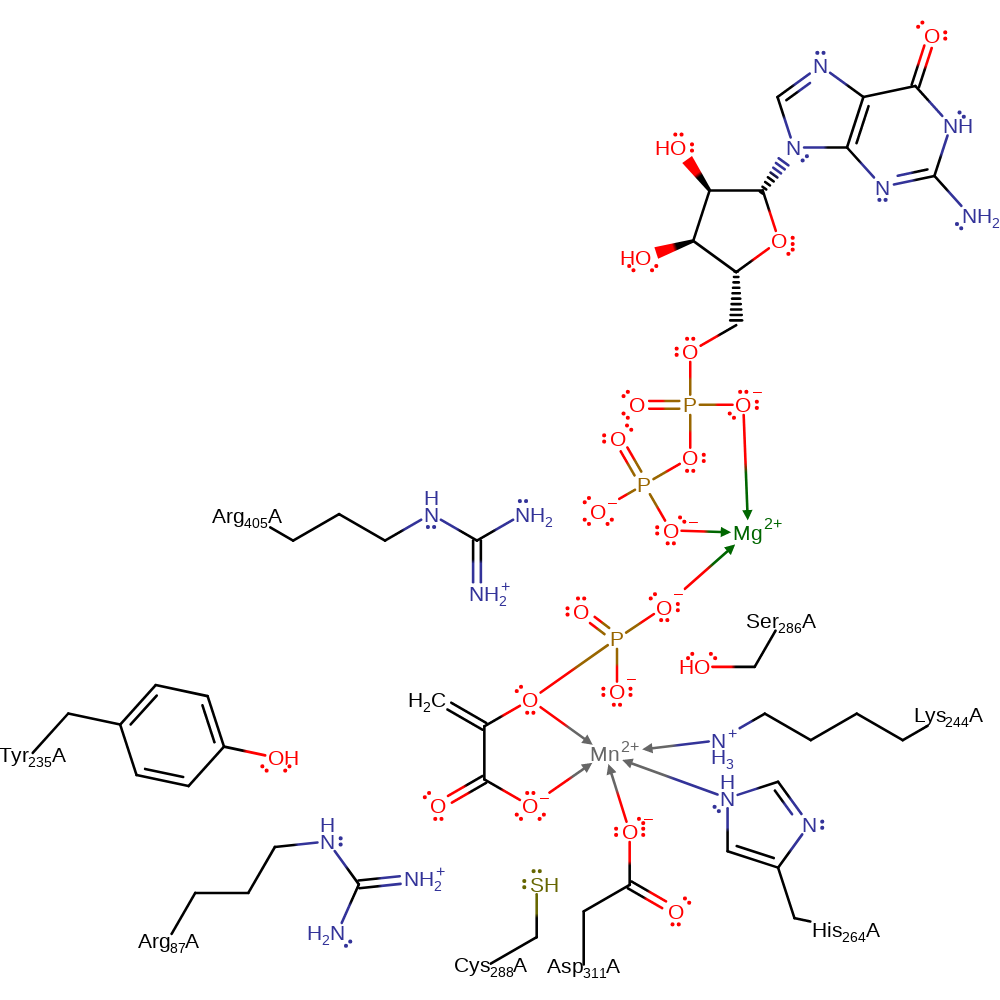 Download:
Download: