Cysteine desulfurase
The NifS-like protein belongs to the alpha family of pyridoxal-5' phosphate dependent enzymes also known as the aminotransferase class V. They act to remove the sulphur from L-Cysteine in a stereo conserved mechanism, forming L-Alanine and an enzyme-sulphanyl-cysteine component which loses the additional sulphur to acceptor proteins (the mechanism for this last step is not covered in this entry). The sulphur can be used to make compounds such as Iron-Sulphur clusters, biotin and tRNA thio-nucleotides.
The Escheria Coli protein is also able to catalyse selenocysteine deselenation in which L-selenocysteine is converted to selenium in the form of hydrogen selenium and L-alanine. Selenocysteine lyase has the ability to discriminate between selenium and sulfur, whereas many sulphur enzymes cannot. There are few examples of selenium-containing substrates.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P77444
 (2.8.1.7, 4.4.1.16)
(2.8.1.7, 4.4.1.16)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1i29
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CSDB COMPLEXED WITH L-PROPARGYLGLYCINE
(2.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.640.10
 3.90.1150.10
3.90.1150.10  (see all for 1i29)
(see all for 1i29)
- Cofactors
- Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate(2-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.8.1.7)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Cysteine desulfurases are thought to share a common mechanism. The first step is the transimination through the substrate cysteine displacing Lys226 from Lys-PLP to form Cys-PLP via a tetrahedral geminal diamine intermediate. The Schiff base linkage and pyridine ring has a conjugated pi electron withdrawing effect, facilitating deprotonation of C-alpha. Deprotonation is most likely by a nearby histidine, His123. Kinetic, mutagenesis and inhibition studies have ruled out Lys226 or the cys substrate itself behaving as a general base. Cys364 acts as a general acid to protonate C4. The first committed step in the reaction is the now thiolate on Cys364 to attack as a nucleophile, forming the enzyme persulfide-covalent intermediate and ala-PLP intermediate. Subsequent proton transfers between His123 and C-alpha and C4 via ketimine and quinonoid intermediates occurs. Finally, the reverse transimination reaction takes place via aldimine and a tetrahedral geminal diamine intermediate restore the cofactor for catalysis. The reduced Cys364 is used in numerous sulphur containing reactions such as in biosynthesis of Fe-S clusters, biotin and thio-tRNA-nucleosides.
Out of the two proposed mechanisms, this is favoured due to clear evidence ruling out Lys226 and the cysteine substrate acting as general bases. That being said, more work is needed to be done to identify exactly the catalytic residues involved (His123 has been used here to act as both the general acid and base, may in fact be more residues with these roles). One of the substrate cysteines is apart of the enzyme, labelled Cys364 in both mechanism proposals.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1i29) | ||
| Lys226 | Lys226A | In the ground state of the enzyme this residue is covalently attached to the PLP cofactor. Acts as both a general acid/base and catalytic nucleophile. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, electron pair acceptor |
| His123 | His123A | Conserved residue that acts as a general acid/base. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Gln203, Asp200 | Gln203A, Asp200A | Asp200 and Gln203 form hydrogen bonds with N7 and O3 of the pyridine ring in PLP helps stabilise the intermediates generated in the reaction. | polar interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys364 | Cys364A | Acts as a catalytic nucleophile in the sulfonation reaction. | covalently attached, nucleophile, proton donor |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, proton transfer, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, schiff base formed, charge delocalisation, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme is not regenerated, overall product formed, native state of cofactor regeneratedReferences
- Black KA et al. (2015), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1853, 1470-1480. Shared-intermediates in the biosynthesis of thio-cofactors: Mechanism and functions of cysteine desulfurases and sulfur acceptors. DOI:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.10.018. PMID:25447671.
- Behshad E et al. (2009), Biochemistry, 48, 12014-12023. Kinetic analysis of cysteine desulfurase CD0387 from Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803: formation of the persulfide intermediate. DOI:10.1021/bi802161u. PMID:19883076.
- Kaiser JT et al. (2000), J Mol Biol, 297, 451-464. Crystal structure of a NifS-like protein from Thermotoga maritima: implications for iron sulphur cluster assembly. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2000.3581. PMID:10715213.
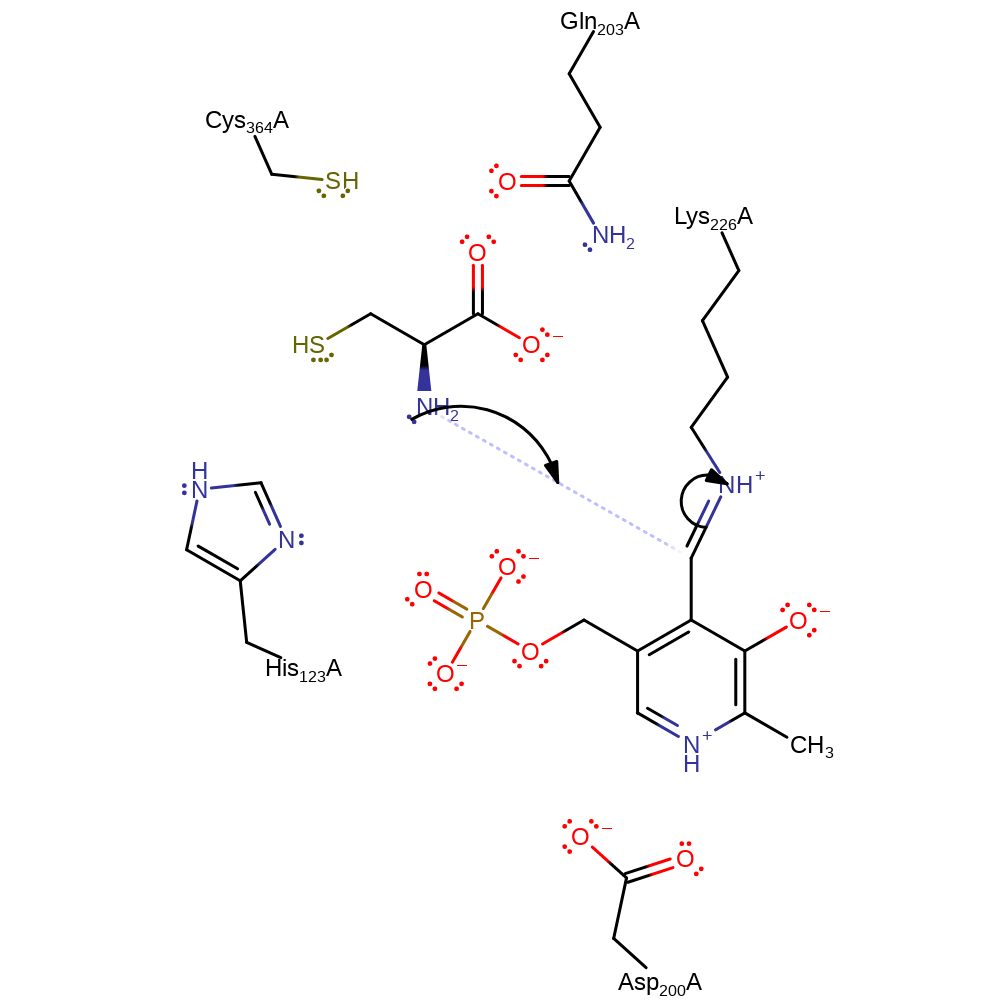
Step 1. Nucleophilic attack on C4A by cysteine amino to form a tetrahedral geminal diamine intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Asp200A | polar interaction |
| Lys226A | covalently attached |
| Asp200A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used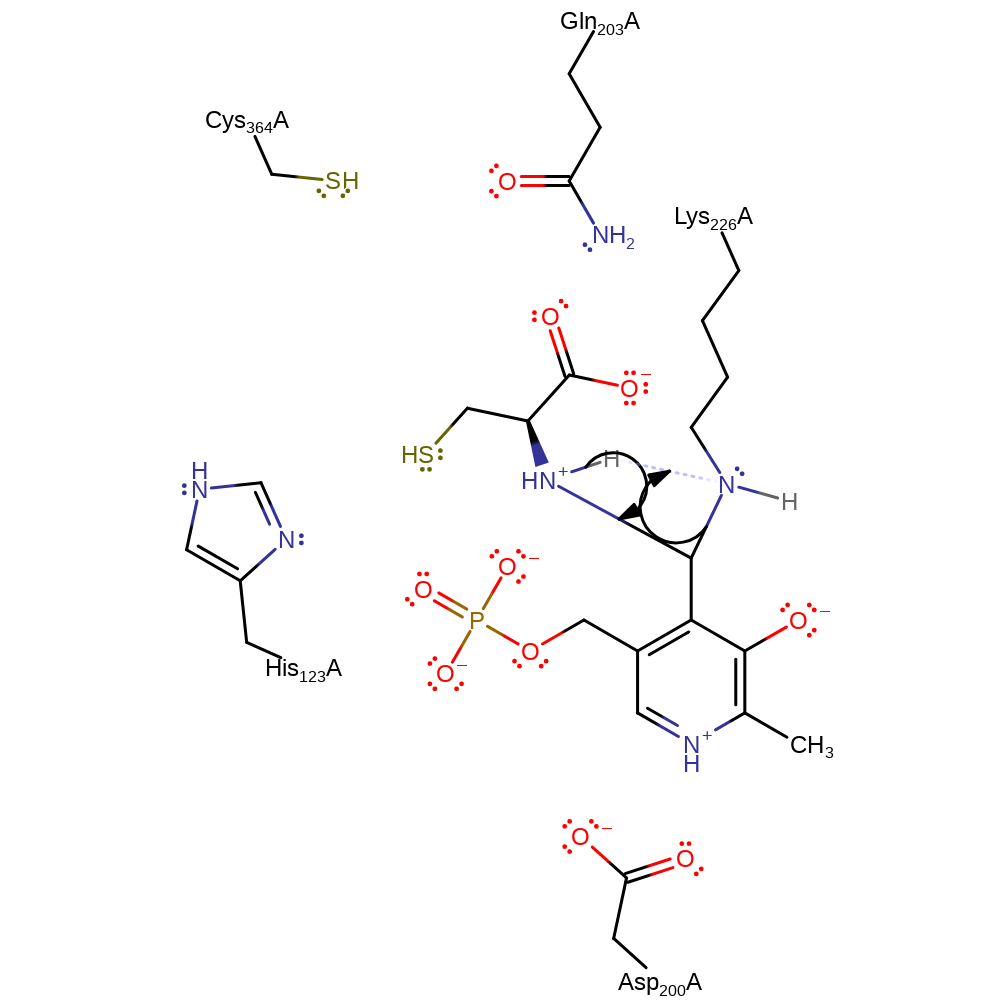
Step 2. Proton transfer coupled with tetrahedral intermediate collapse to form another Schiff base.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Asp200A | polar interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, schiff base formed
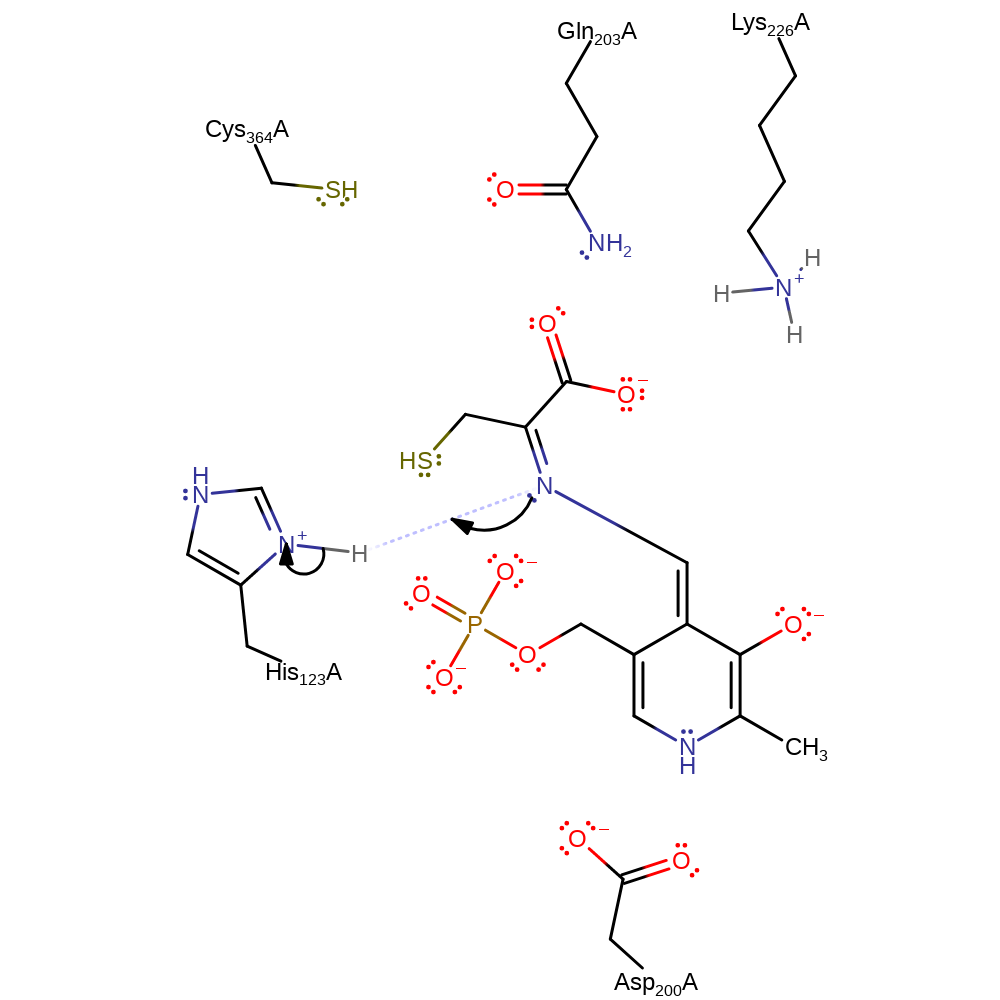
Step 3. PLP acts as an electron sink, facilitating deprotonation of C-alpha to form a Cys quinonoid intermediate. It is proposed His123 acts as the general base.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Asp200A | polar interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His123A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
charge delocalisation, proton transfer, intermediate collapse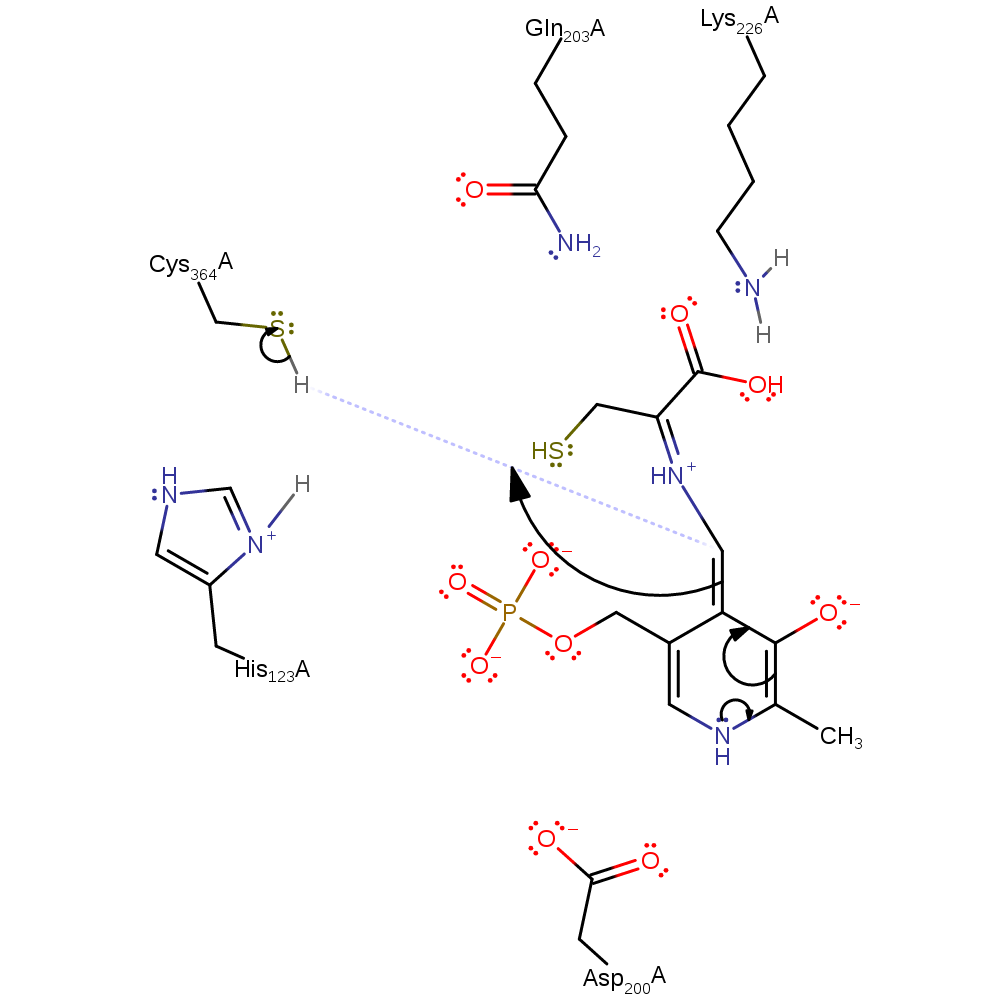
Step 4. Cys354 acts as a general acid to protonate C4 to form a ketimine intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Asp200A | polar interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys364A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
intermediate collapse, proton transfer, charge delocalisation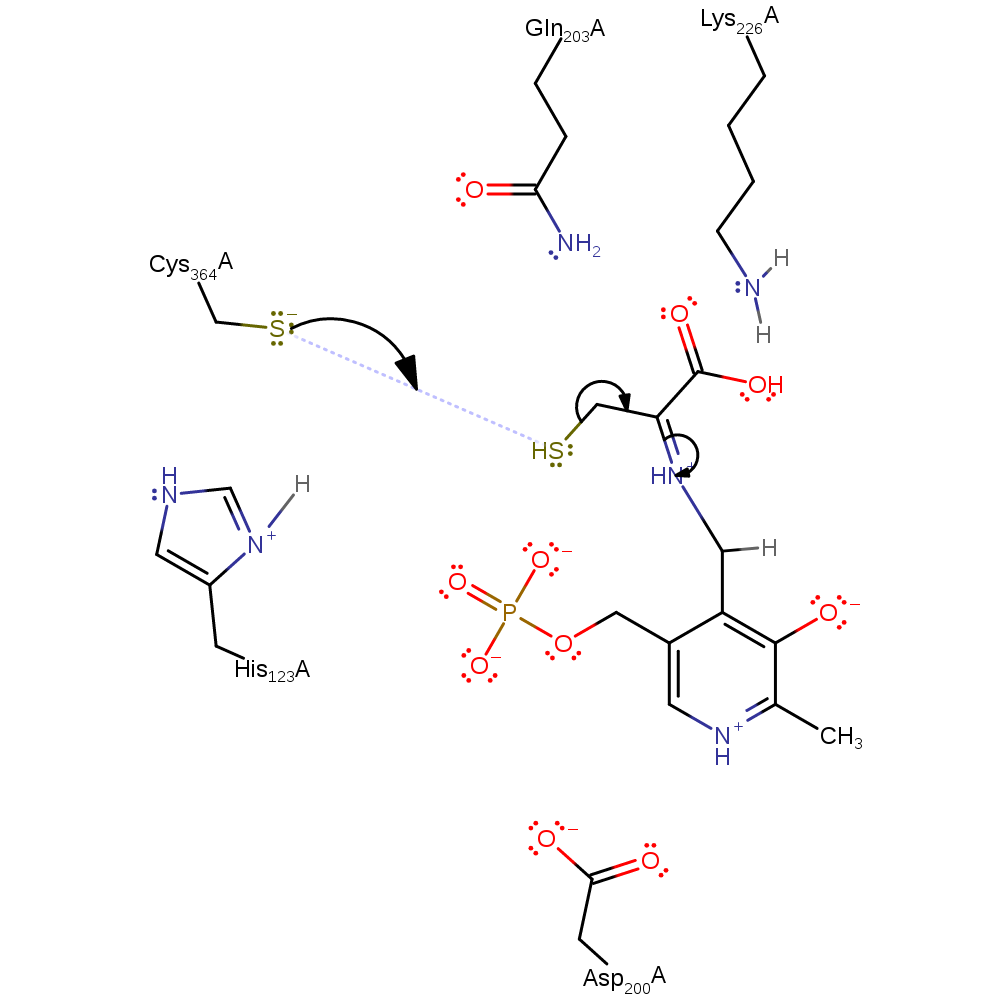
Step 5. Cys364 is activated to act as a nucleophile and attack the thiol group on the substrate cysteine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp200A | polar interaction |
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Cys364A | covalently attached |
| Asp200A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys364A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate collapse
Step 6. Ala-enamine intermediate is protonated at C-beta by His123 to form Ala-ketamine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp200A | polar interaction |
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Cys364A | covalently attached |
| Asp200A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His123A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate collapse
Step 7. His123 deprotonates C4 on Ala-ketimine to form Ala-quinonoid intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp200A | polar interaction |
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Cys364A | covalently attached |
| Asp200A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His123A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate collapse
Step 8. Quinonoid intermediate deprotonates His123 to form an Ala-aldimine intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys364A | covalently attached |
| Asp200A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His123A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate collapse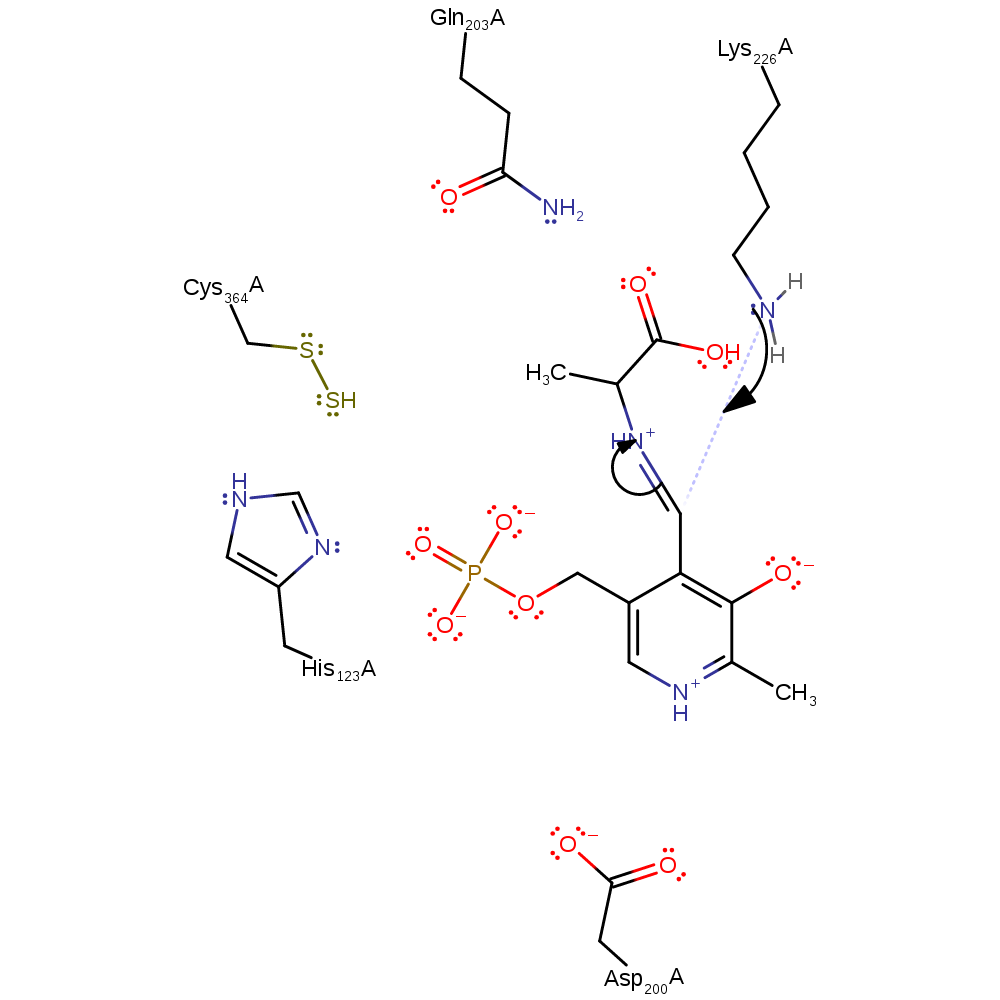
Step 9. Lys226 acts as a nucleophile and attacks C4 to again form a geminal diamine intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp200A | polar interaction |
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Lys226A | covalently attached |
| Cys364A | covalently attached |
| Asp200A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
intermediate collapse, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition
Step 10. Like before, tetrahedral intermediate collapse is coupled to proton transfer releasing L-alanine product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys226A | covalently attached |
| Asp200A | polar interaction |
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Asp200A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys364A | covalently attached |
| Lys226A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
schiff base formed, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme is not regenerated, overall product formed, native state of cofactor regeneratedIntroduction
Lys226 forms an imine linkage with PLP in the free enzyme. The catalytic residue His123 deprotonates the substrate amino group. The substrate cysteine then acts as a nucleophile to displace the Lys226 via a tetrahedral geminal diamine intermediate and forms a Schiff base with PLP. Schiff base and pyridine ring has a conjugated pi electron withdrawing effect, facilitating deprotonation of C-alpha on the substrate by Lys226. His123 activates Cys364 for nucleophilic attack in a substitution reaction on the cysteine-PLP intermediate, so that the intermediate thiol group is now bound to Cys364. To ready the enzyme for another round of catalysis, the PLP intermediate is protonated by His99 to form a ketimine intermediate, where PLP acts to push electrons for C-alpha to deprotonate Lys226. Lys226 subsequently acts as a nucleophile to attack the C4 on the PLP-intermediate to release L-alanine, regenerating the internal aldimine.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1i29) | ||
| Lys226 | Lys226A | In the ground state of the enzyme this residue is covalently attached to the PLP cofactor. Acts as both a general acid/base and catalytic nucleophile. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
| His123 | His123A | Acts as a general acid/base. | increase basicity, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Gln203, Asp200 | Gln203A, Asp200A | Asp200 and Gln203 form hydrogen bonds with N7 and O3 of the pyridine ring in PLP helps stabilise the intermediates generated in the reaction. | polar interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys364 | Cys364A | Acts as a catalytic nucleophile in the sulfonation reaction. | nucleophile, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, cofactor used, schiff base formed, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, charge delocalisation, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex formation, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme is not regeneratedReferences
- Kaiser JT et al. (2000), J Mol Biol, 297, 451-464. Crystal structure of a NifS-like protein from Thermotoga maritima: implications for iron sulphur cluster assembly. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2000.3581. PMID:10715213.
- Black KA et al. (2015), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1853, 1470-1480. Shared-intermediates in the biosynthesis of thio-cofactors: Mechanism and functions of cysteine desulfurases and sulfur acceptors. DOI:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.10.018. PMID:25447671.
- Mihara H et al. (2002), J Biochem, 131, 679-685. Structure of External Aldimine of Escherichia coli CsdB, an IscS/Nifs Homolog: Implications for Its Specificity toward Selenocysteine. DOI:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a003151. PMID:11983074.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp200A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | covalently attached |
| Asp200A | polar interaction |
| Gln203A | polar interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His123A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used
Step 2. Nucleophilic attack on C4 by cysteine amino group coupled to proton transfer between species.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys226A | covalently attached |
| Asp200A | polar interaction |
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Asp200A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | proton acceptor, electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, cofactor used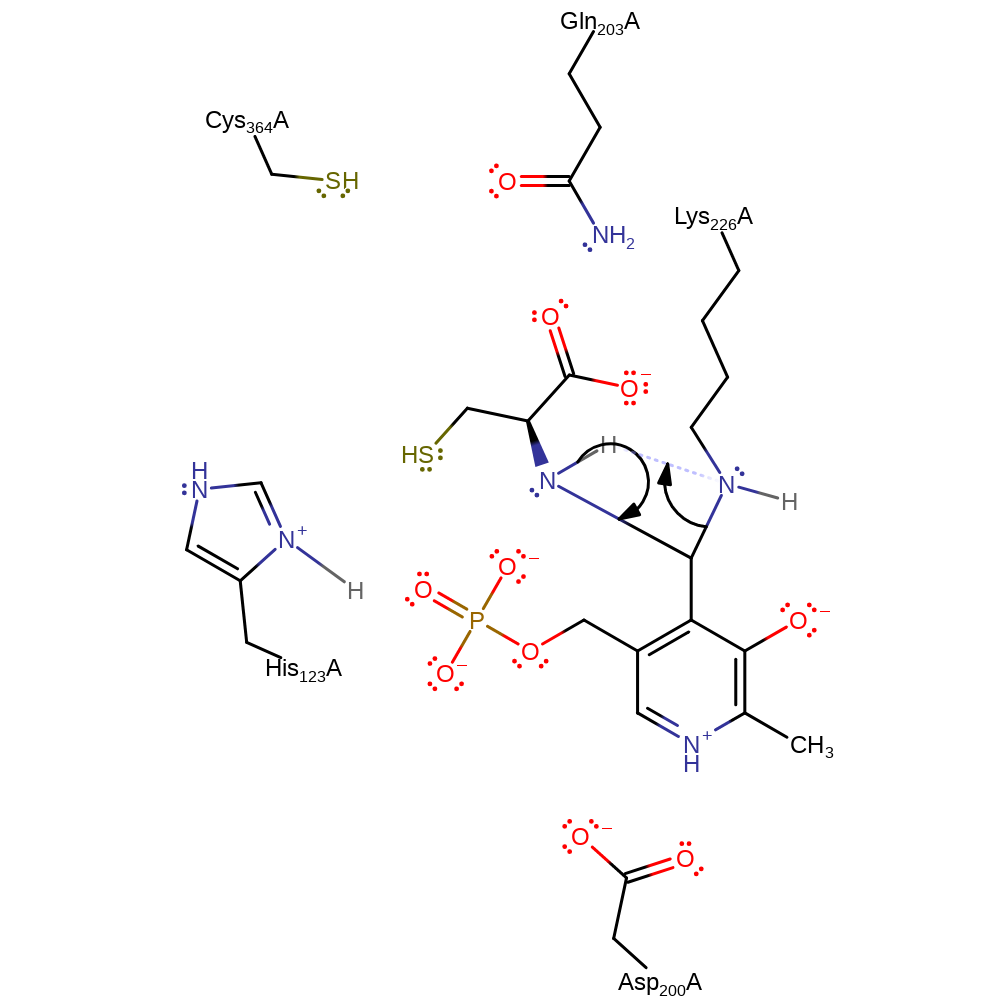
Step 3. Proton transfer coupled with tetrahedral intermediate collapse.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp200A | polar interaction |
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Asp200A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | proton acceptor, nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
schiff base formed, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage
Step 4. PLP acts as an electron sink, facilitating deprotonation by Lys226.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp200A | polar interaction |
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Asp200A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, charge delocalisation, intermediate collapseCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp200A | polar interaction |
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Asp200A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His123A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate collapse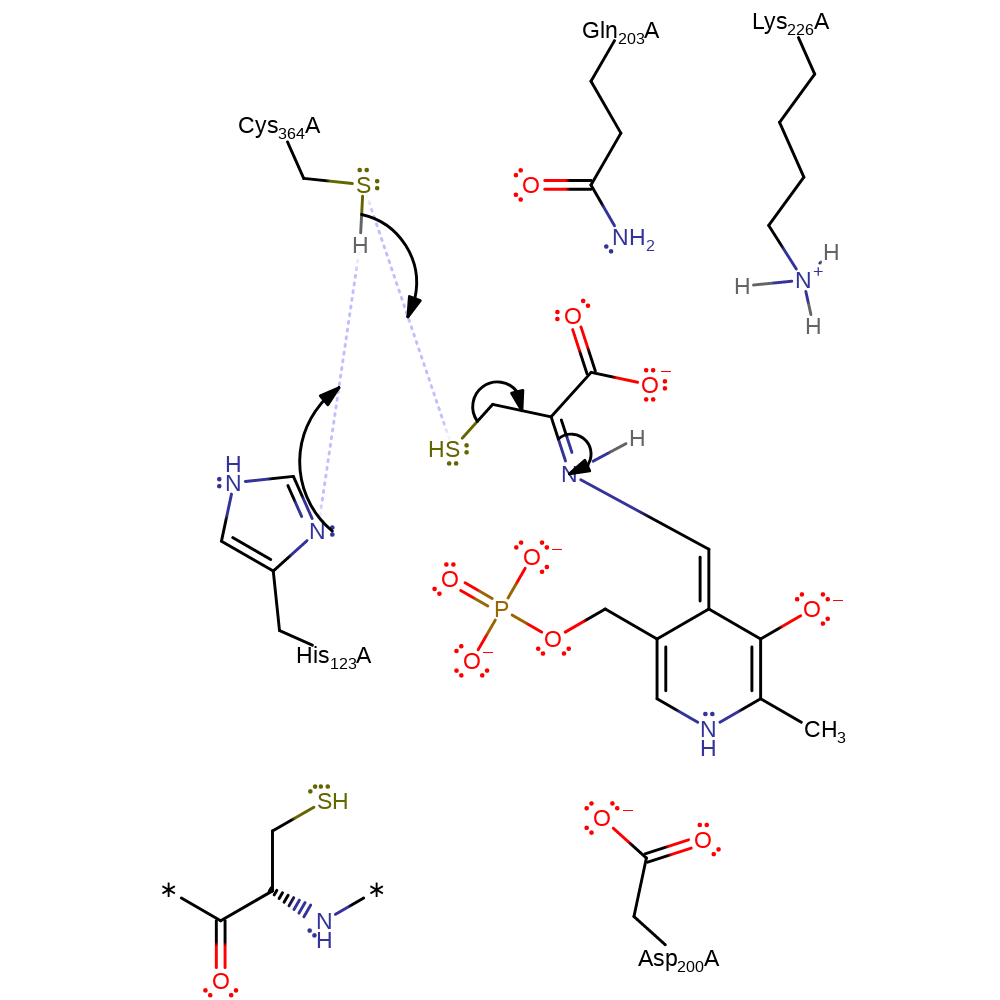
Step 6. Cys364 acts as a nucleophile to attack the thiol group on substrate cysteine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp200A | polar interaction |
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Asp200A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His123A | proton acceptor |
| Cys364A | nucleophile, proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall product formed, intermediate collapse, overall reactant usedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp200A | polar interaction |
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Asp200A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His123A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate collapse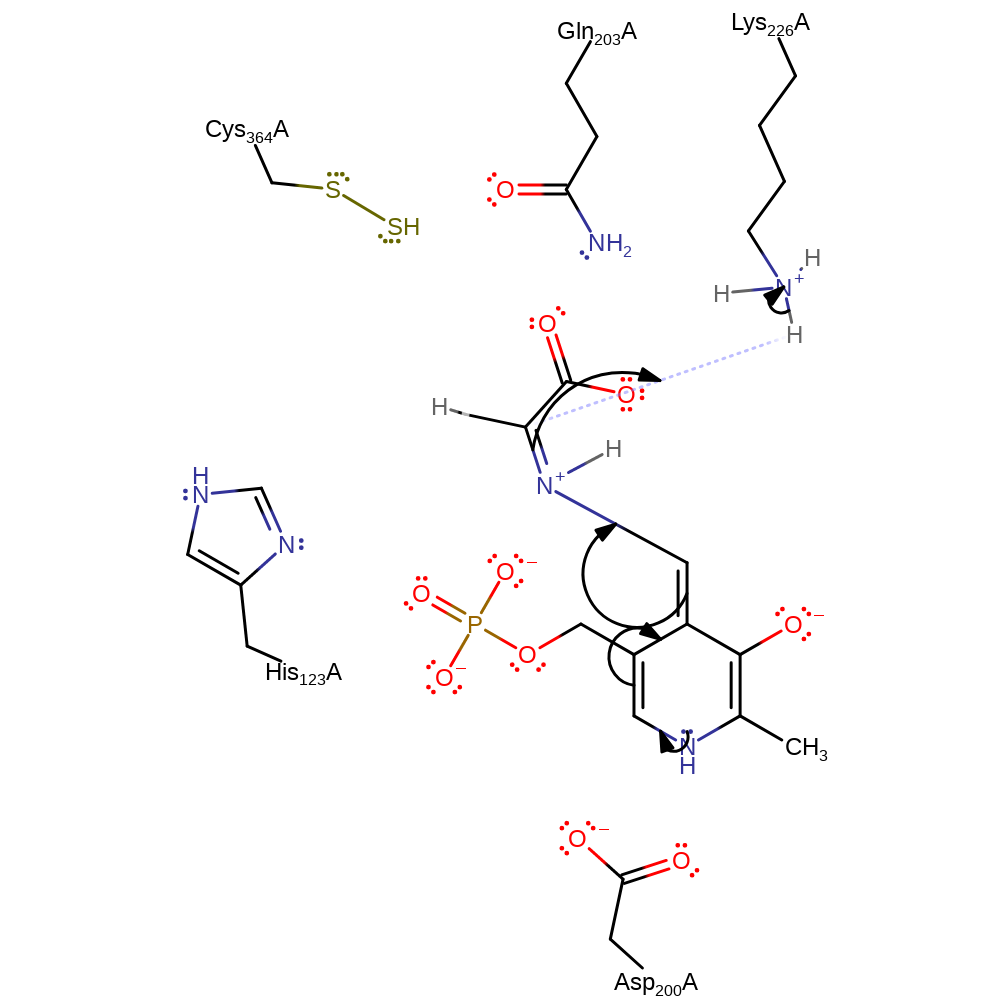
Step 8. His123 increases C4 of the intermediate's basicity to deprotonate Lys226.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His123A | increase basicity |
| Asp200A | polar interaction |
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Asp200A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate collapse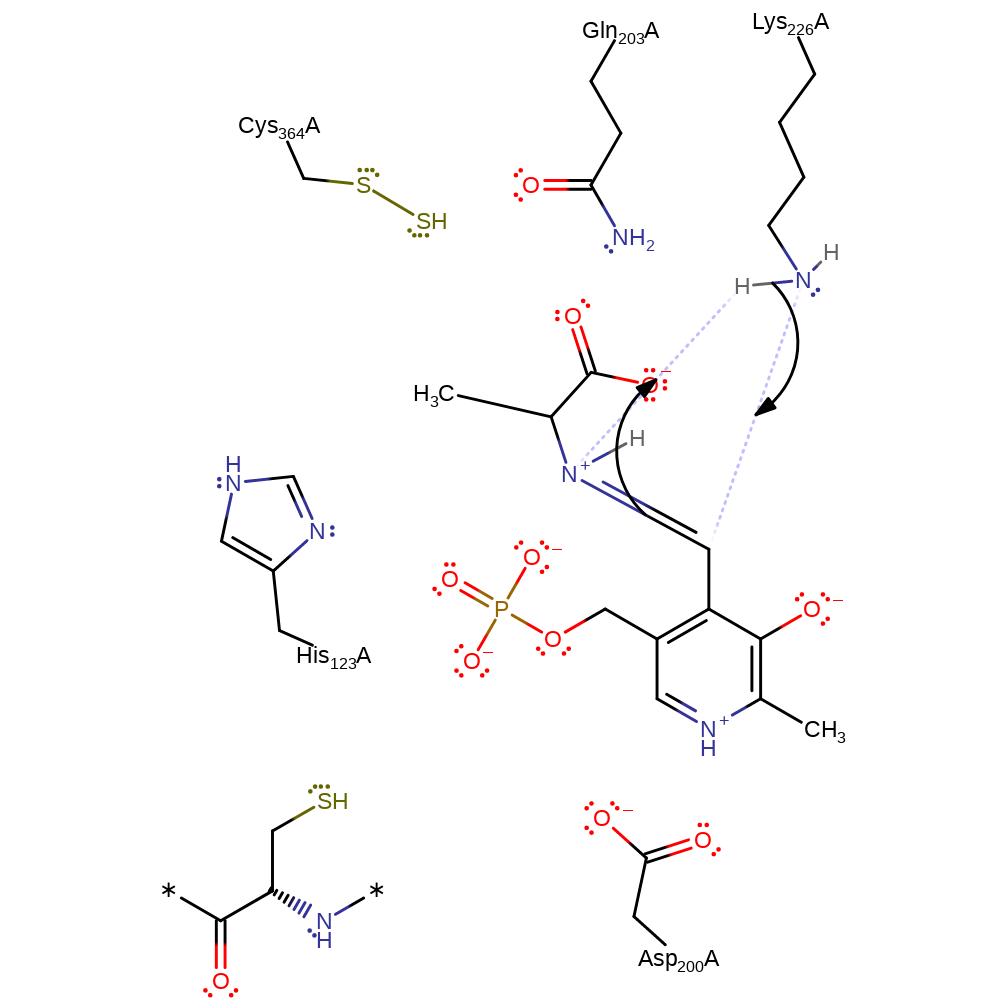
Step 9. Lys226 performs a nuclephilic attack to form another tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys226A | covalently attached |
| Asp200A | polar interaction |
| Gln203A | polar interaction |
| Asp200A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys226A | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys226A | covalently attached, proton donor, electron pair donor |




 Download:
Download: 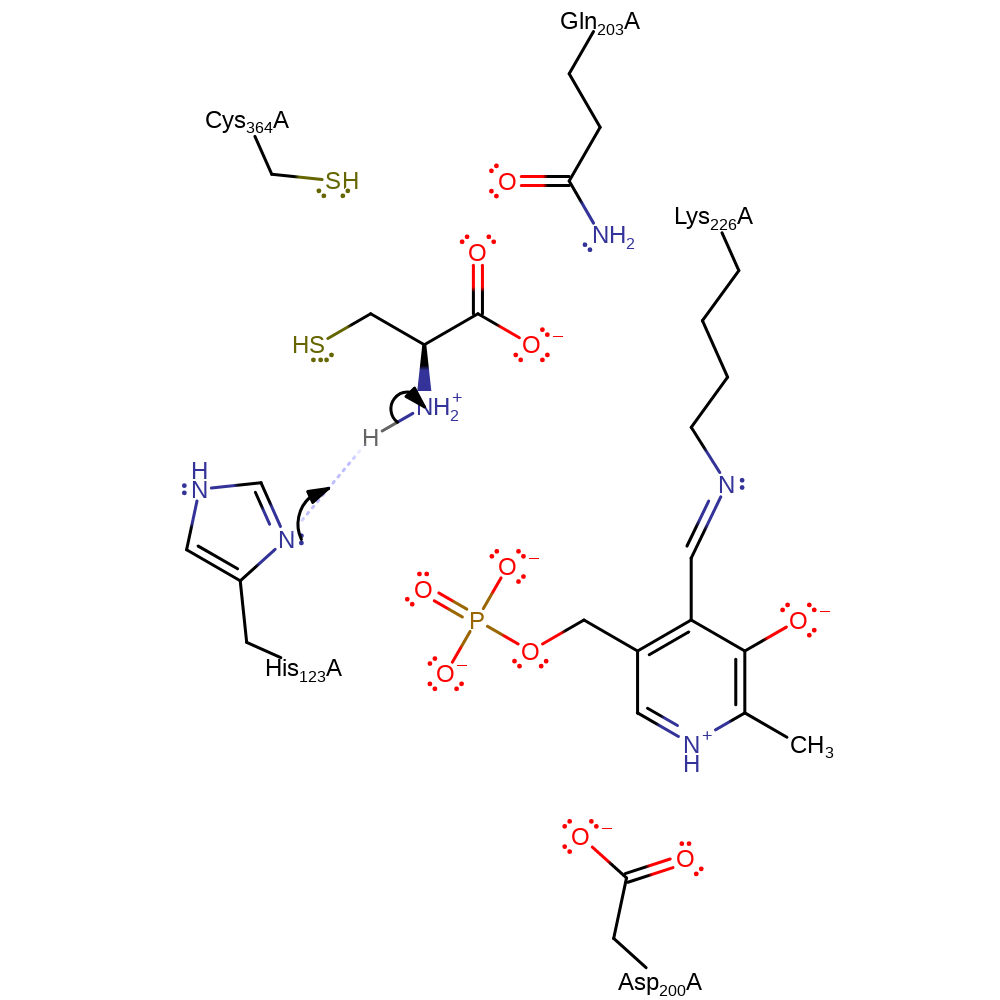


 Download:
Download: