2-dehydro-3-deoxyglucarate aldolase
5-keto-4-deoxy-D-glucarate aldolase GarL is involved in step 2 of the subpathway that synthesizes D-glycerate from galactarate. It catalyses the reversible retro-aldol cleavage of both 5-keto-4-deoxy-D-glucarate and 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-glucarate to pyruvate and tartronic semialdehyde.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P23522
 (4.1.2.20)
(4.1.2.20)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1dxe
- 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-galactarate aldolase from Escherichia coli
(1.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.60
 (see all for 1dxe)
(see all for 1dxe)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1), Water (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.1.2.20)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The Asp89-His50 intersubunit dyad deprotonates the metal-bound water molecule. The condensed substrate binds to the metal ion in a bidentate fashion with the C3 carbonyl and C4 hydroxyl interacting with Arg75. The metal-bound hydroxide ion, activated by the intersubunit Asp89-His50 dyad, abstracts the C4 hydroxyl proton, coupled with breakage of the C3−C4 carbon−carbon bond. The resulting aldehyde product and pyruvate enolate are stabilised by the metal ion and Arg74. Protonation of pyruvate enolate at C3 by the Asp89-His50-metal-bound water results in the other product pyruvate, returning the enzyme to the ground state and completing the catalytic cycle.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1dxe) | ||
| Arg75 | Arg75A | Helps stabilise the transition state. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu153, Asp179 | Glu153A, Asp179A | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
| His50 | His50A | Acts as a general acid/base. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp89 | Asp89A(AA) | Increases basicity of active site His50. | modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular elimination, overall product formed, overall reactant used, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Rea D et al. (2008), Biochemistry, 47, 9955-9965. Crystal structure and functional assignment of YfaU, a metal ion dependent class II aldolase from Escherichia coli K12. DOI:10.1021/bi800943g. PMID:18754683.
- Wang W et al. (2008), FEBS Lett, 582, 3385-3388. The role of a conserved histidine residue in a pyruvate-specific Class II aldolase. DOI:10.1016/j.febslet.2008.08.032. PMID:18775708.
- Rea D et al. (2007), J Mol Biol, 373, 866-876. Structure and mechanism of HpcH: a metal ion dependent class II aldolase from the homoprotocatechuate degradation pathway of Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.06.048. PMID:17881002.
- Wang W et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 9447-9455. Purification and biochemical characterization of a pyruvate-specific class II aldolase, HpaI. DOI:10.1021/bi050607y. PMID:15996099.
- Izard T et al. (2000), EMBO J, 19, 3849-3856. Crystal structures of the metal-dependent 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-galactarate aldolase suggest a novel reaction mechanism. DOI:10.1093/emboj/19.15.3849. PMID:10921867.
- Hubbard BK et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 14369-14375. Evolution of Enzymatic Activities in the Enolase Superfamily: Characterization of the (D)-Glucarate/Galactarate Catabolic Pathway inEscherichia coli†. DOI:10.1021/bi981124f. PMID:9772162.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp89A(AA) | modifies pKa |
| Arg75A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp179A | metal ligand |
| Glu153A | metal ligand |
| His50A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer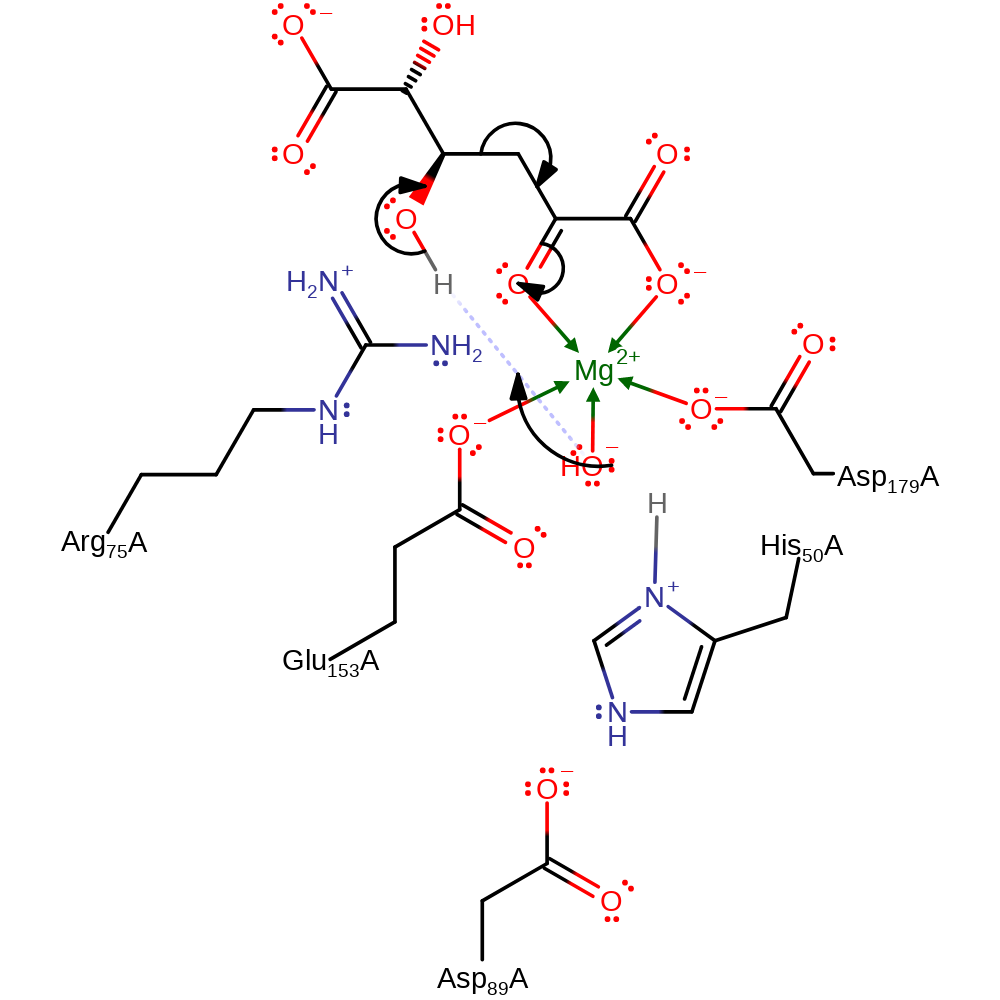
Step 2. The activated water abstracts a proton from the substrate, forming the aldehyde product and the pyruvoyl intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg75A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp89A(AA) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp179A | metal ligand |
| Glu153A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular elimination, overall product formed, overall reactant used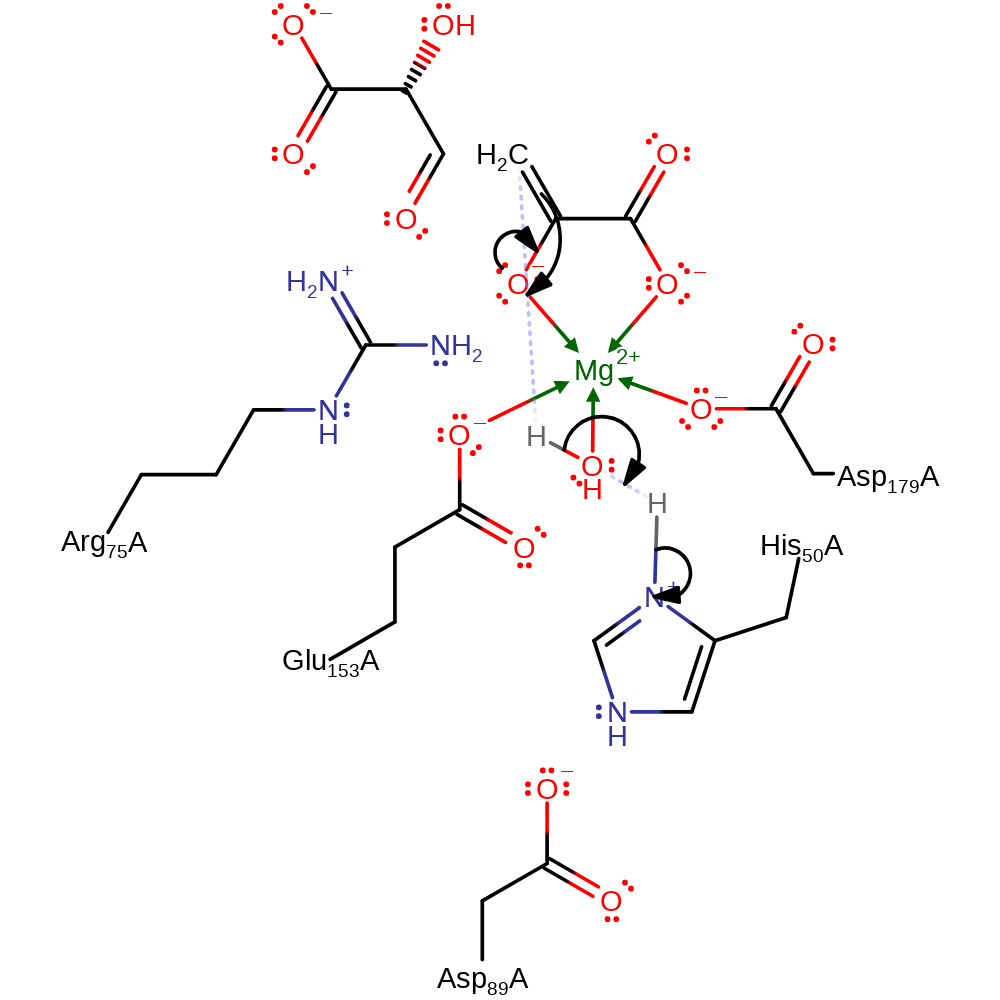
Step 3. The enolate intermediate collapses with concomitant deprtonation of the water molecule, which in turn abstracts a proton from His50.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp89A(AA) | modifies pKa |
| Arg75A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp179A | metal ligand |
| Glu153A | metal ligand |
| His50A | proton donor |



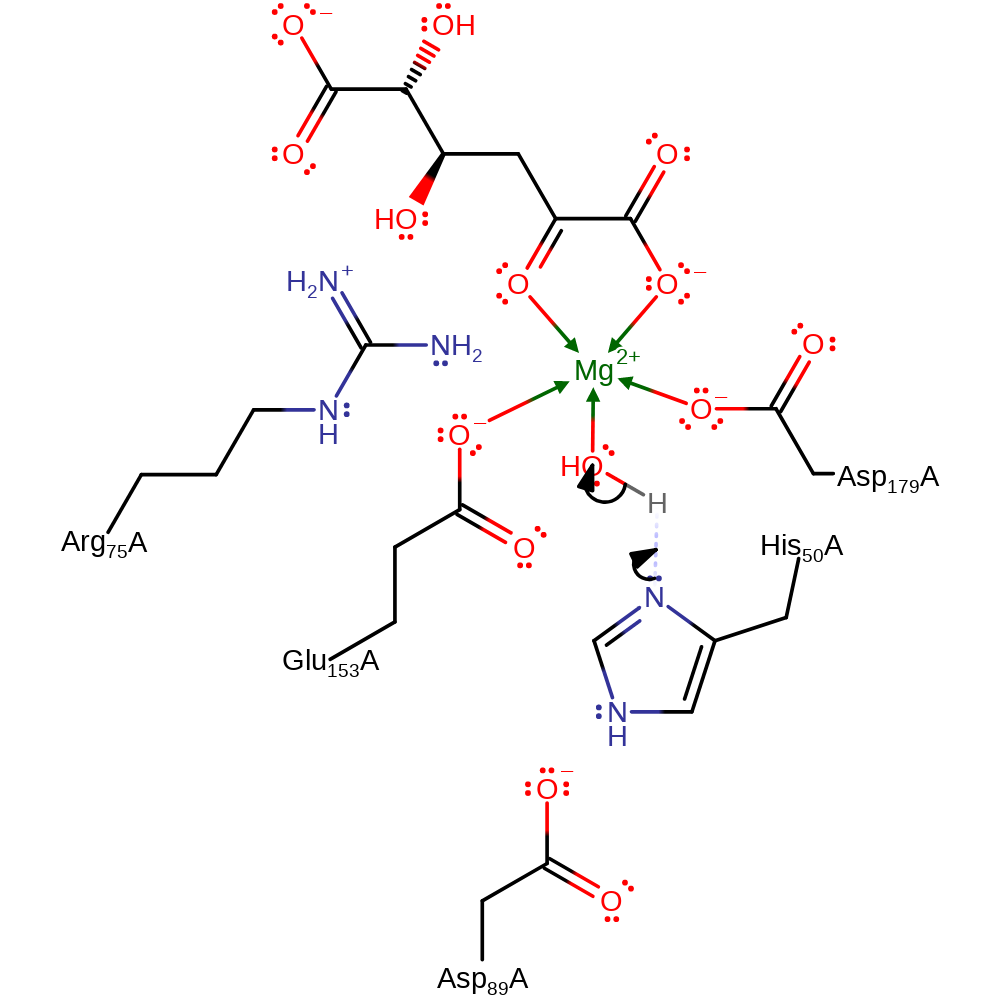
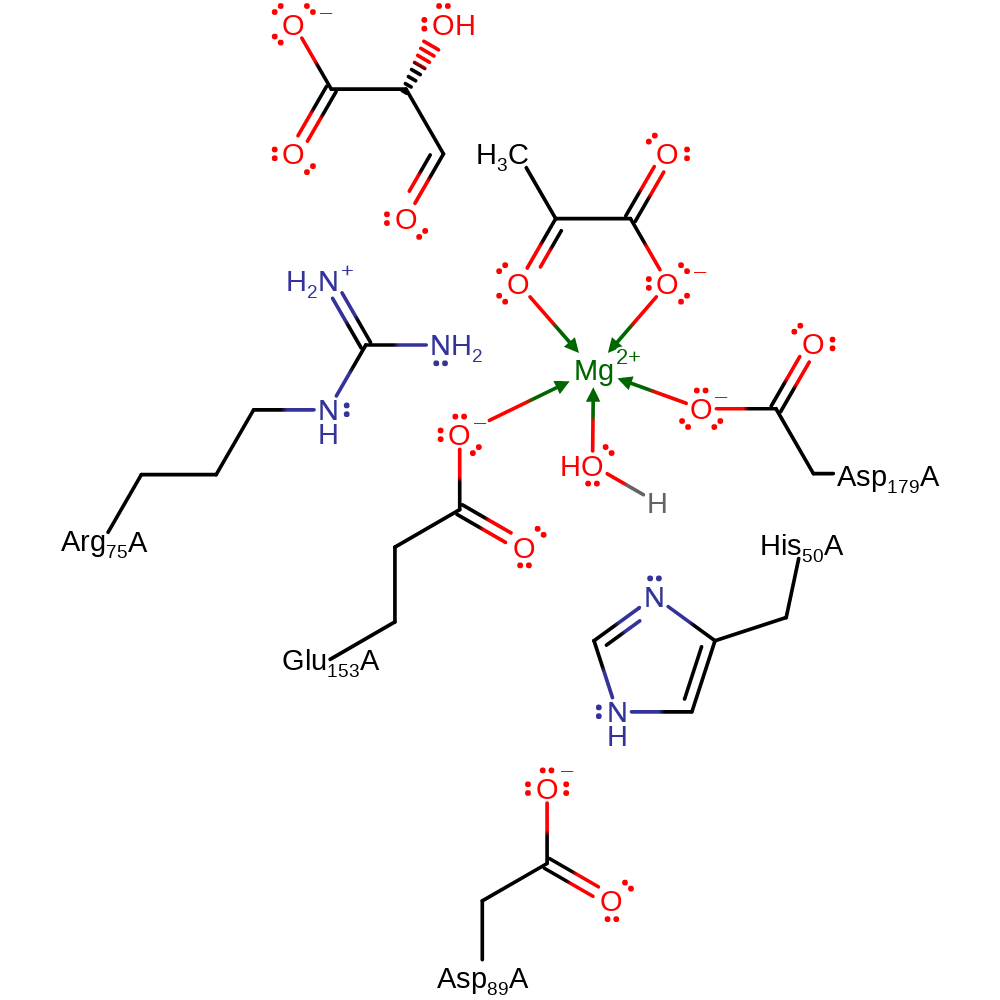 Download:
Download: