6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase
The enzyme 6-pyruvoyl tetrahyropterin synthase catalyses the second of three steps in the de novo biosynthesis of tetrahydrobiopterin, the conversion of dihydroneopterin triphosphate to 6-pyruvoyl tetrahyropterin. Tetrahydrobiopterin is the natural cofactor for several enzymes such as phenylalanine hydroxylase, tyrosine hydroxylase and tryptophan hydroxylase, nitric oxide synthase and glycerol ether monooxygenase. Lack of tetrahydrobiopterin leads to hyperphenylalaninaemia and a deficiency of the biogenic amine neurotransmitters, dopamine and serotonin and is accompanied by severe progressive mental retardation.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P27213
 (4.2.3.12)
(4.2.3.12)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat)

- PDB
-
1b66
- 6-PYRUVOYL TETRAHYDROPTERIN SYNTHASE
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.479.10
 (see all for 1b66)
(see all for 1b66)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.2.3.12)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The reaction involves a complex mechanism via a base catalysed redox transfer and a triphosphate elimination. Each of the six active sites are located at the interface of three subunits: two subunits, A and A', from one trimer and one, B, from another trimer. A Glu107 forms a salt bridge and A Met70 and A Thr106 form hydrogen bonds with the substrate. The active site zinc ion is coordinated by A His23, A His48 and A His50 as well as by a water molecule in the resting state. However when the substrate is bound a pentavalent coordination occurs with two hydroxyl groups from the substrate acting as ligands allowing the energetically unfavourable conformation of the complex to exist. The intersubunit catalytic triad consists of A Cys42, B His89 and B Asp88. It is thought that the residues of the catalytic triad activate the nucleophile A Cys42 for proton abstraction from the substrate leading to an enol intermediate which is stabilised by electrostatic interaction with Zn(II). The next step is the stereospecific protonation of the intermediate catalysed by A Glu133 to produce a 6_R stereoisomer followed by formation of a keto group. A Cys42 is now deprotonated possibly by the catalytic triad to enable abstraction of a second proton followed by the triphosphate elimination and keto-enol tautomerisation yielding the product 2-amino-4-oxo-6-7-8- dihydroneopterin.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1b66) | ||
| Cys42 | Cys42(38)A | Acts as a general acid/base. Part of the catalytic Asp-His-Cys triad. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu133 | Glu133(129)A | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His48, His50, His23 | His48(44)A, His50(46)A, His23(19)A | Forms part of the zinc binding site. | metal ligand |
| His89 | His89(85)B(BB) | The general acid/base, part of the catalytic Asp-His-Cys triad, that is responsible for activating the catalytic cysteine. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp88 | Asp88(84)B(BB) | Activates the histidine of the catalytic Asp-His-Cys triad to act as the general acid/base responsible for deprotonating the catalytic Cys. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, bimolecular elimination, dephosphorylation, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Ploom T et al. (1999), J Mol Biol, 286, 851-860. Crystallographic and kinetic investigations on the mechanism of 6-pyruvoyl tetrahydropterin synthase. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1998.2511. PMID:10024455.
- Miles ZD et al. (2014), J Biol Chem, 289, 23641-23652. Biochemical and Structural Studies of 6-Carboxy-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropterin Synthase Reveal the Molecular Basis of Catalytic Promiscuity within the Tunnel-fold Superfamily. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m114.555680. PMID:24990950.
- Bürgisser DM et al. (1995), J Mol Biol, 253, 358-369. 6-Pyruvoyl Tetrahydropterin Synthase, An Enzyme With a Novel Type of Active Site Involving Both Zinc Binding and an Intersubunit Catalytic Triad Motif; Site-directed Mutagenesis of the Proposed Active Center, Characterization of the Metal Binding Site and Modelling of substrate Binding. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1995.0558. PMID:7563095.
- Nar H et al. (1994), EMBO J, 13, 1255-1262. Three-dimensional structure of 6-pyruvoyl tetrahydropterin synthase, an enzyme involved in tetrahydrobiopterin biosynthesis. PMID:8137809.

Step 1. His89B, part of a Asp-His-Cys triad, deprotonates Cys42. The substrate deprotonates Glu133.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys42(38)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp88(84)B(BB) | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| His89(85)B(BB) | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| His48(44)A | metal ligand |
| His50(46)A | metal ligand |
| His23(19)A | metal ligand |
| Glu133(129)A | electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| His89(85)B(BB) | proton acceptor |
| Cys42(38)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation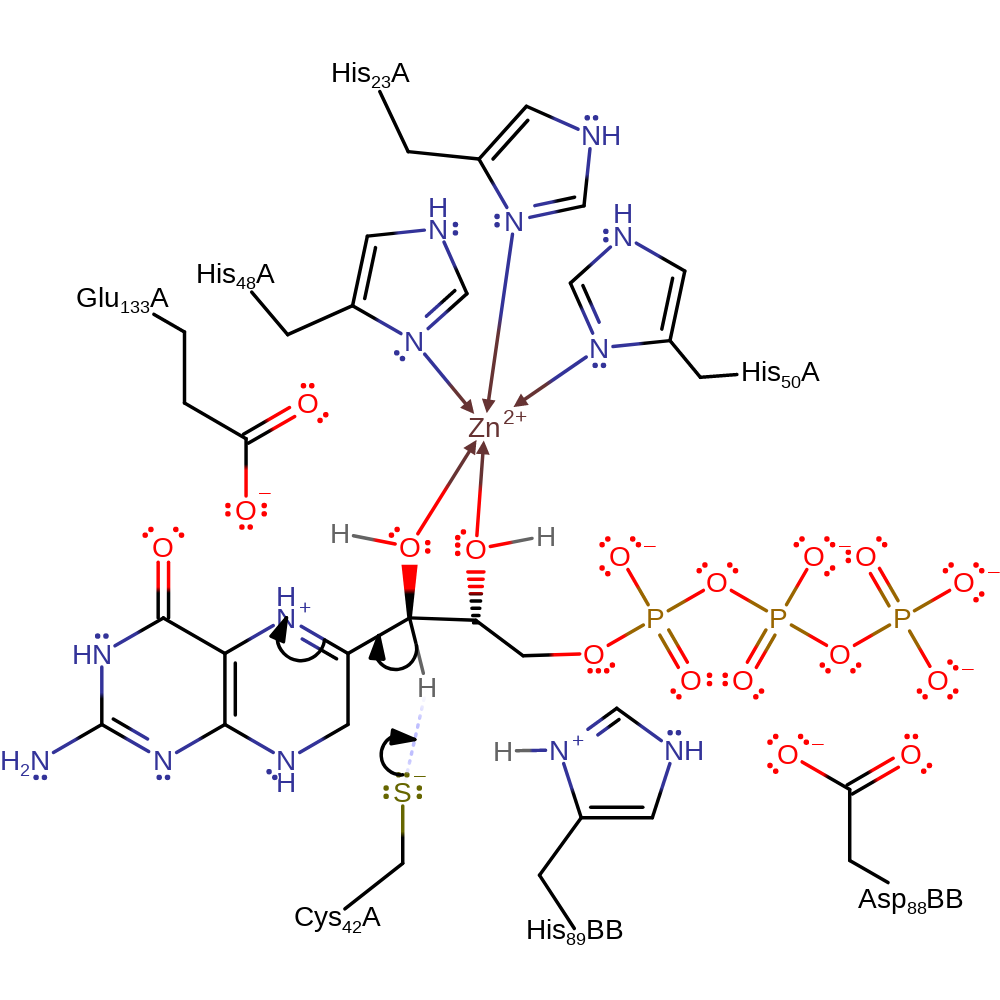
Step 2. Cys42 deprotonates the substrate, initiating double bond rearrangement for which the now positively charged secondary amine acts as an electron sink.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys42(38)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu133(129)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp88(84)B(BB) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His89(85)B(BB) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His48(44)A | metal ligand |
| His50(46)A | metal ligand |
| His23(19)A | metal ligand |
| Cys42(38)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), intermediate formation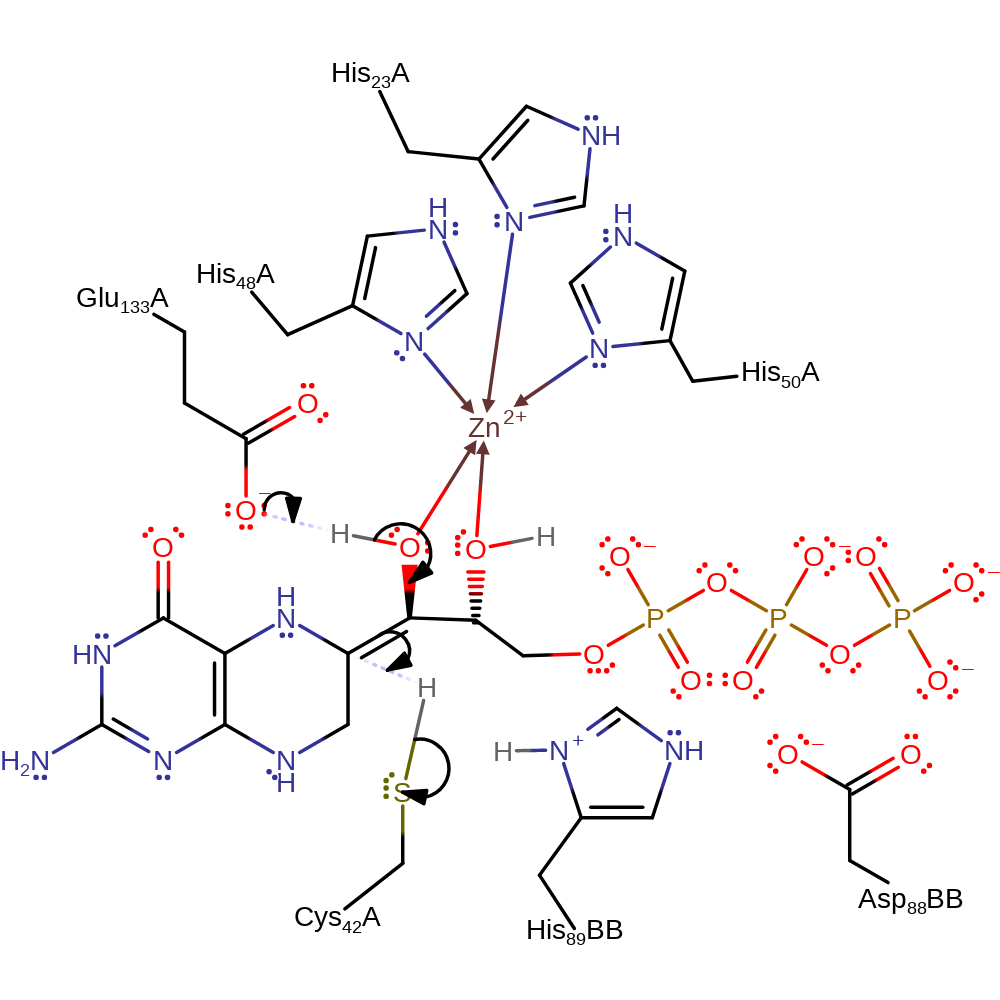
Step 3. Glu133 deprotonates the alcohol on the same carbon attacked by Cys42. This formed the keto-group and causes the double bond to deprotonate the Cys42.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys42(38)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu133(129)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp88(84)B(BB) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His89(85)B(BB) | hydrogen bond donor |
| His48(44)A | metal ligand |
| His50(46)A | metal ligand |
| His23(19)A | metal ligand |
| Cys42(38)A | proton donor |
| Glu133(129)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intermediate formation
Step 4. Cys42 deprotonates the second carbon of the substrate carbon chain, which causes the formation of a new double bond and elimination of the diphosphate group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys42(38)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu133(129)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp88(84)B(BB) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His89(85)B(BB) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His48(44)A | metal ligand |
| His50(46)A | metal ligand |
| His23(19)A | metal ligand |
| Cys42(38)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, dephosphorylation, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation
Step 5. The newly released diphosphate deprotonates the remaining alcohol group, which forms the ketol-form of the intermediate and causes the double bond to deprotonate Cys42.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys42(38)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu133(129)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp88(84)B(BB) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His89(85)B(BB) | hydrogen bond donor |
| His48(44)A | metal ligand |
| His50(46)A | metal ligand |
| His23(19)A | metal ligand |
| Cys42(38)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall product formed, intermediate terminatedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys42(38)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp88(84)B(BB) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His89(85)B(BB) | hydrogen bond donor |
| His48(44)A | metal ligand |
| His50(46)A | metal ligand |
| His23(19)A | metal ligand |
| Asp88(84)B(BB) | activator |
| Cys42(38)A | proton acceptor |
| His89(85)B(BB) | proton donor |





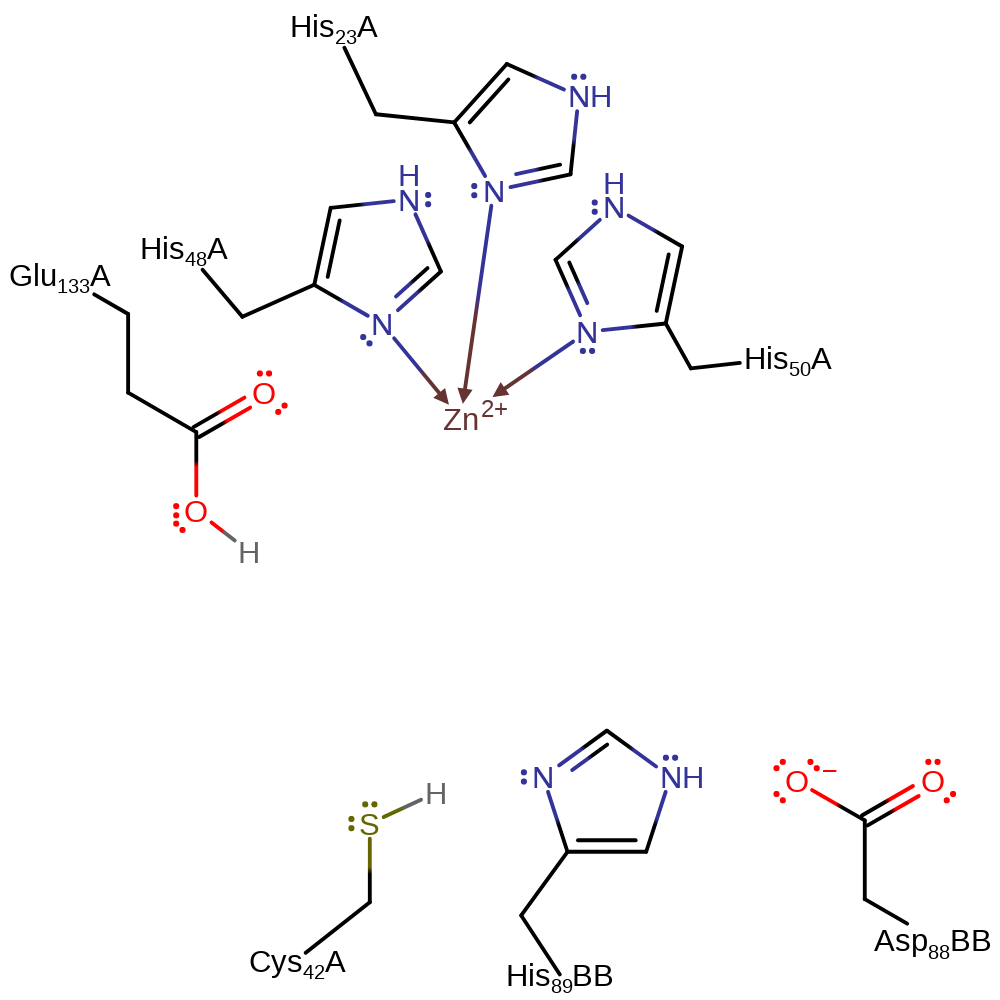 Download:
Download: