Ubiquitinyl hydrolase 1 (peptidase C30 type)
The SARS coronavirus main protease dimer (Mpro) is the key enzyme in the processing of the viral polyproteins and thus an attractive target for the discovery of drugs against SARS. The SARS CoV main protease is a cysteine proteinase with a chymostrypsin-like fold. The enzyme cleaves the two overlapping translation products of the SARS coronavirus replicase gene. Hence, inhibition of Mpro leads to prevention of the proteolytic processing of coronavirus replicase polyproteins, stopping the production of of infectious virus particles. The dimer is the enzymatically active species and the conformational state of Mpro is highly pH-sensitive due to the pH-dependence of the protonation state of two histidine residues in the substrate binding site.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0C6X7
 (2.1.1.-, 2.7.7.48, 3.1.-.-, 3.1.13.-, 3.4.19.12, 3.4.22.-, 3.4.22.69, 3.6.4.12, 3.6.4.13)
(2.1.1.-, 2.7.7.48, 3.1.-.-, 3.1.13.-, 3.4.19.12, 3.4.22.-, 3.4.22.69, 3.6.4.12, 3.6.4.13)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus

- PDB
-
2bx4
- Crystal Structure of SARS Coronavirus Main Proteinase (P21212)
(2.79 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.40.10.10
 (see all for 2bx4)
(see all for 2bx4)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.19.12)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The Mpro active site is situated in a cleft between domains I (residues 8-101) and II (residues 102-184) and comprises a catalytic dyad consiting of conserved residues Cys 3385 and His 3281. A buried water molecule is hydrogen bonded to His 3281 and is considered the third component of a catalytic triad. The fold of the Mpro enzyme at the catalytic site resembles that of the serine proteinase, chymotrypsin, but with an active-site serine-to-cysteine substitution. The catalytic site contains a hydrogen bonded thiol....imidazole ion pair , with the uncharged thiol acting as the nucleophile, and the His 3821 as a general base. Deprotonation of the Cys 3385 sulfhydryl by an adjacent residue with a basic side chain. The thiolate ion is stabilised through the formation of an ion pair with the neighbouring imidazolium group of His 3821. A buried water molecule completes the catalytic triad by forming a hydrogen bond to the N(e2)H of His 3821. This effect of this is to both stabilise the ion pair and also keep the imidazole ring of the His residue in favourable orientation. The oxyanion is stabilised by an oxyanion hole, the amide backbone of Cys 3385 and Gly 3383. Nucleophilic attack of the anionic cysteine S (thiolate ion) on the peptide carbonyl carbon. In this step, a fragment of the substrate is released with an amine terminus, the histidine residue in the protease is restored to its deprotonated form, and a thioester intermediate linking the new carboxy-terminus of the substrate to the cysteine thiol is formed. The thioester bond is subsequently hydrolysed to generate a carboxylic acid moiety on the remaining substrate fragment, whilst regenerating the free enzyme
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2bx4) | ||
| Cys3385 (main-N), Gly3383 (main-N) | Cys145A (main-N), Gly143A (main-N) | Stabilises the tetrahedral intermediate by reducing the negative charge on the oxyanion with Cys 3385 by the amide hydrogen bonding to the oxygen. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys3385 | Cys145A | Deprotonation of Cys 145 activates it towrads nucleophilic attack of the peptide bond in the substrate. The thiolate ion is stabilised by the formation of an active site ion pair with the His 41 imidazole ring. The main chain NH of Cys 145 forms part of the oxyanion hole, which stabilises the transition state. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His3281 | His41A | The basic side chain of the His residue deprotonates the Cys thiol, activating it towards nucleophilic attack, The His imidazole ring forms an active site ion pair with the Cys thiol. His 41 also forms a hydrogen bond to the buried water molecule that completes that catalytic triad. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Tan J et al. (2005), J Mol Biol, 354, 25-40. pH-dependent Conformational Flexibility of the SARS-CoV Main Proteinase (Mpro) Dimer: Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Multiple X-ray Structure Analyses. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.09.012. PMID:16242152.
- Paasche A et al. (2014), Biochemistry, 53, 5930-5946. Evidence for substrate binding-induced zwitterion formation in the catalytic Cys-His dyad of the SARS-CoV main protease. DOI:10.1021/bi400604t. PMID:25196915.
- Solowiej J et al. (2008), Biochemistry, 47, 2617-2630. Steady-state and pre-steady-state kinetic evaluation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) 3CLpro cysteine protease: development of an ion-pair model for catalysis. DOI:10.1021/bi702107v. PMID:18237196.
- Yin J et al. (2007), J Mol Biol, 371, 1060-1074. A mechanistic view of enzyme inhibition and peptide hydrolysis in the active site of the SARS-CoV 3C-like peptidase. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.06.001. PMID:17599357.
- Du QS et al. (2004), Peptides, 25, 1857-1864. Polyprotein cleavage mechanism of SARS CoV Mpro and chemical modification of the octapeptide. DOI:10.1016/j.peptides.2004.06.018. PMID:15501516.

Step 1. His3281 deprotonates Cys3385 which actiavtes it so it can attack the carbon of the carbonyl in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly143A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys145A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys145A | nucleophile, proton donor |
| His41A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates an elimination which results in the cleavage of the peptide bond. The N-terminal product accepts a proton from His3281.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly143A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys145A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His41A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, overall product formed
Step 3. His3281 abstracts a proton from a water which activates it to attack the carbon of the thioester bond in a nuclophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly143A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys145A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His41A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used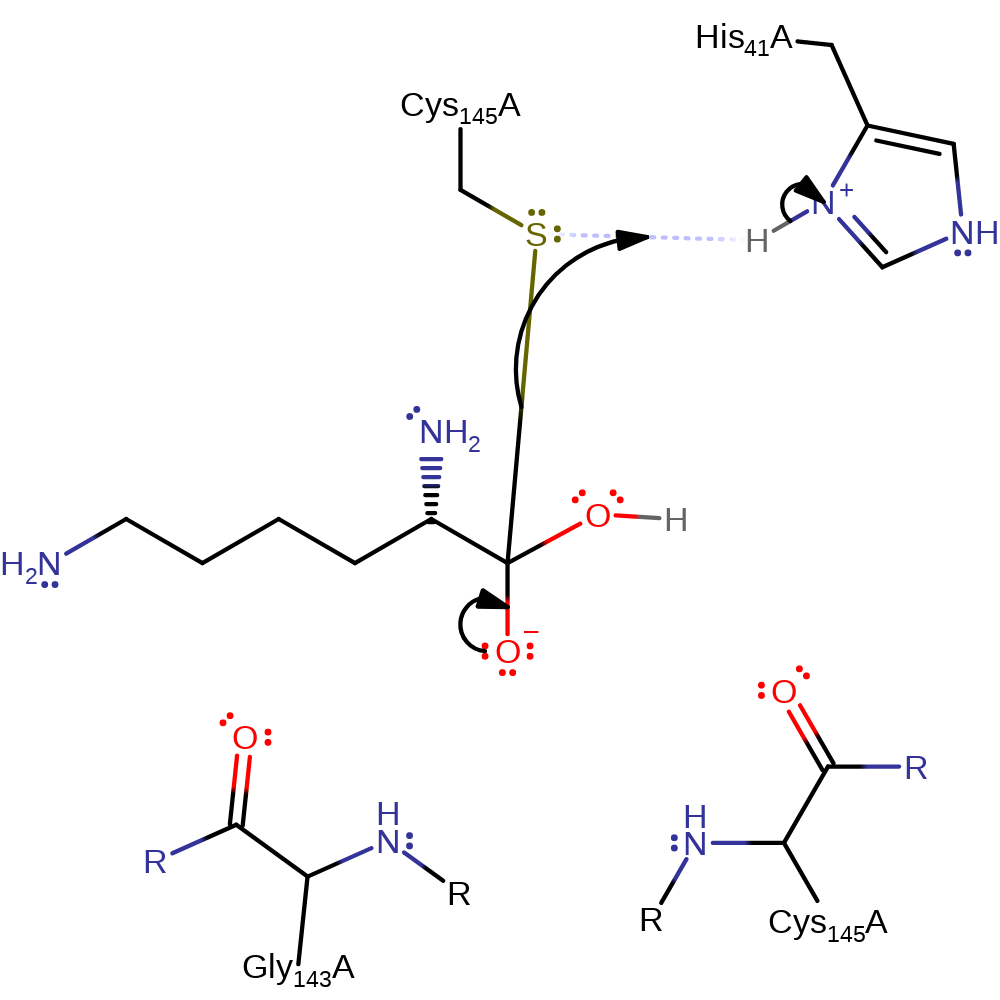
Step 4. The oxyanion initiates another elimination which results in the cleavage of the thioester bond. The released Cys3385 now accepts a proton from His3281 which returns the enzyme to its native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly143A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys145A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys145A | proton acceptor |
| His41A | proton donor |
| Cys145A | nucleofuge |




 Download:
Download: