ADP-ribose diphosphatase
The ADP-ribose-specific Nudix hydrolase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MT-ADPRase or ADPR pyrophosphatase) is part of the family of Nudix hydrolases with the characteristic Nudix box that catalyse hydrolysis of nucleoside diphosphate derivatives. Divalent magnesium or manganese ions are required for activity. Differences in binding sites of the M. tuberculosis enzyme and the human homologue suggest a possible target for antituberculosis drug treatment.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
O33199

 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis CDC1551 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1mqw
- Structure of the MT-ADPRase in complex with three Mn2+ ions and AMPCPR, a Nudix enzyme
(2.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.79.10
 (see all for 1mqw)
(see all for 1mqw)
- Cofactors
- Manganese(2+) (3)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.6.1.13)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Glu 142, activated by a metal ion, acts as a general base catalyst in activating a water molecule for nucleophilic attack on the alpha-phosphate of the substrate. the water is also activated by binding to two manganese ions. The charges in the alpha-phosphate are stabilised by the metal ions. Charges in the beta-phosphate are stabilised by a metal ion and the Arg 64 side-chain.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1mqw) | ||
| Arg64 | Arg64A | Activates the substrate and stabilises the leaving group | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu142 | Glu142A | Acts as a general base catalyst to deprotonate the water molecule thus activating it as a nucleophile. | metal ligand, proton acceptor |
| Glu93, Glu97, Ala76 (main-C), Glu142 | Glu93A, Glu97A, Ala76A (main-C), Glu142A | Form metal binding site | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, coordination to a metal ion, overall reactant used, overall product formedReferences
- Kang LW et al. (2003), Structure, 11, 1015-1023. Structure and Mechanism of MT-ADPRase, a Nudix Hydrolase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(03)00154-0. PMID:12906832.
- Furuike Y et al. (2016), Biochemistry, 55, 1801-1812. ADP-Ribose Pyrophosphatase Reaction in Crystalline State Conducted by Consecutive Binding of Two Manganese(II) Ions as Cofactors. DOI:10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00886. PMID:26979298.
- Mildvan AS et al. (2005), Arch Biochem Biophys, 433, 129-143. Structures and mechanisms of Nudix hydrolases. DOI:10.1016/j.abb.2004.08.017. PMID:15581572.
- Gabelli SB et al. (2002), Biochemistry, 41, 9279-9285. Mechanism of theEscherichia coliADP-Ribose Pyrophosphatase, a Nudix Hydrolase†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi0259296. PMID:12135348.
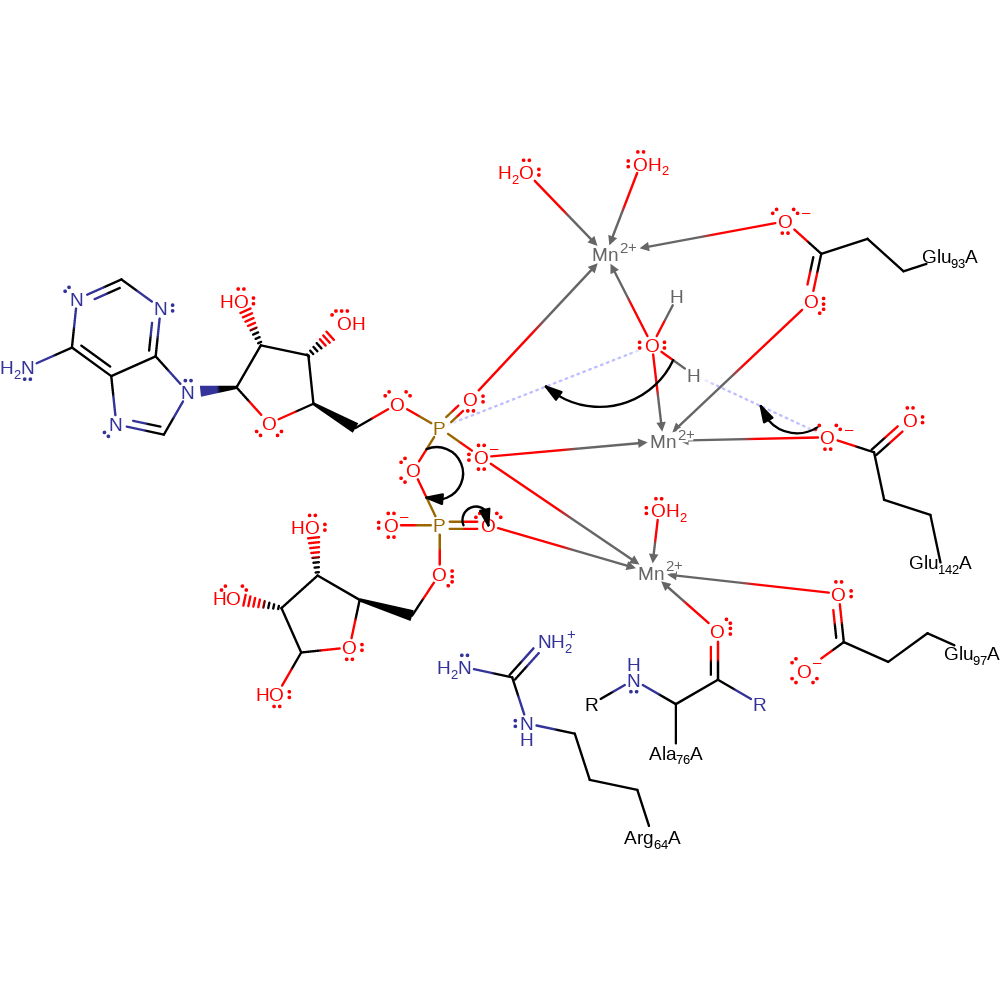
Step 1. A water molecule is activated for nucleophilic attack through polarization by Mn2+ and through its deprotonation by Glu 142. The activated water then attacks the Phosphorus of the alpha-phosphate which results in the cleavage of the phosphoanhydride bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg64A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala76A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu93A | metal ligand |
| Glu97A | metal ligand |
| Glu142A | metal ligand |
| Glu142A | proton acceptor |





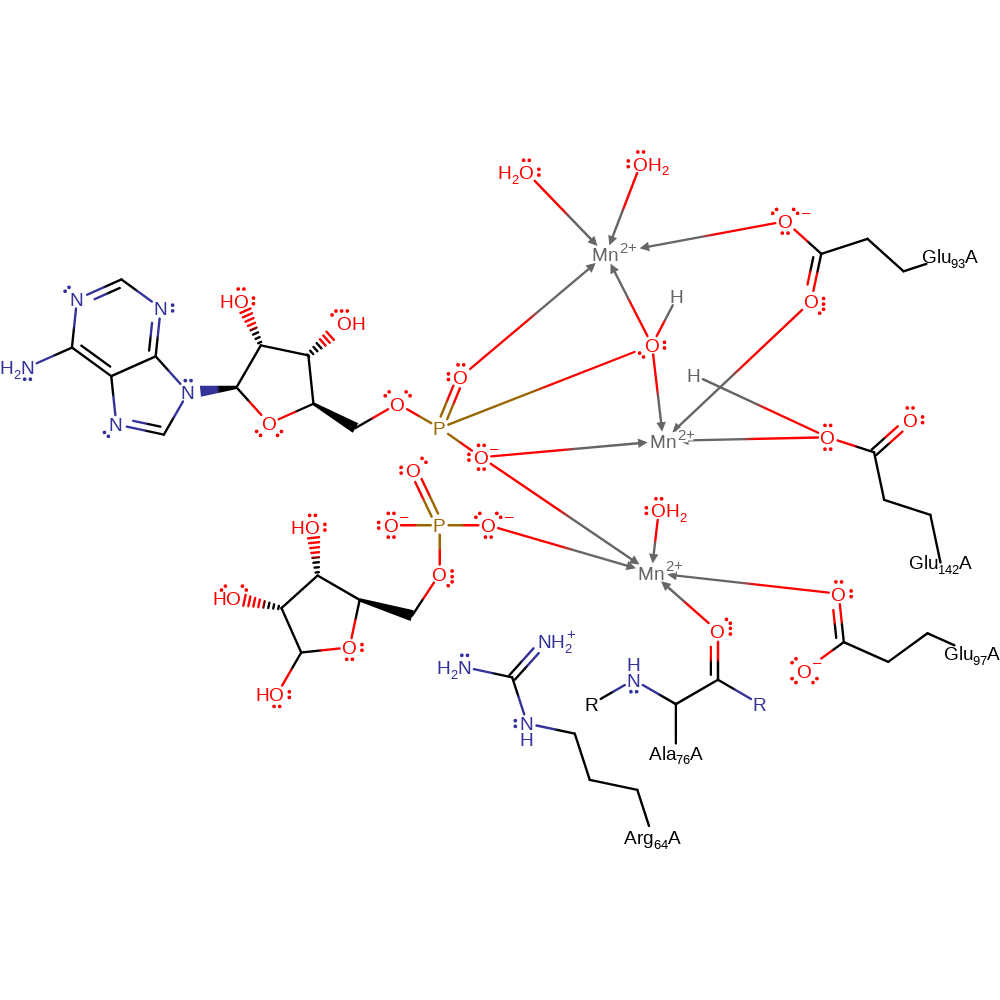 Download:
Download: