Chitinase (GH18, class II)
Chitinase A1 from Bacillus circulans catalyses the hydrolysis of the 1,4-beta linkages of N-acetyl-D glucosamine polymers of chitin. For bacteria, this hydrolysis is utilised primarily as carbon and energy sources. Chitinase A1 is proposed to be very similar to hen egg-white lysozyme, differing only in that it undergoes a 'substrate assisted' mechanism.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P20533
 (3.2.1.14)
(3.2.1.14)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bacillus circulans (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1itx
- Catalytic Domain of Chitinase A1 from Bacillus circulans WL-12
(1.1 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.80
 (see all for 1itx)
(see all for 1itx)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.2.1.14)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The nitrogen atom of the substrate pushes electrons up toward the acetyl group, causing the oxygen atom of the acetyl to nucleophilically attack the C1 atom of the substrate. This breaks the C1-O bond, and the leaving group oxygen atom is protonated by Glu 204. Asp 202 and Tyr 279 distort the substrate to encourage the intiatial nucleophilic attack. Asp 200, Asp202 and Tyr279 stabilise the positive charge on the substrate. Glu 204 then acts as a general base, deprotonating a water molecule and activating it for nucleophilic attack on the substrate C1 atom. The N-acetyl group is reformed, and the product leaves.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1itx) | ||
| Asp202, Tyr279 | Asp202(170)A, Tyr279(247)A | Stabilise the positive charge of the intermediate and distort the substrate to encourage the formation of the intermediate. | electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Asp200 | Asp200(168)A | The side chain of Asp 200 stabilises the positively charged intermediate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu204 | Glu204(172)A | Glu 204 acts as a general acid/base by protonating the leaving group, and by deprotonating a water molecule to activate it. | proton acceptor, proton donor, activator, increase nucleophilicity, promote heterolysis |
Chemical Components
overall product formed, overall reactant used, proton transfer, intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, cyclisation, native state of enzyme regenerated, decyclisation, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, hydrolysisReferences
- Watanabe T et al. (1993), J Biol Chem, 268, 18567-18572. Identification of glutamic acid 204 and aspartic acid 200 in chitinase A1 of Bacillus circulans WL-12 as essential residues for chitinase activity. PMID:8103047.
- Synstad B et al. (2004), Eur J Biochem, 271, 253-262. Mutational and computational analysis of the role of conserved residues in the active site of a family 18 chitinase. DOI:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03923.x.
- Tews I et al. (1997), J Am Chem Soc, 119, 7954-7959. Substrate-Assisted Catalysis Unifies Two Families of Chitinolytic Enzymes. DOI:10.1021/ja970674i.
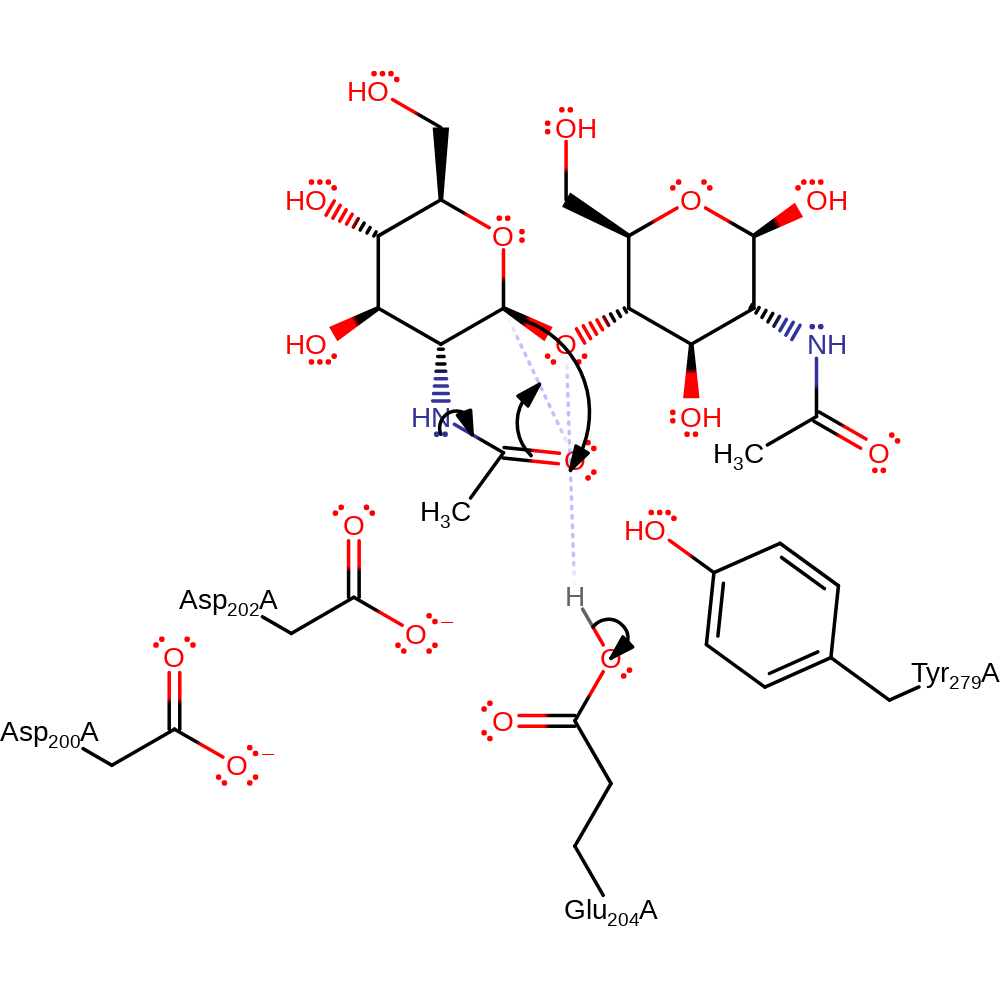
Step 1. The substrate is distorted in the active site this causes the nitrogen of the N-acetyl group to push electrons into the carbonyl oxygen which then attacks C1 of the glycosidic bond. This causes the bond to be broken upon protonation from Glu204 and a cyclic oxazolinium ion to be formed. This is stabilized by Asp200, Asp202 and Tyr279.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp200(168)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp202(170)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr279(247)A | electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Glu204(172)A | promote heterolysis |
| Asp202(170)A | steric role |
| Glu204(172)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
overall product formed, overall reactant used, proton transfer, ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, cyclisation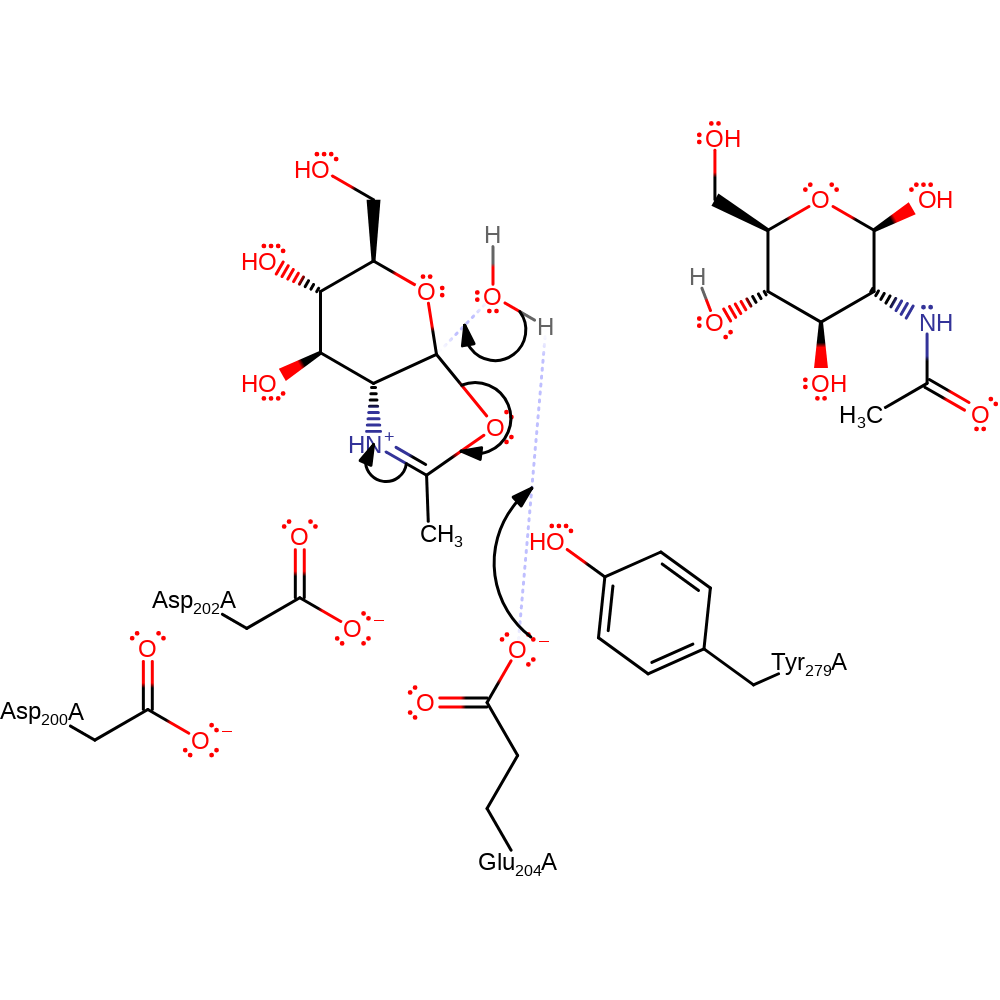
Step 2. Glu204 activates a water molecule which hydrolyses the cyclic intermediate and the product is formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp200(168)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp202(170)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr279(247)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu204(172)A | activator, increase nucleophilicity, proton acceptor |



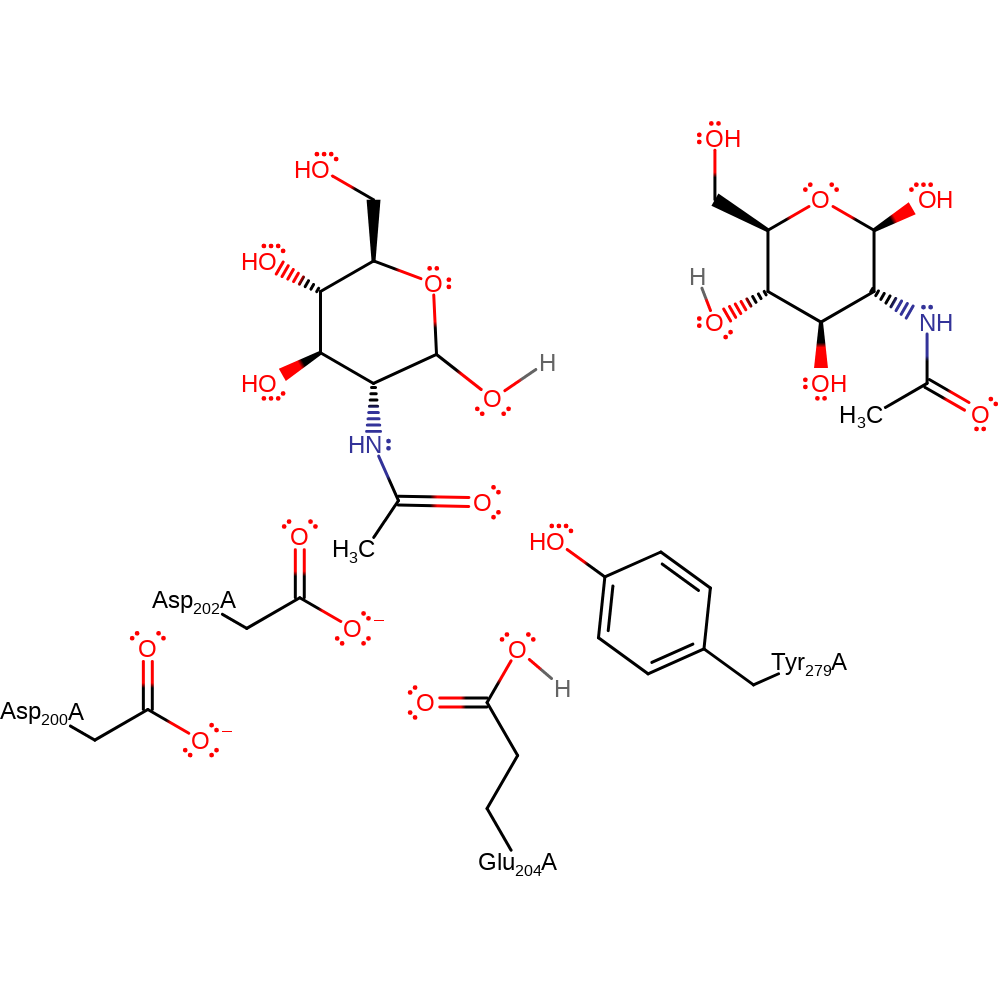 Download:
Download: