Gingipain R
Gingipains are key virulence factors of Porphyromonas gingivalis. They are cysteine proteinases with a high specificity for Arg-Xaa or Lys-Xaa. These proteins are single polypeptides with two domains that show homology to the caspases. Gingipain R is implicated in tissue inflammation associated with periodontal diseases. Elucidation of a chemical mechanism for the active site of gingipain R may be useful in design of drugs in the fight against peridontal diseases.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P95493
 (3.4.22.37)
(3.4.22.37)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis W83 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1cvr
- Crystal structure of the Arg specific cysteine proteinase gingipain R (RGPB)
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1460
 (see all for 1cvr)
(see all for 1cvr)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.22.37)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Cys437 acts as a nucleophile to attack the carbonyl carbon of the peptide bond, forming a tetrahedral intermediate stabilised by an oxyanion hole formed by the backbone amide groups of Cys437 and Gly441. His440 then protonates the leaving group, with Glu381 acting to facilitate this. Activation of water by His440 then occurs to allow hydrolysis of the thiol intermediate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1cvr) | ||
| Gly441 (main-N) | Gly212A (main-N) | Forms part of the oxyanion hole to stabilise the carbonyl oxygen of the tetrahedral intermediate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys473 (main-N) | Cys244A (main-N) | The main-chain nitrogen is involved in formation of the oxyanion hole to stabilise the carbonyl oxygen in the tetrahedral intermediate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His440 | His211A | Protonates leaving group N-terminal amide nitrogen to facilitate collapse of tetrahedral intermediate. Activates water to allow hydrolysis of thiol enzyme intermediate. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Cys473 | Cys244A | The s-gamma atom makes a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the peptide bond, forming a covalent intermediate. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Glu381 | Glu152A | Facilitates transfer of a proton from His440 to the Xaa leaving group N-terminal nitrogen. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Eichinger A et al. (1999), EMBO J, 18, 5453-5462. Crystal structure of gingipain R: an Arg-specific bacterial cysteine proteinase with a caspase-like fold. DOI:10.1093/emboj/18.20.5453. PMID:10523290.

Step 1. His440 deprotonates Cys473 which activates it so that it can attack the carbon of the carbonyl in a nucleophilic addition which produces the oxyanion intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly212A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu152A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys244A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His211A | proton acceptor |
| Cys244A | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used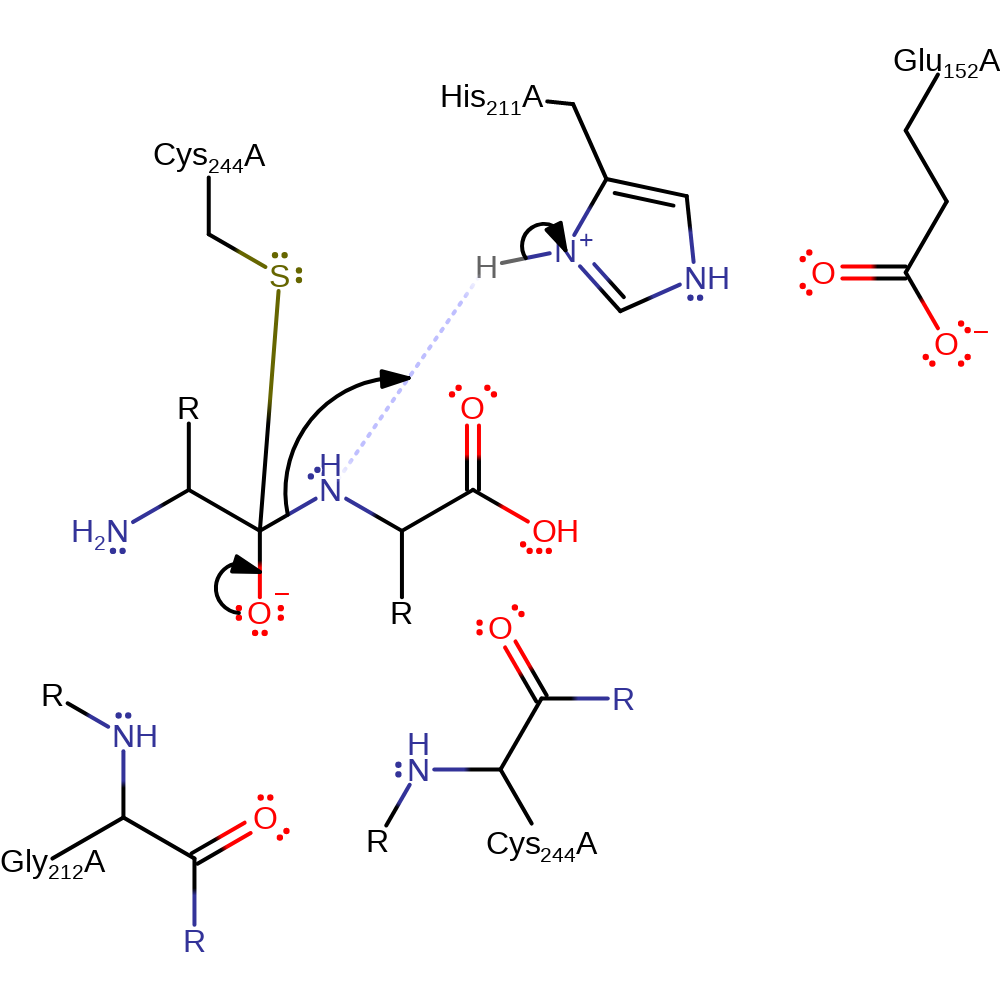
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates an elimination resulting in the cleavage of the peptide bond. The amino group of the N-terminal product accepts a proton from His440 and this prevents reformation of the peptide bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu152A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly212A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys244A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His211A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, overall product formed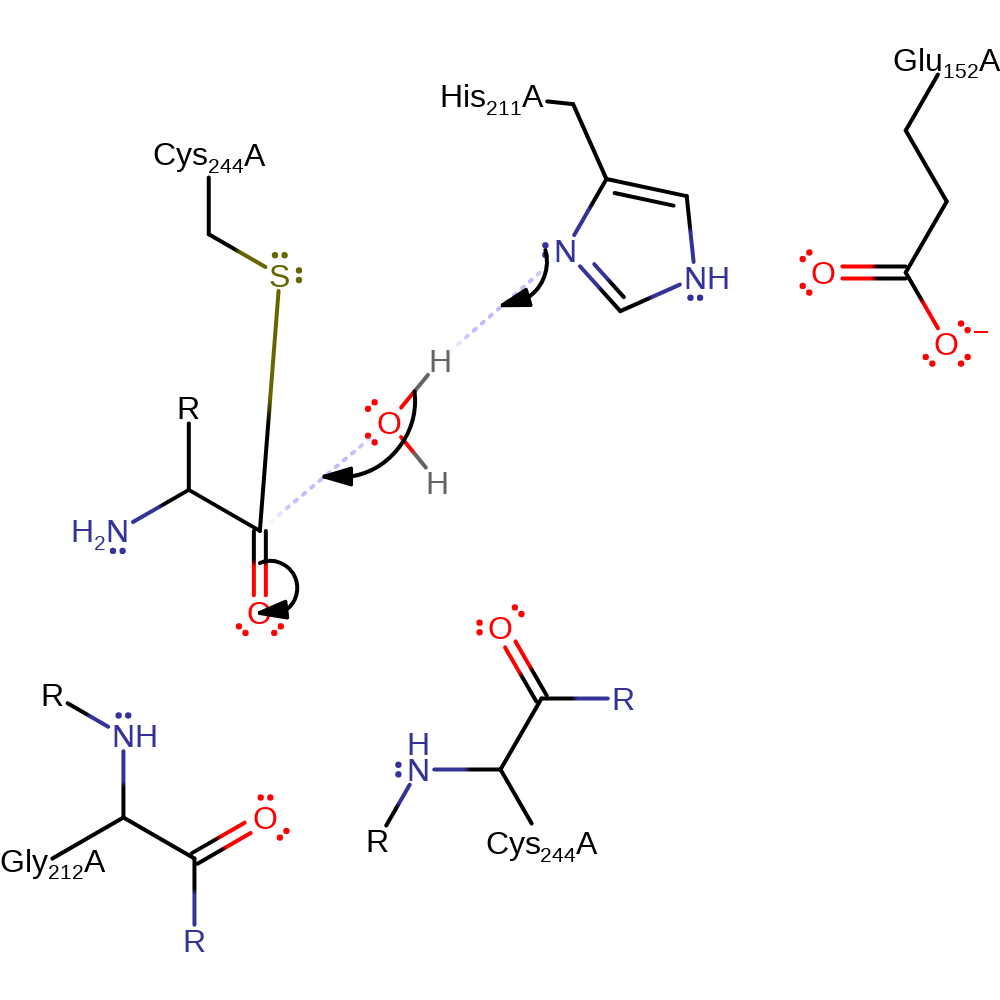
Step 3. His440 deprotonates a water, activating the water so that it can attack the carbon of the thioester bond in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu152A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly212A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys244A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His211A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used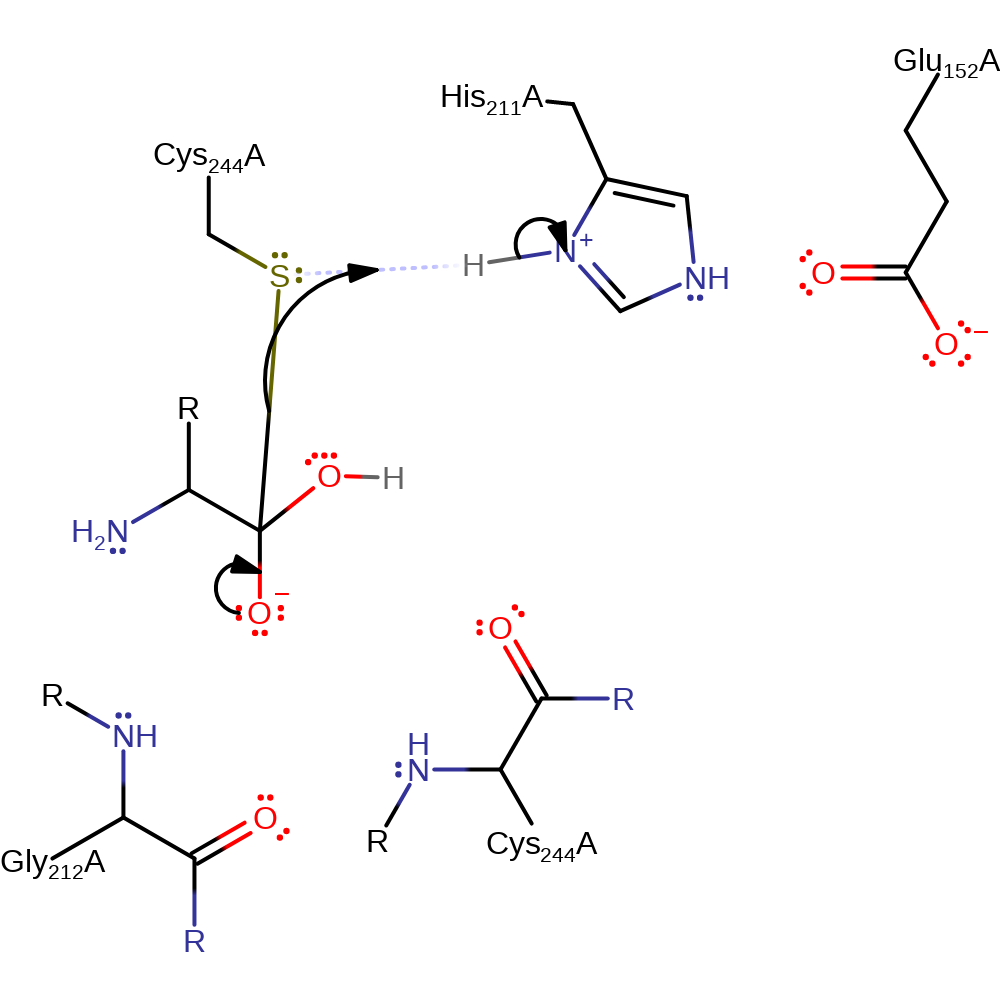
Step 4. The oxyanion initiates another elimination which results in the cleavage of the thioester bond. The released Cys437 now accepts an electron from His440 which returns the enzyme to its native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu152A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly212A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys244A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His211A | proton donor |
| Cys244A | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |



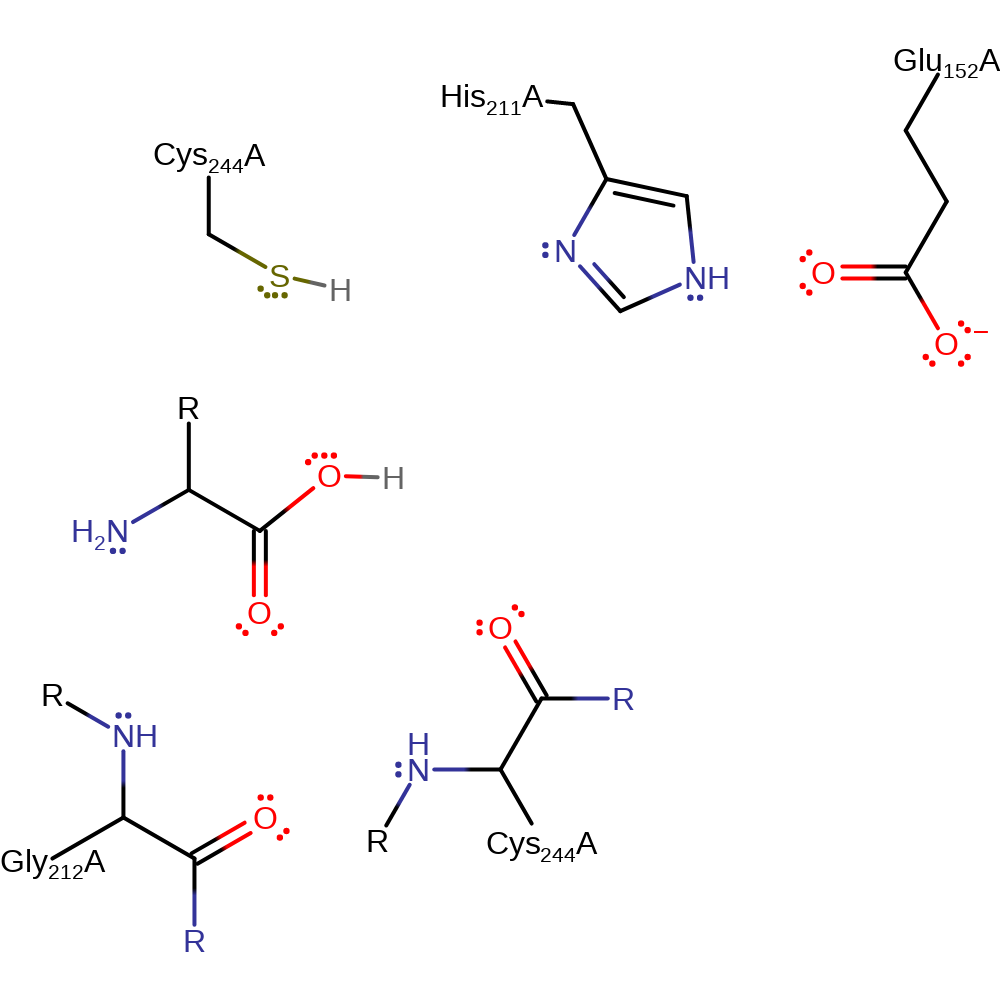 Download:
Download: