Aldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD+) (class 2)
Aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) catalyses the oxidation of toxic aldehydes to their corresponding acids, using NAD. The human mitochondrial form of ALDH is called class 2 ALDH.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P05091
 (1.2.1.3)
(1.2.1.3)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1o04
- Cys302Ser mutant of human mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase complexed with NAD+ and Mg2+
(1.42 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.309.10
 3.40.605.10
3.40.605.10  (see all for 1o04)
(see all for 1o04)
- Cofactors
- Nadph(4-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.2.1.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The catalysis follows a sequential mechanism in which NAD+ binds prior to aldehyde. The aldehyde then undergoes nucleophilic attack by Cys302, forming a covalent intermediate. Next, the carbonyl hydride is transferred to the A-side of the nicotinamide ring. In the rate-limiting step, Glu268 activates a water molecule for nucleophilic attack at the acyl-sulphur bond, releasing the acid product prior to NADH dissociation. Lys192 and Glu399 stabilise the transition state during the hydride transfer.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1o04) | ||
| Glu285 | Glu268A | It acts as a base to deprotonate a water molecule for nucleophilic attack at the acyl-sulphur bond. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Cys319 | Ser302A | It acts as a nucleophile to attack the aldehyde to form a covalent enzyme-substrate intermediate. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys209, Glu416 | Lys192A, Glu399A | It stabilises the transition state during hydride transfer from the enzyme-substrate intermediate to NAD+. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation, aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, hydride transfer, cofactor used, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Sheikh S et al. (1997), J Biol Chem, 272, 18817-18822. The Potential Roles of the Conserved Amino Acids in Human Liver Mitochondrial Aldehyde Dehydrogenase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.272.30.18817. PMID:9228056.
- Ni L et al. (1997), J Biol Chem, 272, 18823-18826. Involvement of Glutamate 399 and Lysine 192 in the Mechanism of Human Liver Mitochondrial Aldehyde Dehydrogenase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.272.30.18823. PMID:9228057.
- Farrés J et al. (1995), Biochemistry, 34, 2592-2598. Investigation of the Active Site Cysteine Residue of Rat Liver Mitochondrial Aldehyde Dehydrogenase by Site-Directed Mutagenesis. DOI:10.1021/bi00008a025. PMID:7873540.
- Wang X et al. (1995), Biochemistry, 34, 237-243. Involvement of Glutamate 268 in the Active Site of Human Liver Mitochondrial (Class 2) Aldehyde Dehydrogenase As Probed by Site-Directed Mutagenesis. DOI:10.1021/bi00001a028. PMID:7819202.

Step 1. Glu268 acts as a base to abstract a proton from a water molecule which then activates Cys302.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys192A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu399A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser302A | proton donor |
| Glu268A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 2. There is nucleophilic attack on the electrophilic aldehyde by the thiolate group of Cys302, forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys192A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser302A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu399A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser302A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation
Step 3. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses and a hydride is transferred to NAD, forming NADH.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser302A | covalently attached |
| Lys192A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu268A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu399A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, hydride transfer, cofactor used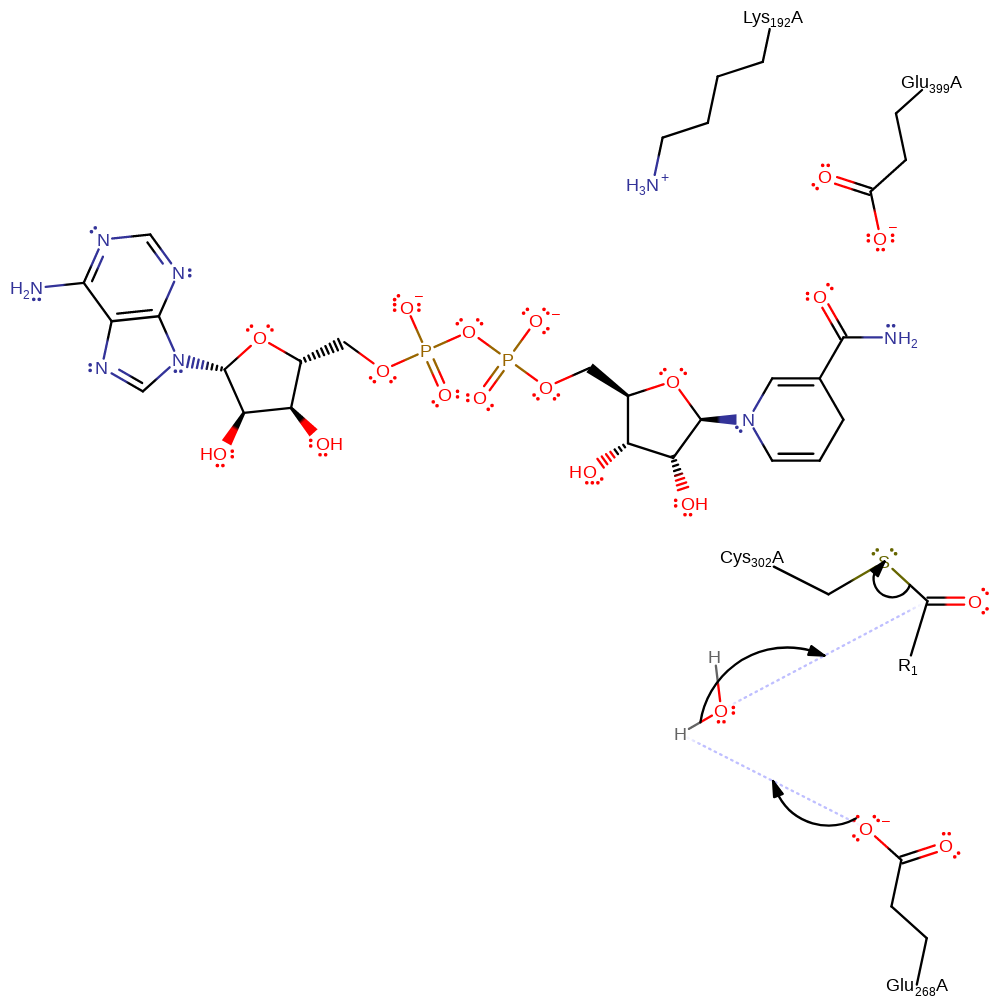
Step 4. Glu268 activates a water molecule for nucleophilic attack on the aldehyde intermediate, eliminating Cys302 and forming the product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser302A | covalently attached |
| Lys192A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser302A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu399A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu268A | proton acceptor |
| Ser302A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage
Step 5. In an inferred reaction step Cys302 is reprotonated and Glu268 is protonated to regenerate the native state of the enzyme.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu268A | proton donor |
| Ser302A | proton acceptor |






 Download:
Download: