Colicin-E9
Colicin E9 from Escherichia coli is a non-specific endonuclease. This extracellular toxin is secreted by strains of Escherichia coli to kill competing bacteria. It kills the cell by enzymatic cleavage of nucleic acids once it has entered the cell. Since colicin E9 is non-specific, it can hydrolyse both single and double stranded DNA.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequences
-
P13479

P09883 (3.1.-.-)
(3.1.-.-)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1fr2
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE E9 DNASE DOMAIN WITH A MUTANT IMMUNITY PROTEIN IM9(E41A)
(1.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.540.10
 (see all for 1fr2)
(see all for 1fr2)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.21.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
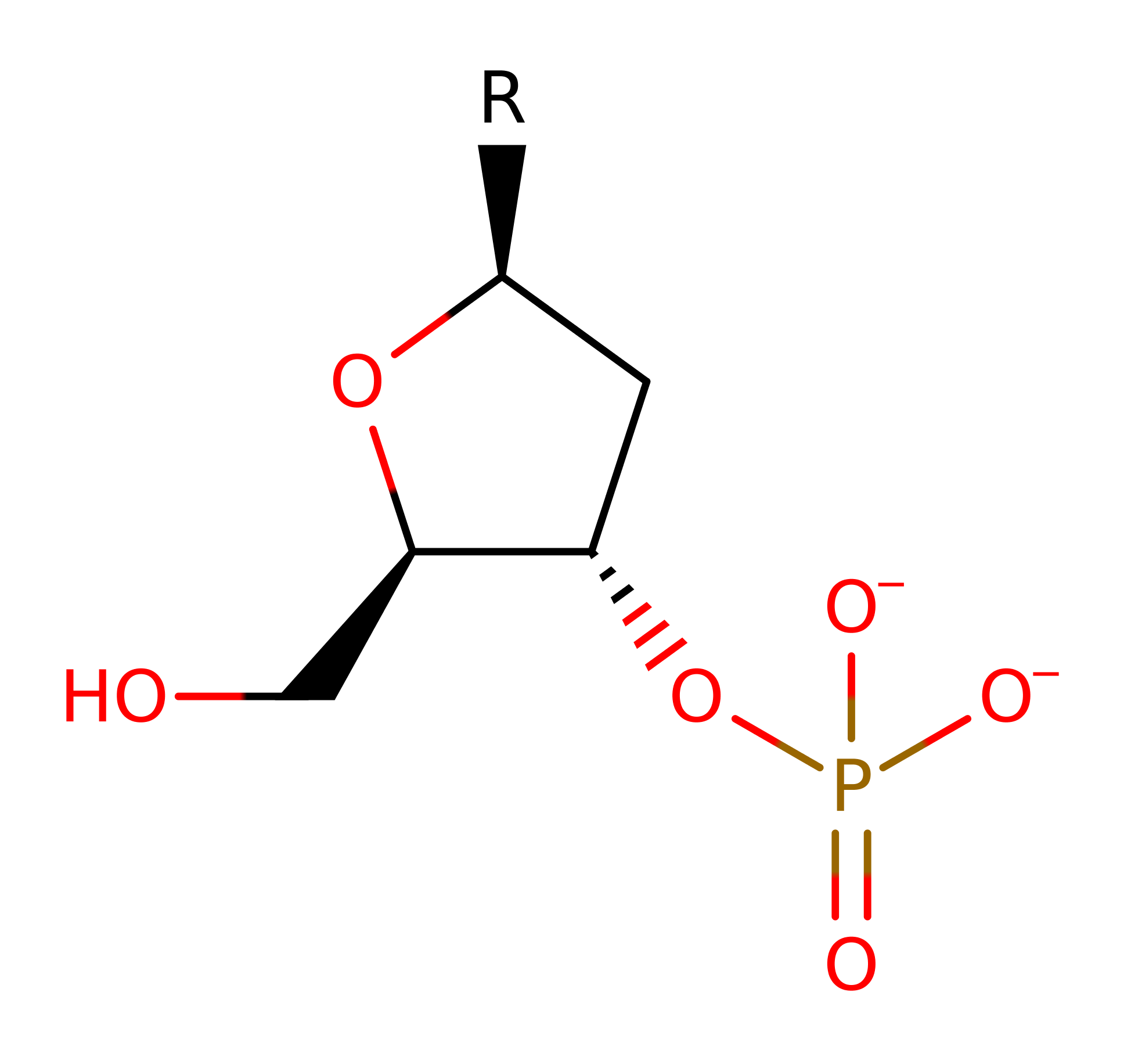
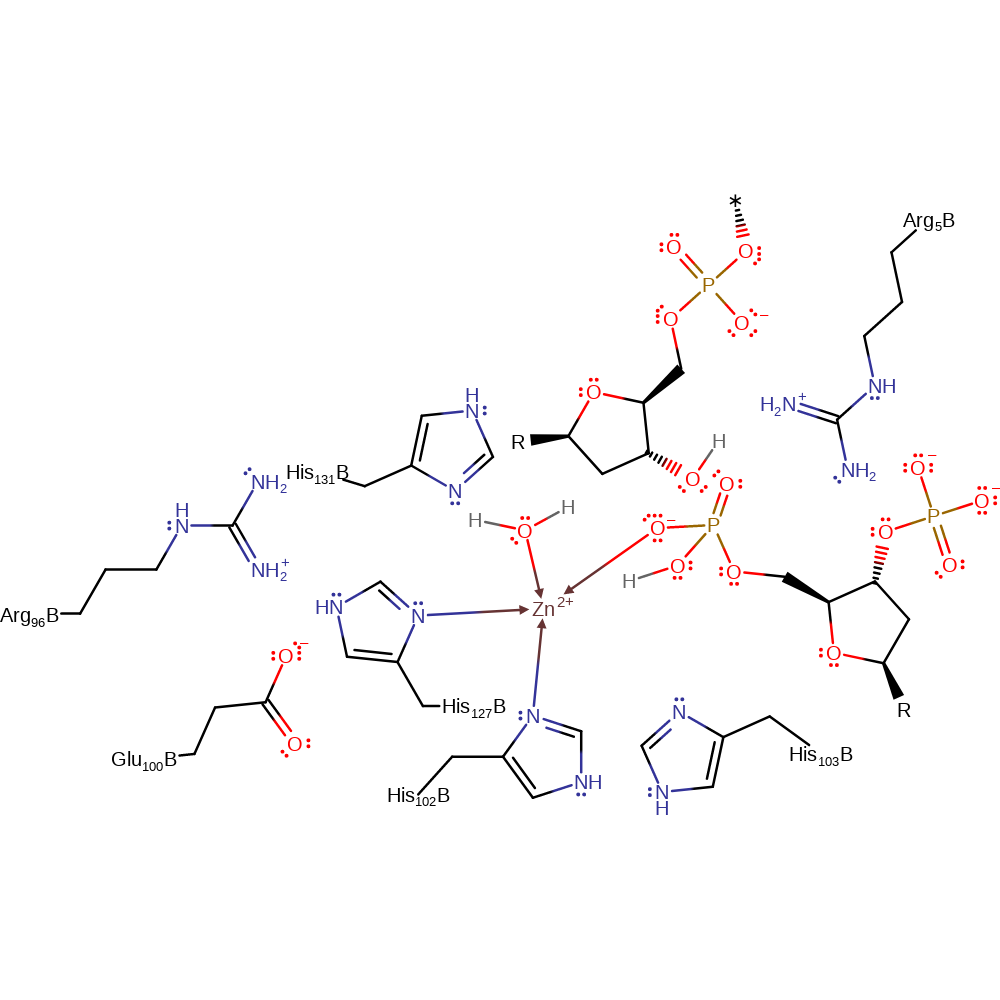
His 103 acts as a general base by abstracting a proton from a water molecule, activating it for nucleophilic attack on the scissile phosphorus atom. This leads to a penta-covalent intermediate being formed. The Zn ion activates a water molecule so it will donate a proton to the 3' hydroxyl leaving group. The intermediate then collapses forming the products.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1fr2) | ||
| Glu548, Arg544 | Glu100B, Arg96B | Stabilize the histidine residues involved in metal coordination. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His575, His579, His550 | His127B, His131B, His102B | Coordinate the Zn ion | metal ligand |
| His551 | His103B | Acts as a general base by deprotonating a water molecule, activating it for nucleophilic attack on the phosphorus atom. | increase nucleophilicity, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Arg453 | Arg5B | Stabilizes the negatively charged intermediate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, overall reactant used, coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion, overall product formed, heterolysis, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Pommer AJ et al. (2001), J Mol Biol, 314, 735-749. Mechanism and cleavage specificity of the H-N-H endonuclease colicin E9. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5189. PMID:11733993.
- Maté MJ et al. (2004), J Biol Chem, 279, 34763-34769. Structure-based analysis of the metal-dependent mechanism of H-N-H endonucleases. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M403719200. PMID:15190054.
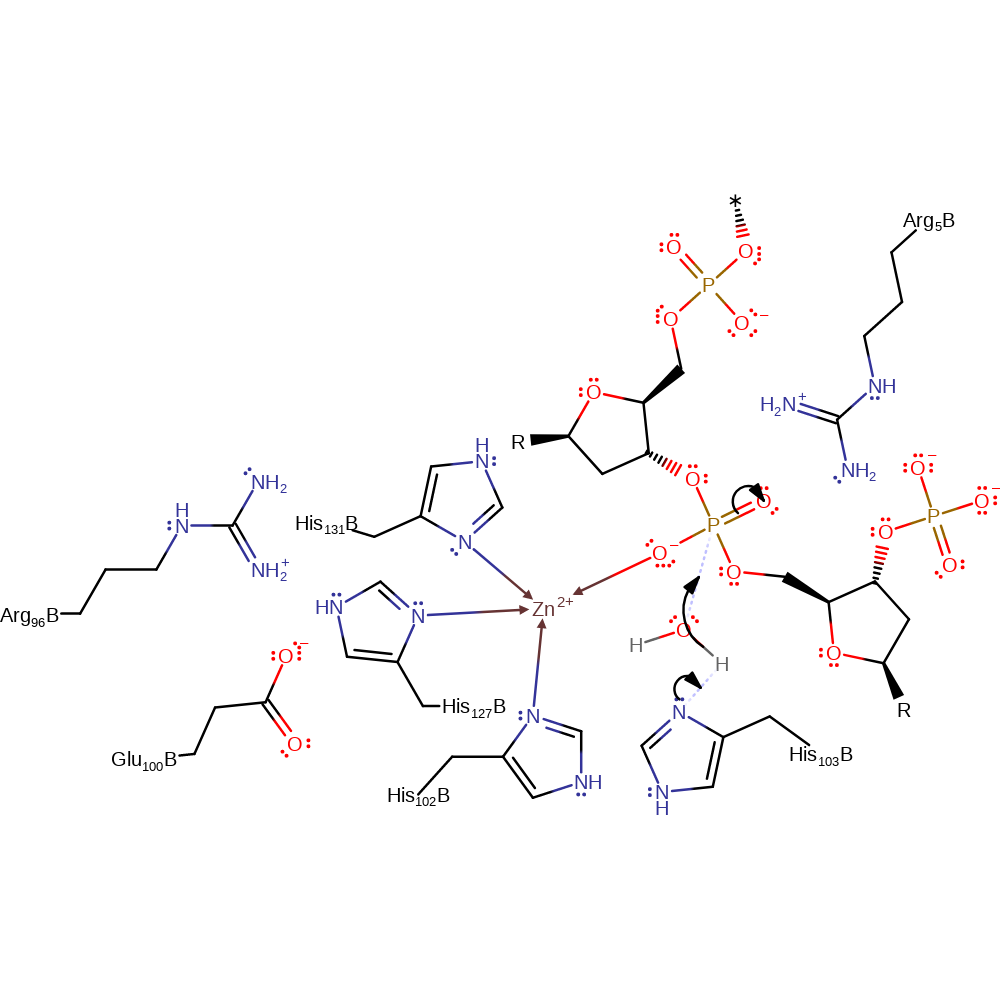
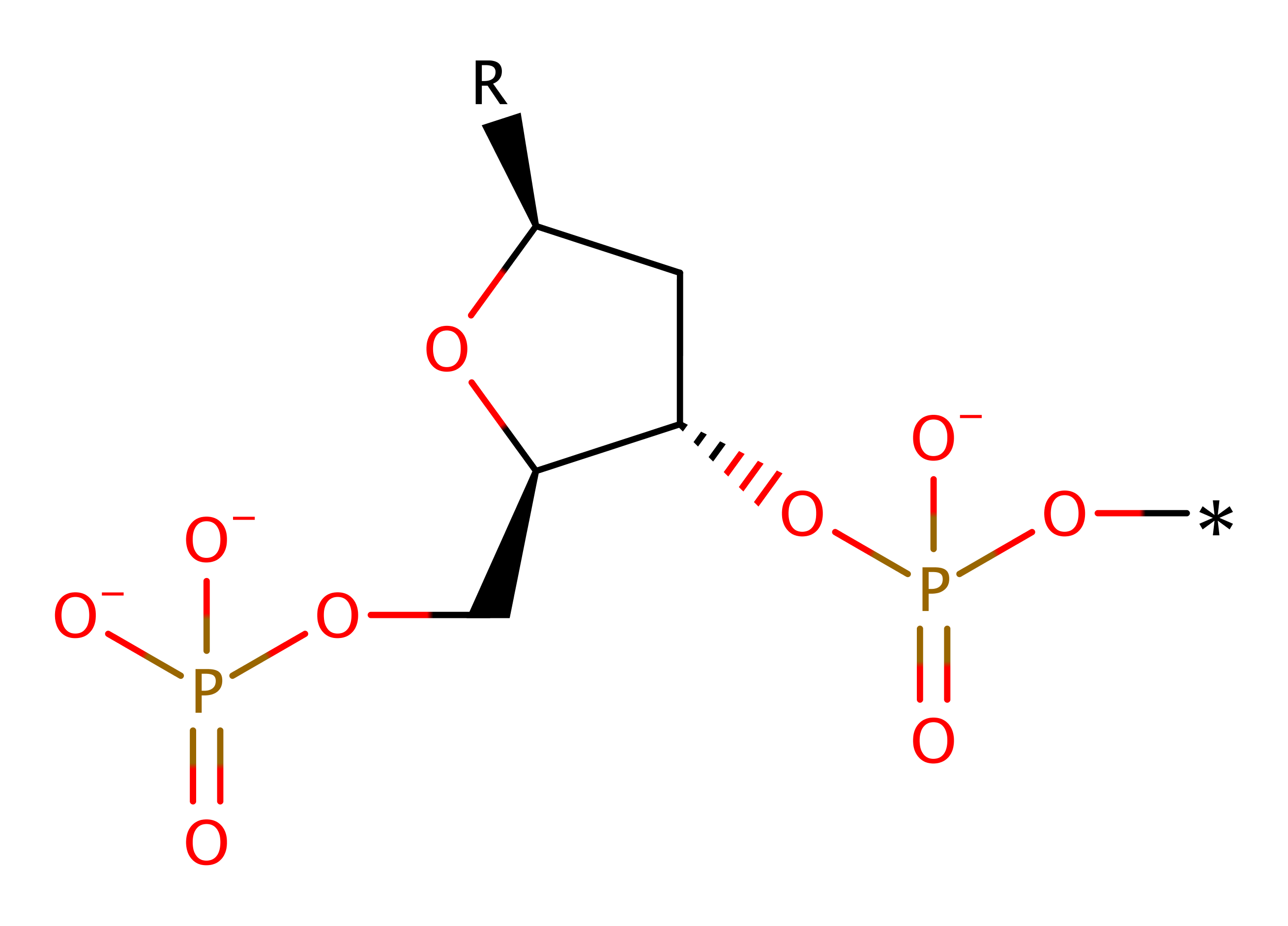
Step 1. His551 activates a water molecule allowing the water to perform a nucleophilic attack on the scissile phosphate group. This leads to a penta-covalent intermediate being formed which is stabilized by Arg453. After this has occurred a second water molecule replaces His579 in its coordination to the Zn ion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu100B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg5B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His103B | increase nucleophilicity |
| His102B | metal ligand |
| His127B | metal ligand |
| His131B | metal ligand |
| Arg96B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His103B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, overall reactant used, coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion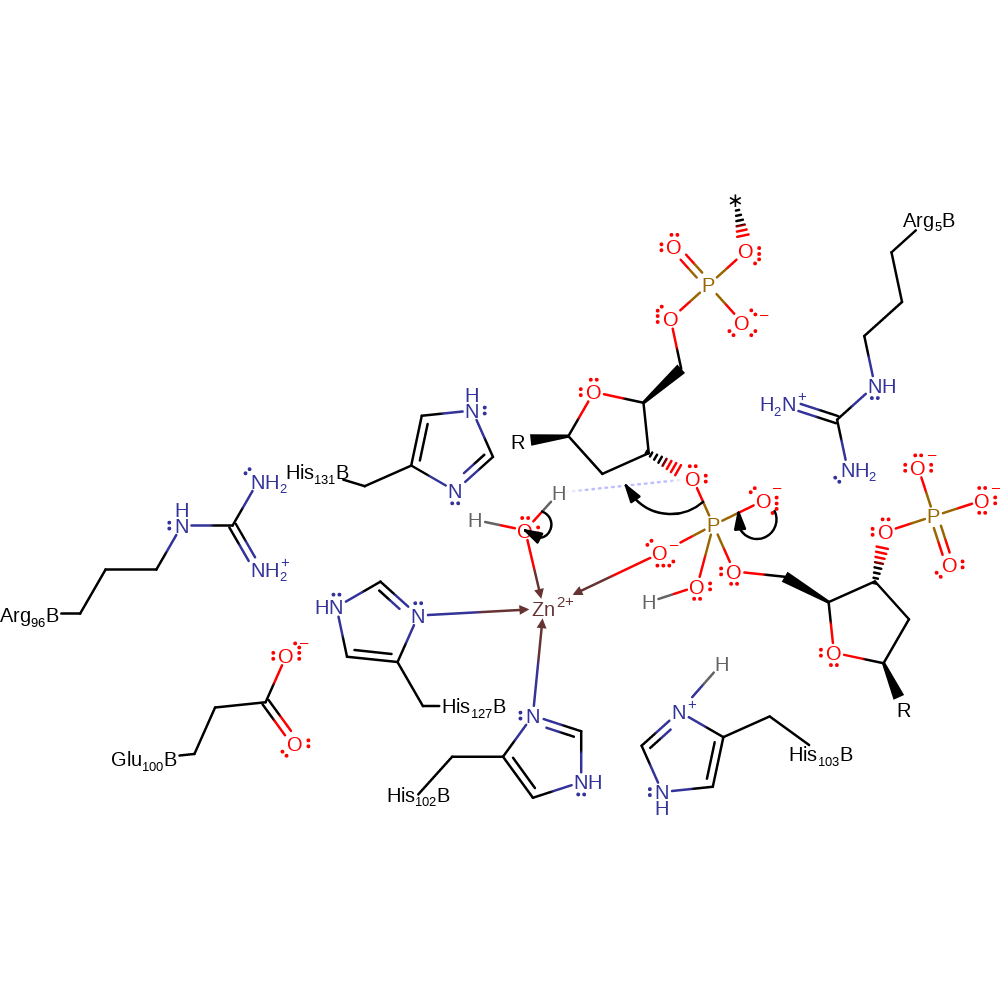
Step 2. The second water molecule is activated by the Zn ion allowing it to transfer a proton to the 3' hydroxyl leaving group. This proton transfer facilitates the collapse of the intermediate and the formation of the products.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His102B | metal ligand |
| His127B | metal ligand |
| Arg5B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg96B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu100B | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
overall product formed, proton transfer, heterolysis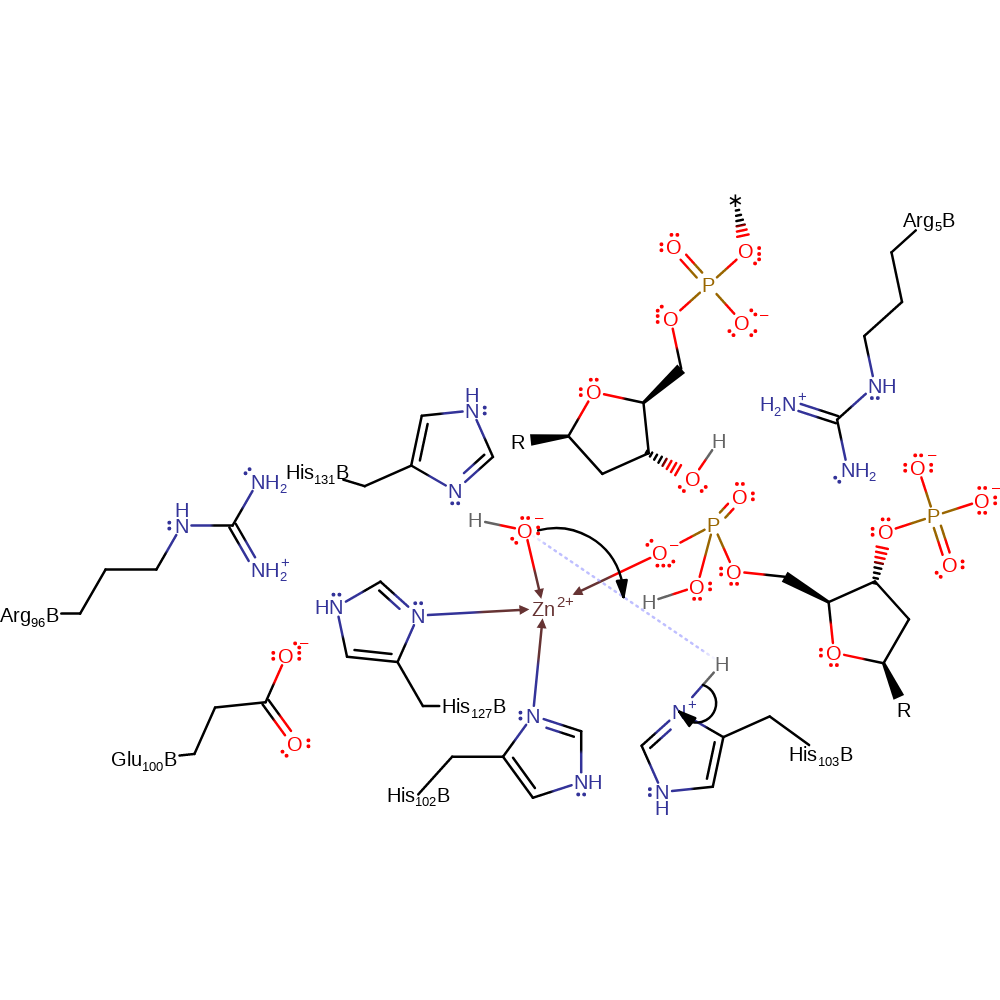
Step 3. In this inferred reaction step His551 donates a proton to the hydroxide ion to regenerate the active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His102B | metal ligand |
| His127B | metal ligand |
| His103B | proton donor |


 Download:
Download: