Nicotinate-nucleotide-dimethylbenzimidazole phosphoribosyltransferase
Nicotinate mononucleotide:5,6- dimethylbenzimidazole (DMB) phosphoribosyltransferase (CobT) is crucial in the synthesis of alpha-ribose-5'-phosphate, a precursor to the lower ligand of colbamin. The biosynthesis of colbamin requires more than 25 committed enzymes, and the biosynthetic pathway has received much interest because of its complexity. Colbamin synthesis is also of interest in evolutionary biology because of its utilisation by early forms of bacteria and Archaea.
The enzyme has also been shown to act on benzimidazole, and the clostridial enzyme acts on adenine to form 7-alpha-D-ribosyladenine 5'-phosphate.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q05603
 (2.4.2.21)
(2.4.2.21)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1d0s
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF NICOTINATE MONONUCLEOTIDE : 5,6-DIMETHYLBENZIMIDAZOLE PHOSPHORIBOSYLTRANSFERASE (COBT) FROM SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM COMPLEXED WITH 5, 6-DIMETHYLBENZIMIDAZOLE
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.10210
 (see all for 1d0s)
(see all for 1d0s)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.4.2.21)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The carboxylate side chain of Glu317 acts as a catalytic base, abstracting the proton of the N3 of DMB, whereupon the N1 atom attacks the C1' carbon of ribose with concerted displacement of the nicotinate ring. This leads to the direct displacement reaction, with a inversion of configuration of the carbon centre.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1d0s) | ||
| Glu317 | Glu317A | The residue acts as a general base towards the DMB substrate, deprotonating the N3 position. This leads to conjugate attack through the N1 atom at the nictotinate D-ribonucleotide substrate in a concerted SN2 displacement reaction, resulting in an inversion of configuration at the carbon centre. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, proton acceptor |
| Glu174 | Glu174A | Plays a role in stabilising Glu317 (the proposed general acid/base) in the active conformation. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, proton transfer, rate-determining stepReferences
- Cheong CG et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 16125-16135. The Three-Dimensional Structures of Nicotinate Mononucleotide:5,6-Dimethylbenzimidazole Phosphoribosyltransferase (CobT) fromSalmonella typhimuriumComplexed with 5,6-Dimethybenzimidazole and Its Reaction Products Determined to 1.9 Å Resolution†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi991752c. PMID:10587435.
- Chan CH et al. (2014), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1840, 464-475. Dissecting cobamide diversity through structural and functional analyses of the base-activating CobT enzyme of Salmonella enterica. DOI:10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.09.038. PMID:24121107.
- Crofts TS et al. (2013), Chem Biol, 20, 1265-1274. Cobamide Structure Depends on Both Lower Ligand Availability and CobT Substrate Specificity. DOI:10.1016/j.chembiol.2013.08.006. PMID:24055007.
- Claas KR et al. (2010), J Bacteriol, 192, 145-154. Functional Analysis of the Nicotinate Mononucleotide:5,6-Dimethylbenzimidazole Phosphoribosyltransferase (CobT) Enzyme, Involved in the Late Steps of Coenzyme B12 Biosynthesis in Salmonella enterica. DOI:10.1128/jb.01159-09. PMID:19880598.
- Cheong CG et al. (2002), J Biol Chem, 277, 41120-41127. Capture of a Labile Substrate by Expulsion of Water Molecules from the Active Site of Nicotinate Mononucleotide:5,6-Dimethylbenzimidazole Phosphoribosyltransferase (CobT) from Salmonella enterica. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m203535200. PMID:12101181.
- Cheong CG et al. (2001), J Biol Chem, 276, 37612-37620. Structural Investigation of the Biosynthesis of Alternative Lower Ligands for Cobamides by Nicotinate Mononucleotide: 5,6-Dimethylbenzimidazole Phosphoribosyltransferase from Salmonella enterica. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m105390200. PMID:11441022.
- Trzebiatowski JR et al. (1994), J Bacteriol, 176, 3568-3575. The cobT gene of Salmonella typhimurium encodes the NaMN: 5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole phosphoribosyltransferase responsible for the synthesis of N1-(5-phospho-alpha-D-ribosyl)-5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole, an intermediate in the synthesis of the nucleotide loop of cobalamin. PMID:8206834.
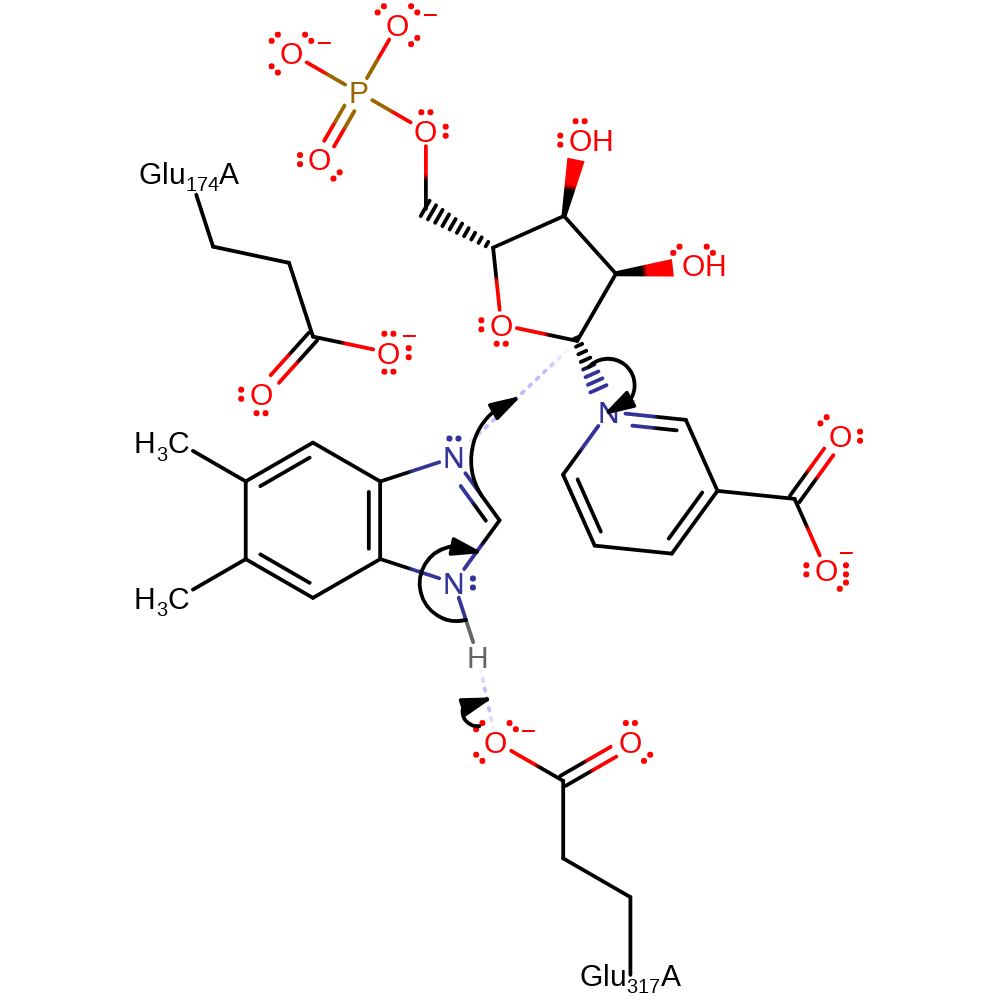
Step 1. The N1 of dimethylbenzimidazole initiates a nucleophilic attack on the C1 of the nicotinate D-ribonucleotide in a substitution reaction, eliminating nicotinate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu317A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Glu174A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu317A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, proton transfer, rate-determining stepIntroduction
Mutagenesis experiments indicate the importance of Glu174 and Glu317 in positioning the substrate and stabilising the active site. This differs from the other mechanism proposal in which Glu317 acts as a general base catalyst. However, the in vitro enzymatic assays to support this non-catalytic role conclusion were done at pH10, far from the physiological pH so caution should be taken when deciding between the two mechanisms. Regardless, nucleophilic attack occurs from N1 dimethylbenzimidazole on C1 of nicotinate D-ribonucleotide, releasing the nicotinate. Dimethylbenzimidazole product needs to be deprotonated to form the final product, N1-(5-phospho-alpha-D-ribosyl)-5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole (and nicotinate).
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1d0s) | ||
| Glu317, Glu174 | Glu317A, Glu174A | Proposed substrate binding role as well as stabilising the active site. | unknown |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, proton transfer, overall product formed, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Chan CH et al. (2014), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1840, 464-475. Dissecting cobamide diversity through structural and functional analyses of the base-activating CobT enzyme of Salmonella enterica. DOI:10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.09.038. PMID:24121107.
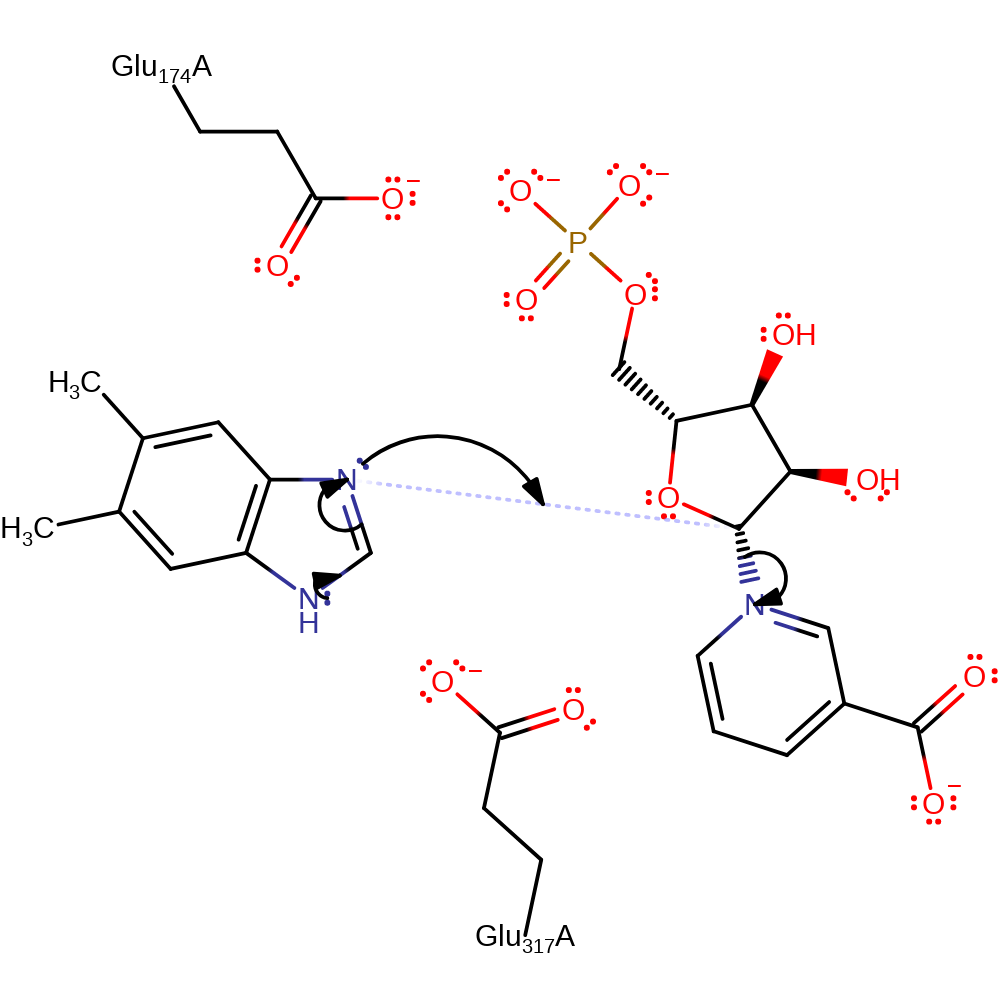
Step 1. The N1 of dimethylbenzimidazole initiates a nucleophilic attack on the C1 of the nicotinate D-ribonucleotide in a substitution reaction, eliminating nicotinate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu174A | unknown |
| Glu317A | unknown |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used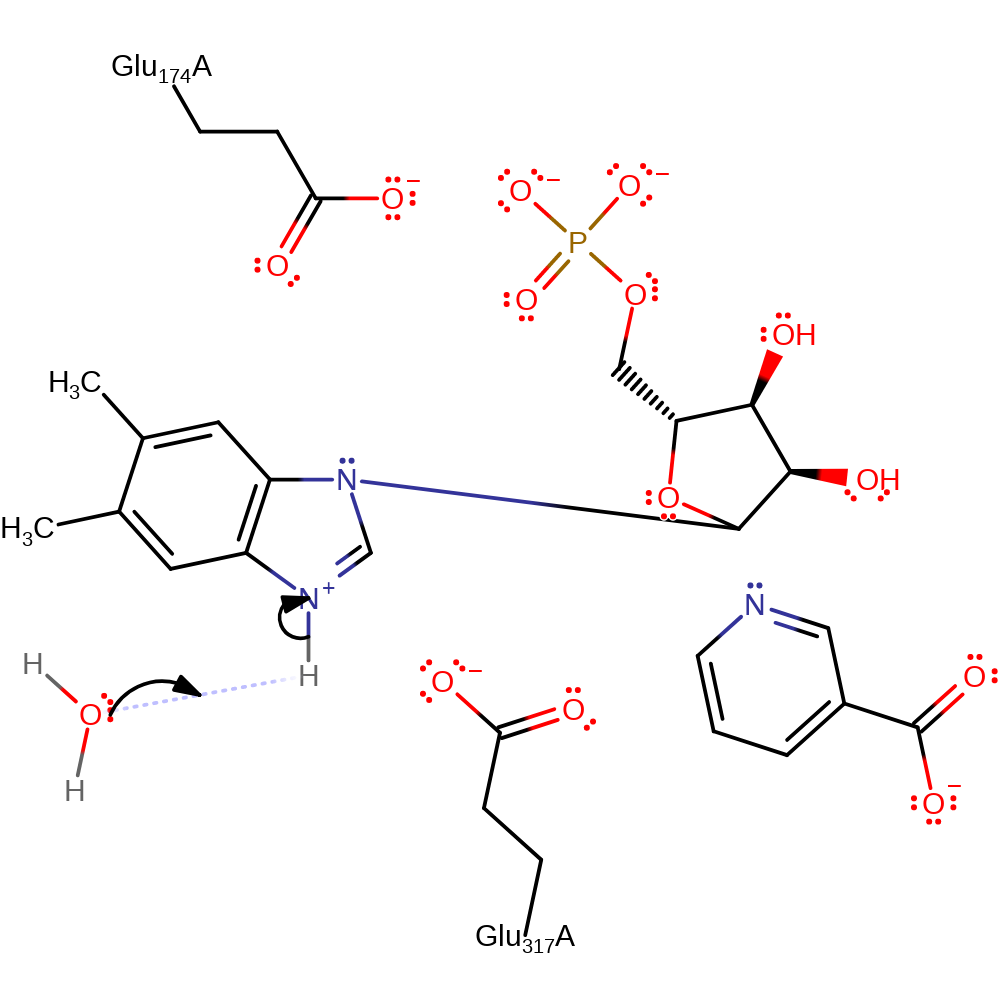
Step 2. N3 on Dimethylbenzimidazole is deprotonated by a water molecule.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|





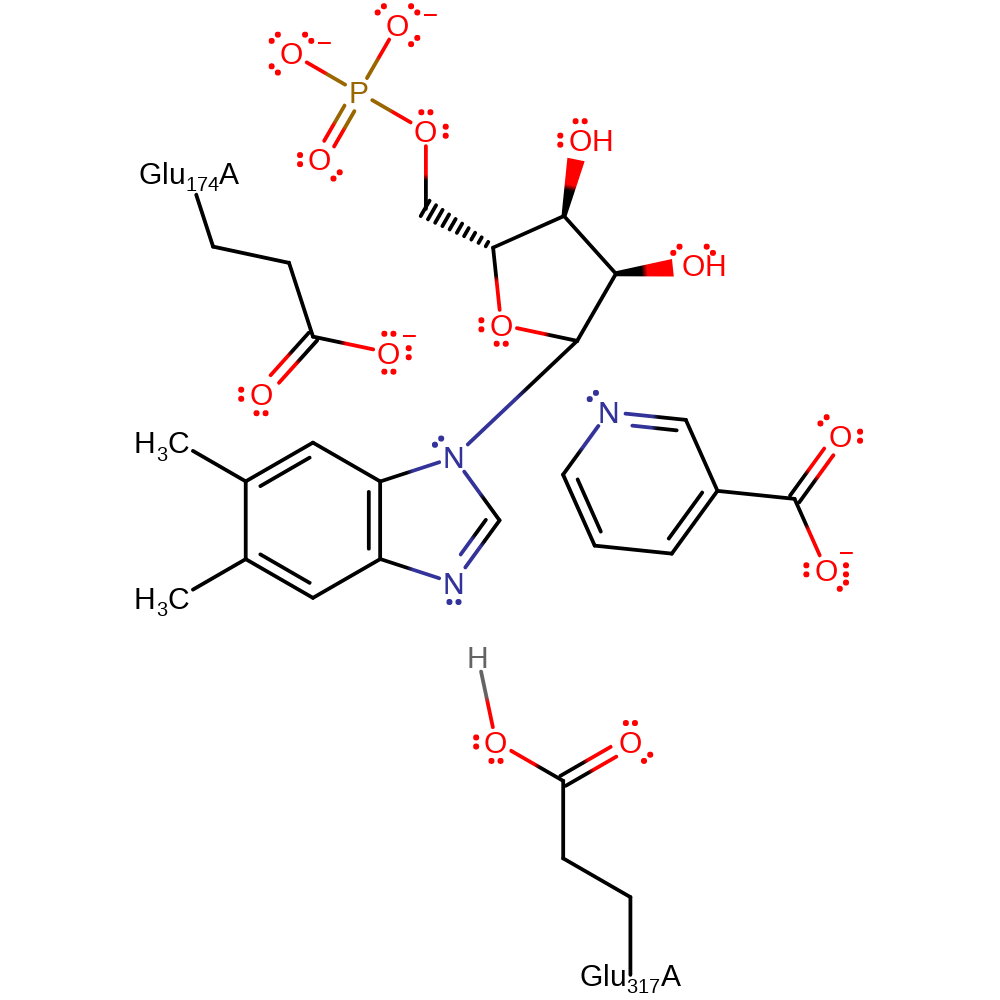 Download:
Download: 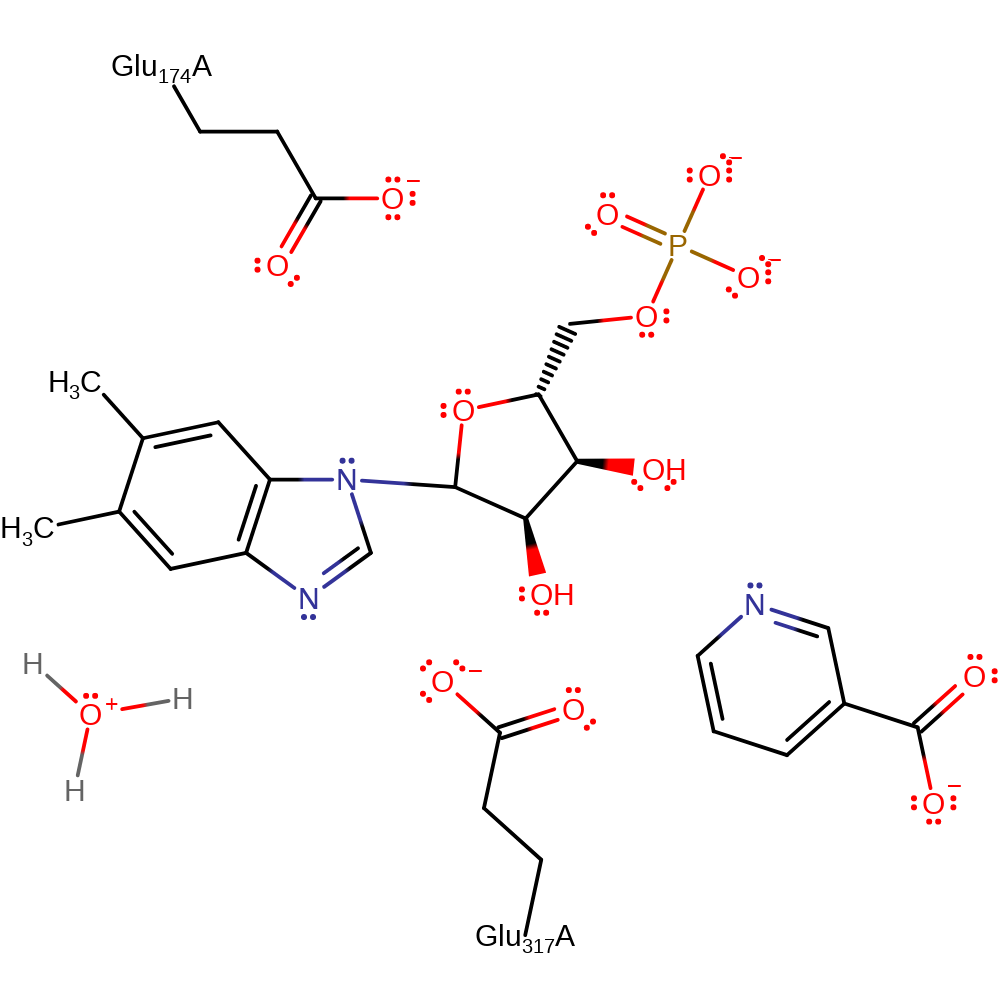 Download:
Download: