UDP-N-acetylmuramoylpentapeptide-lysine N6-alanyltransferase
FemX uses aminoacyl-tRNA as an amino acid donor to synthesise the peptide cross-bridge in peptidoglycan, apart of the cell wall of gram-positive bacteria. FemX belongs to the Fem family of nonribosomal peptidyl transferases . FemX is required for cell survival and is a target for beta-lactam antibiotics.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9EY50
 (2.3.2.10)
(2.3.2.10)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Weissella viridescens (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1p4n
- Crystal Structure of Weissella viridescens FemX:UDP-MurNAc-pentapeptide complex
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.630.30
 (see all for 1p4n)
(see all for 1p4n)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.3.2.10)


Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The reaction is thought to proceed in a substrate-assisted manner, with no acid or base catalyst within range. Substrate-lysine performs a nucleophilic attack on the Ala-tRNA ester bond to form a negatively charged tetrahedral intermediate, stabilised by Lys306. The intermediate collapses from concomitant internal proton shuttle to form the products; tRNA and alanyl-UM5P, a peptidoglycan precursor. Phe305 is also conserved in Fem aminoacyl transferases, pi-stacking with the C75 ribose ring which when mutated significantly decreased enzymatic turnover.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1p4n) | ||
| Lys306 | Lys305A | Hydrogen bond donor to the oxyanion intermediate, helping stabilise the negative charge on the carbonyl oxygen. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe305 | Phe304A | Catalytically conserved residue in Fem aminoacyl transferases that has pi-stacking interactions with the ribose sugar on tRNA. | van der waals interaction, pi-pi interaction |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate terminated, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, proton relayReferences
- Fonvielle M et al. (2013), Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 52, 7278-7281. The structure of FemX(Wv) in complex with a peptidyl-RNA conjugate: mechanism of aminoacyl transfer from Ala-tRNA(Ala) to peptidoglycan precursors. DOI:10.1002/anie.201301411. PMID:23744707.
- Moutiez M et al. (2017), Chem Rev, 117, 5578-5618. Aminoacyl-tRNA-Utilizing Enzymes in Natural Product Biosynthesis. DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00523. PMID:28060488.
- Favrot L et al. (2016), Biochemistry, 55, 989-1002. Bacterial GCN5-Related N-Acetyltransferases: From Resistance to Regulation. DOI:10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01269. PMID:26818562.
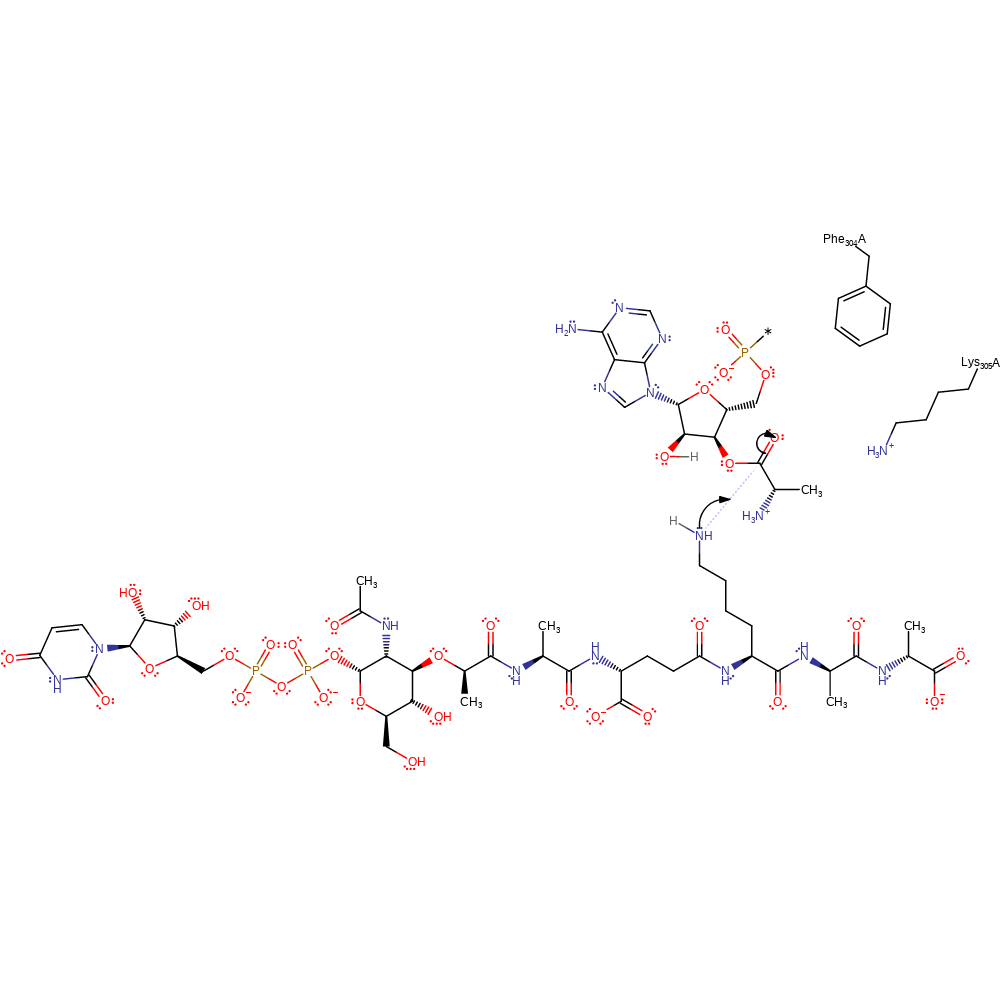
Step 1. Amine on UDP-N-acetyl-muramyl-pentapeptide acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon to form a tetrahedral intermediate. Lys306 stabilises the oxyanion intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys305A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Phe304A | pi-pi interaction, van der waals interaction |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used
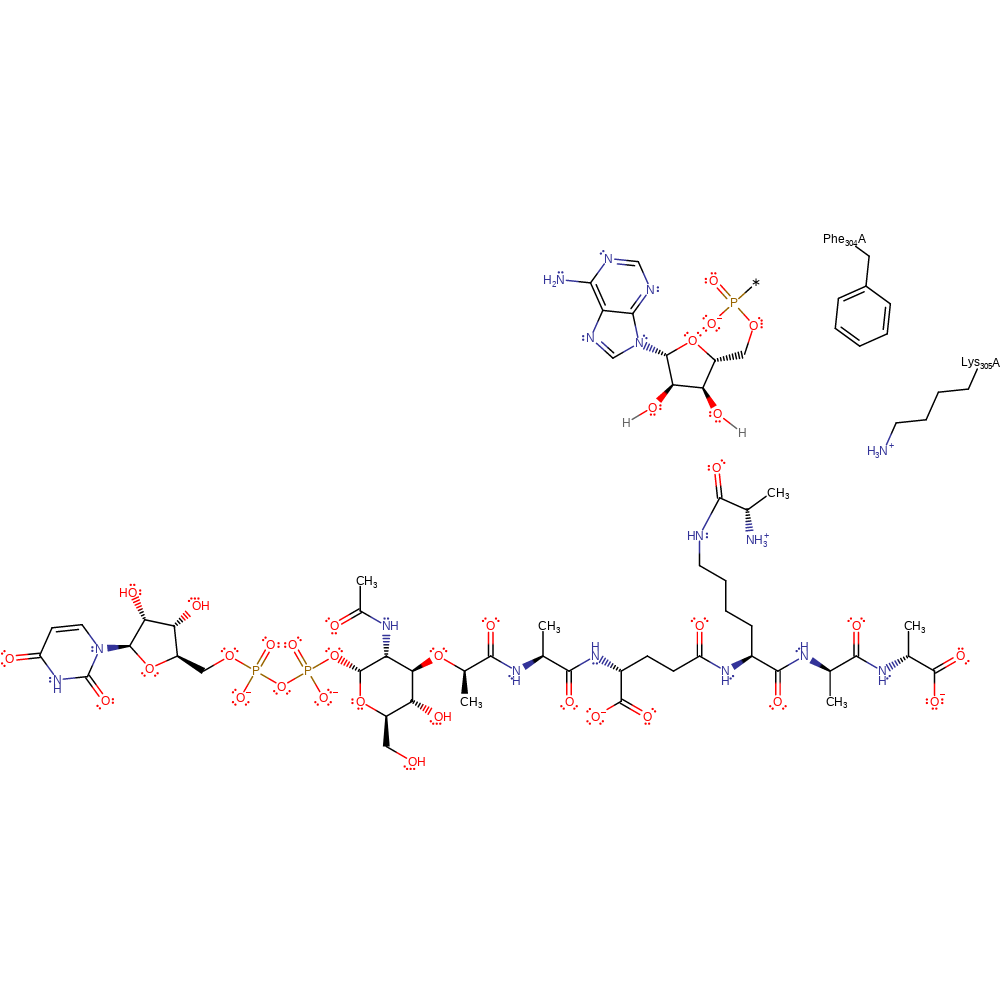
Step 2. Substrate assisted - proton shuttle resulting in collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys305A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu319A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Phe304A | pi-pi interaction, van der waals interaction |
Chemical Components
intermediate terminated, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, proton relayIntroduction
FemX catalyses the transfer of L-Ala onto the cytoplasmic precursor UDP-N-acetyl-muramyl-pentapeptide. Lys36 and Arg211 activate the substrate by maintaining it in a bent conformation. UDP-N-acetyl-muramyl-pentapeptide (UDP-MPP) is bound, followed by Ala-tRNA. Nucleophilic attack occurs with the lysine residue of UDP-MPP on the carbonyl of the aminoacylated-tRNA to generate a tetrahedral intermediate. Collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate is assisted by the action of Glu319 as a general acid to protonate the 3'-OH of the tRNA ribose moiety and Asp108 acting as a general base to abstract a proton from the amino group on UDP-MPP.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1p4n) | ||
| Asp109 | Asp108A | Acts as a general base catalyst in activating the substrate for nucleophilic attack. | proton acceptor |
| Lys37, Arg212 | Lys36A, Arg211A | Activates the substrate sterically. | hydrogen bond donor, steric role |
| Glu320 | Glu319A | Acts as the general acid catalyst in protonation of the leaving group to facilitate cleavage. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate terminated, proton transfer, overall product formed, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Hegde SS et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 22861-22867. Kinetic and Mechanistic Characterization of Recombinant Lactobacillus viridescens FemX (UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl Pentapeptide-lysine N6-Alanyltransferase). DOI:10.1074/jbc.m301565200. PMID:12679335.
- Fonvielle M et al. (2013), Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 52, 7278-7281. The structure of FemX(Wv) in complex with a peptidyl-RNA conjugate: mechanism of aminoacyl transfer from Ala-tRNA(Ala) to peptidoglycan precursors. DOI:10.1002/anie.201301411. PMID:23744707.
- Maillard AP et al. (2005), J Bacteriol, 187, 3833-3838. Structure-Based Site-Directed Mutagenesis of the UDP-MurNAc-Pentapeptide-Binding Cavity of the FemX Alanyl Transferase from Weissella viridescens. DOI:10.1128/jb.187.11.3833-3838.2005. PMID:15901708.

Step 1. Amine on UDP-N-acetyl-muramyl-pentapeptide acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon to form a tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys36A | steric role |
| Arg211A | steric role |
| Lys36A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg211A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation
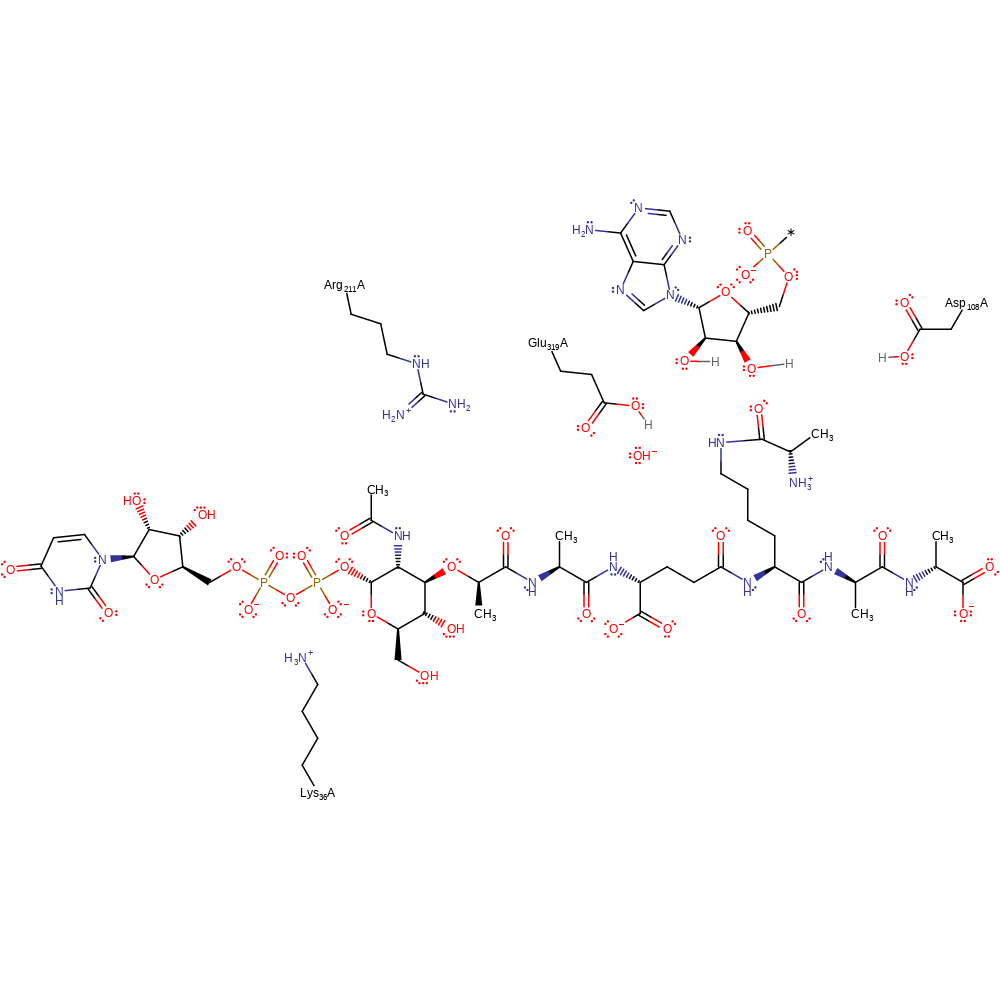
Step 2. Collapse of tetrahedral intermediate with Glu319 and Asp108 acting as a general acid and base to form the reaction products.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys36A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg211A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys36A | steric role |
| Arg211A | steric role |
| Asp108A | proton acceptor |
| Glu319A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate terminated, proton transfer, overall product formedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu319A | proton acceptor |


 Download:
Download: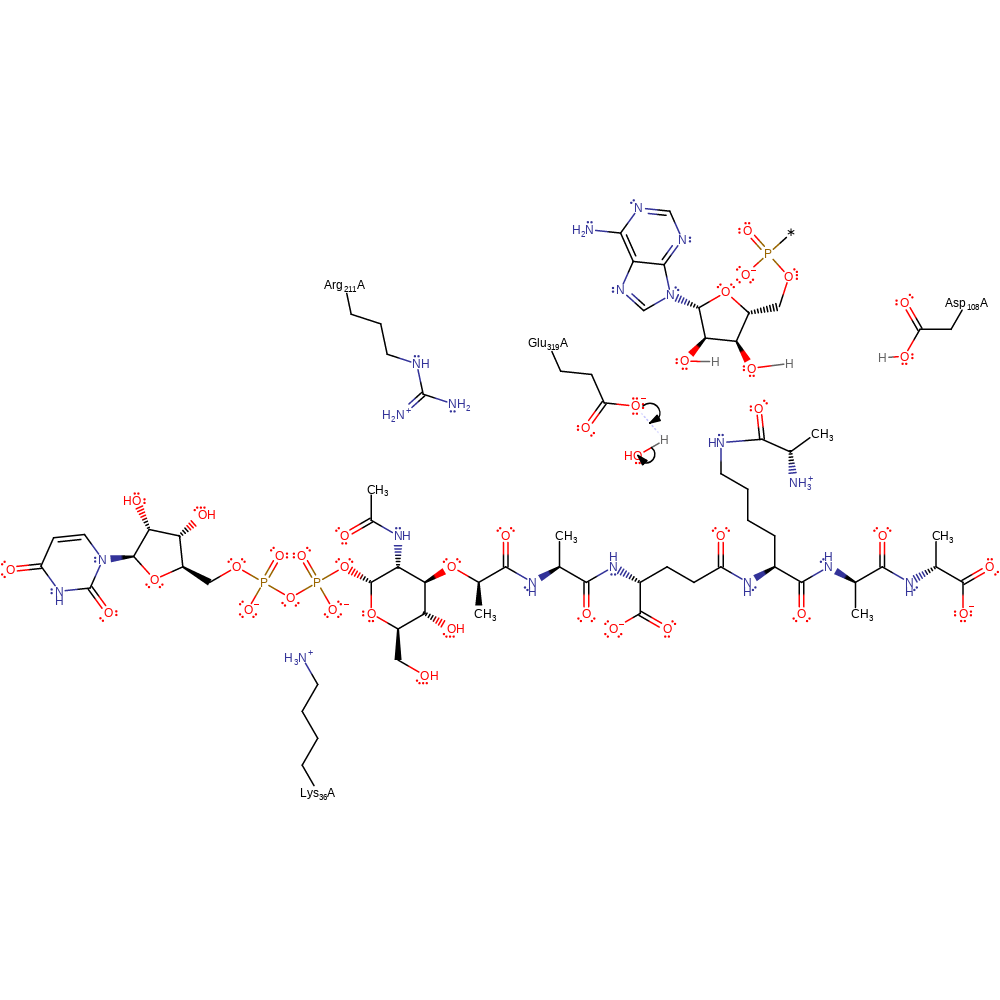 
 Download:
Download: